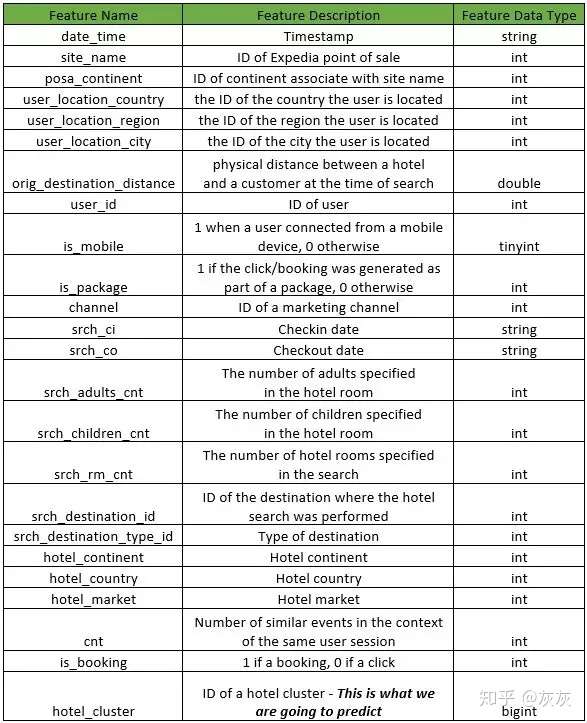
1. 数据
数据是匿名用户的,并且所有字段都是数字格式。数据可以在Kaggle中下载,train.csv中记录用户的行为,destinations.csv包含了用户的酒店信息。

