读完Knowledge Graph Embedding with Iterative Guidance from Soft Rules的大致思想后,好奇为什么要用复数来表示一个向量,就想看另一篇论文:
Complex Embeddings for Simple Link Prediction
然后发现,有个博客很好的说了这个事,我就转过来以后学习
博客:论文浅尝 | Complex Embeddings for Simple Link Prediction

论文链接:[Complex Embeddings for Simple Link Pred](http://proceedings.mlr.press/v48/trouillon16.pdf)
在统计关系学习里,链接预测问题是自动理解大规模知识库结构的核心。为了更好得把握知识库二元关系中的对称和非对称关系,本文提出了基于复数的表示方法 ComplEx。
一些研究工作将链接预测看作是三维二元张量补全的问题,张量的每一个slice表示知识库中关于一种关系的临接矩阵。典型的做法是对表示知识库的张量进行低秩分解,用分解得到的矩阵的每一行表示知识库中的一个实体或者一种关系。最后对于一个给定的三元组 r(s,o)(注:即主语 s 和宾语 o 具有关系 r),这个三元组的 score 可以通过对于 s,r,o 的表示向量之间的多线性(multi-linear)乘积计算得到。以往工作的问题在于不能很好地处理非对称关系,因为实数向量之间的点积计算是具有交换性的,即如果实数表示下的 r(s,o) 成立,那么 r(o,s) 也必然成立,但在知识库中非对称关系的比例远多于对称关系的比例。所以本文提出了一个基于复数表示的方法,因为复数之间的埃尔米特乘积(Hermitian dot product)是不具有交换性的,具体做法如下:
每个实体和关系都用一个复数向量表示,每个三元组的 score function 定义如下:
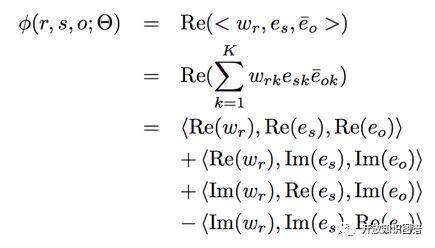
Re(x) 表示取 x 的实部,Im(x) 表示取 x 的虚部,三元组 (s,r,o) 的 score 计算过程为关系 r 的表示向量和主语 s 的表示向量以及宾语 o 的表示向量的共轭向量的乘积,并保留最后结果的实部。最终 (s,r,o) 为真的概率通过下式得到:
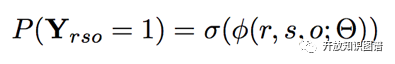
以下是 ComplEx 在对称关系和非对称关系的实验结果:
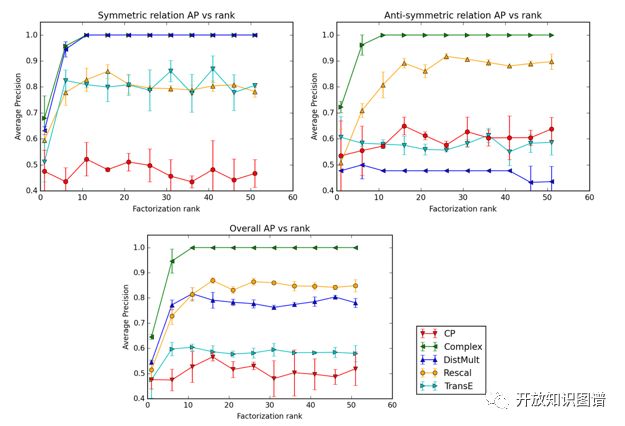
从左上的图中可以看出,Complex 和 DistMult 都可以较好地捕捉对称关系的语义信息并做出正确的预测,从右上的图中可以看出 Complex 对于非对称关系语义的捕捉以及预测效果明显优于其他模型。也验证了模型用复数表示的设计思想。
下图是在 WN18 和 FB15 上的链接预测的实验结果:
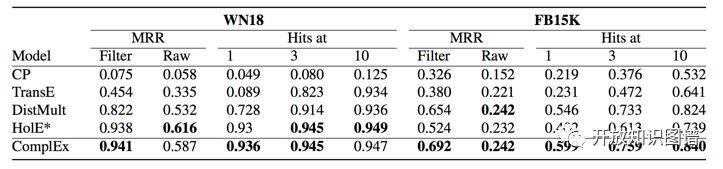
模型简洁的 ComplEx 在两个数据集上都取得了不错的效果,明显好于当时表现优异的 HolE。





 本文探讨了基于复数表示的ComplEx模型如何解决知识图谱中的链接预测问题,尤其在非对称关系上的优势。通过引入复数向量表示,ComplEx能更准确地捕捉实体间复杂的关系特性。
本文探讨了基于复数表示的ComplEx模型如何解决知识图谱中的链接预测问题,尤其在非对称关系上的优势。通过引入复数向量表示,ComplEx能更准确地捕捉实体间复杂的关系特性。
















 2251
2251

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








