1 题目
Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Given the following binary tree: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
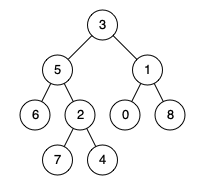
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
2 尝试解
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
vector<TreeNode*> father_p,father_q,temp;
findFather(root,p,temp,father_p);
temp.clear();
findFather(root,q,temp,father_q);
for(int i = 0; i < father_q.size() && i < father_p.size(); i++){
if(i == father_q.size()-1 || i == father_p.size()-1 || father_p[i+1] != father_q[i+1]) return father_p[i];
}
return root;
}
void findFather(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* target,vector<TreeNode*>&temp,vector<TreeNode*>&result){
if(root == NULL) return;
temp.push_back(root);
if(root == target) {
result = temp; return;
}
if(root->left != NULL){
findFather(root->left,target,temp,result);
}
if(root->right != NULL){
findFather(root->right,target,temp,result);
}
temp.pop_back();
}
};
3 标准解
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if (!root || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode* left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode* right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
return !left ? right : !right ? left : root;
}











 本文探讨了在二叉树中寻找两个节点的最低公共祖先(LCA)的问题,提供了两种解决方案:一种是通过记录每个节点的父亲节点路径,然后比较路径找到公共祖先;另一种是递归遍历树,直接返回LCA。
本文探讨了在二叉树中寻找两个节点的最低公共祖先(LCA)的问题,提供了两种解决方案:一种是通过记录每个节点的父亲节点路径,然后比较路径找到公共祖先;另一种是递归遍历树,直接返回LCA。
















 211
211

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