import datetime
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
%matplotlib inline
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn import preprocessing
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn import svm
为了能够在本地运行,我们随机选取了1%的数据,但仍然有24179条数据。
df = pd.read_csv('train.csv.gz', sep=',').dropna()
dest = pd.read_csv('destinations.csv.gz')
df = df.sample(frac=0.01, random_state=99)
df.shape
输出:(241179, 24)
2. 探索性分析
该系统的目的是要根据用户的搜索信息,预测用户将会预定哪种旅馆。总共有100种。换言之,我们是要处理一个100分类问题。
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 6))
sns.distplot(df['hotel_cluster'])
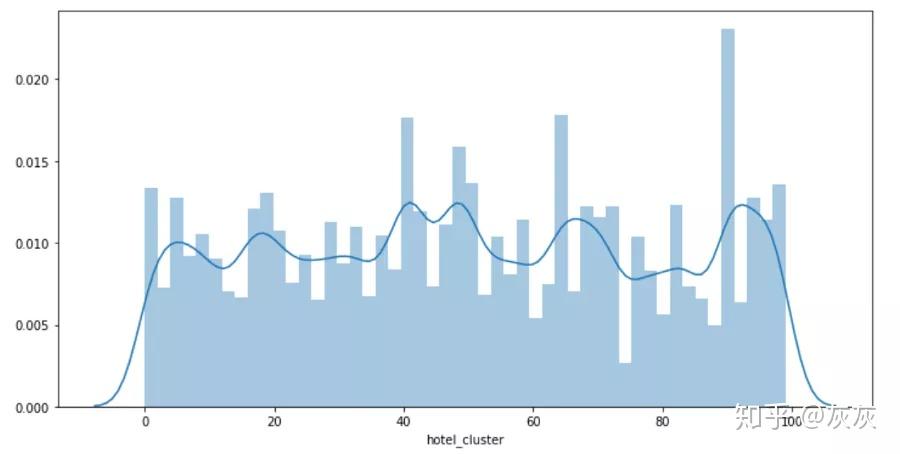
可以看出每个类的分布很均匀。
3. 特征工程
Checkin和checkout列的数据是时间格式的数据,不能直接使用。我们将从中提取出年份和月份。通过定义一个函数取抽取,并将他们合并到destination.csv中。
from datetime import datetime
def get_year(x):
if x is not None and type(x) is not float:
try:
return datetime.strptime(x, '%Y-%m-%d').year
except ValueError:
return datetime.strptime(x, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S').year
else:
return 2013
pass
def get_month(x):
if x is not None and type(x) is not float:
try:
return datetime.strptime(x, '%Y-%m-%d').month
except:
return datetime.strptime(x, '%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S').month
else:
return 1
pass
def left_merge_dataset(left_dframe, right_dframe, merge_column):
return pd.merge(left_dframe, right_dframe, on=merge_column, how='left')
处理时间格式的列:
df['date_time_year'] = pd.Series(df.date_time, index = df.index)
df['date_time_month'] = pd.Series(df.date_time, index = df.index)
from datetime import datetime
df.date_time_year = df.date_time_year.apply(lambda x: get_year(x))
df.date_time_month = df.date_time_month.apply(lambda x: get_month(x))
del df['date_time']
处理srch_ci列:
df['srch_ci_year'] = pd.Series(df.srch_ci, index=df.index)
df['srch_ci_month'] = pd.Series(df.srch_ci, index=df.index)
# convert year & months to int
df.srch_ci_year = df.srch_ci_year.apply(lambda x: get_year(x))
df.srch_ci_month = df.srch_ci_month.apply(lambda x: get_month(x))
# remove the srch_ci column
del df['srch_ci']
处理srch_co列:
df['srch_co_year'] = pd.Series(df.srch_co, index=df.index)
df['srch_co_month'] = pd.Series(df.srch_co, index=df.index)
# convert year & months to int
df.srch_co_year = df.srch_co_year.apply(lambda x: get_year(x))
df.srch_co_month = df.srch_co_month.apply(lambda x: get_month(x))
# remove the srch_co column
del df['srch_co']
4. 初步分析
在创建了一些新列和去除一些无用的列后,我们想要知道每一列跟类标是否有线性关系。这可以让我们更加关注一些特定的特征。
df.corr()["hotel_cluster"].sort_values()
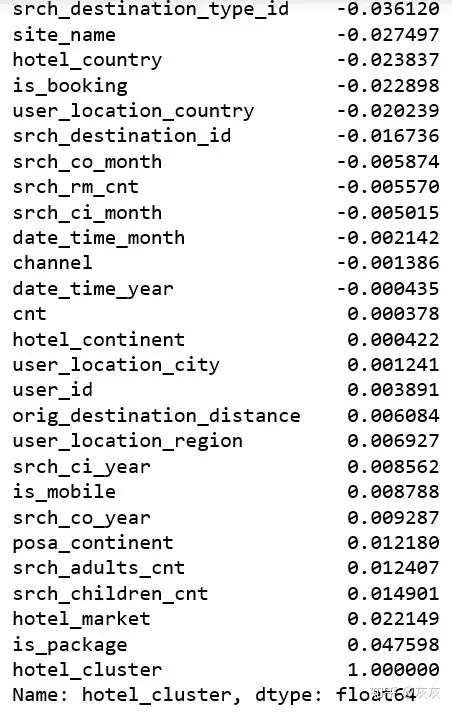
可以看出所有的列都基本跟类标没什么线性关系。这意味着刚才的那些方法对这个问题并不合适。
5. 策略
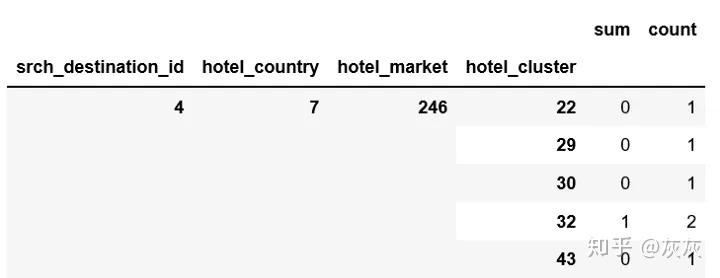
在快速的进行谷歌搜索之后,我们不难发现将目的地、旅馆国家、旅馆超市结合起来能够更加准确的帮助我们找到对应的类标。
pieces = [df.groupby(['srch_destination_id','hotel_country','hotel_market','hotel_cluster'])['is_booking'].agg(['sum','count'])]
agg = pd.concat(pieces).groupby(level=[0,1,2,3]).sum()
agg.dropna(inplace=True)
agg.head()
agg['sum_and_cnt'] = 0.85*agg['sum'] + 0.15*agg['count']
agg = agg.groupby(level=[0,1,2]).apply(lambda x: x.astype(float)/x.sum())
agg.reset_index(inplace=True)
agg.head()
agg_pivot = agg.pivot_table(index=['srch_destination_id','hotel_country','hotel_market'], columns='hotel_cluster', values='sum_and_cnt').reset_index()
agg_pivot.head()
df = pd.merge(df, dest, how='left', on='srch_destination_id')
df = pd.merge(df, agg_pivot, how='left', on=['srch_destination_id','hotel_country','hotel_market'])
df.fillna(0, inplace=True)
df.shape
输出:(241179, 276)
6. 实现算法
我们只对预定的样本有兴趣:
df = df.loc[df['is_booking'] == 1]
得到特征和类标:
X = df.drop(['user_id', 'hotel_cluster', 'is_booking'], axis=1)
y = df.hotel_cluster
朴素贝叶斯:
from sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNB
clf = make_pipeline(preprocessing.StandardScaler(), GaussianNB(priors=None))
np.mean(cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=10))
0.10347912437041926
KNN:
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
clf = make_pipeline(preprocessing.StandardScaler(), KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5))
np.mean(cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=10, scoring='accuracy'))
0.25631461834732266
随机森林:
clf = make_pipeline(preprocessing.StandardScaler(), RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=273,max_depth=10,random_state=0))
np.mean(cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=10))
0.24865023372782996
多分类逻辑回归:
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
clf = make_pipeline(preprocessing.StandardScaler(), LogisticRegression(multi_class='ovr'))
np.mean(cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=10))
0.30445543572367767
支持向量机:很耗时,但是效果更好。
from sklearn import svm
clf = make_pipeline(preprocessing.StandardScaler(), svm.SVC(decision_function_shape='ovo'))
np.mean(cross_val_score(clf, X, y, cv=10))
0.3228727137315005
看起来我们需要做更多的特征工程去优化结果。接下来将会进一步调优。
转自 :磐创AI








 本文介绍了一个基于用户搜索信息预测酒店预订类型的案例研究。通过对原始数据的预处理和特征工程,结合多种机器学习算法进行对比实验,包括朴素贝叶斯、KNN、随机森林、多分类逻辑回归和支持向量机,以寻找最佳的预测模型。
本文介绍了一个基于用户搜索信息预测酒店预订类型的案例研究。通过对原始数据的预处理和特征工程,结合多种机器学习算法进行对比实验,包括朴素贝叶斯、KNN、随机森林、多分类逻辑回归和支持向量机,以寻找最佳的预测模型。
















 1070
1070

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








