整理自:【尚硅谷】Sentinel视频教程丨Alibaba流量控制组件sentinel_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
分布式防控场景-流量控制

Sentinel的核心骨架是ProcessSlotChain,将不同的Slot按照顺序串在一起(责任链模式),从而实现各个功能(系统保护、流量控制、熔断降级)
NodeSelectorSlot:收集资源路径,以树状存储,用于根据调用路径来进行限流
ClusterBuilderSlot: 用于存储资源统计信息以及调用者信息,例如资源RT、QPS、Thread Count等,用于后续多维度限流、降级等
StatisticSlot:用于记录、统计不同维度的runtime指标监控信息
SystemSlot:对应系统规则
DegradeSlot:对应降级规则
AuthoritySlot:对应授权规则
FlowSlot:对应流控规则
ParamFlowSlot: 对应热点流控
1. SPI机制
SPI:服务处理接口[Service Provider Interface],原本是JDK里面的一个服务发现机制,一般都会将其进行扩展,如:Dubbo、Sentinel,因为原生的SPI机制有些缺陷「会加载配置文件里面所有的类」
Sentienl槽链中各Slot的顺序是固定好的,但是绝不是不能改变的。
Sentinel将ProcessSlot作为SPI接口进行扩展,使得slotchain有了扩展的能力,用户可以自定义Slot并编排顺序
2. 理解NodeSelectorSlot
会创建Invocation Tree,一个应用有一个Root节点

另外:Context是调用链路上下文,用于数据在不同的Slot之间传递
从当前线程ThreadLocal获取 Context
即一个请求会占用一个线程,一个线程会绑定一个Context
3. Node之间的关系

Node:用于完成数据统计的接口
StatisticNode:统计节点,是Node的实现类,用于完成数据统计
EntranceNode:入口节点,一个Context会有一个入口节点,用于统计当前Context的总体流量数据
DefaultNode:默认节点,用于统计一个资源在当前Context中的总体流量数据
ClusterNode:集群节点,用于统计一个资源在所有Context中的总体流量数据
4. 创建资源对象
private Entry entryWithPriority(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws BlockException {
// 从ThreadLocal里面获取Context
// 即一个请求会占用一个线程,一个线程会绑定一个Context
Context context = ContextUtil.getContext();
// 若Context是NullContext类型,则表示当前系统中的Context数量超过了阈值
// 即访问请求的数量已经超出了阈值,返回一个无需做规则检测的资源对象
if (context instanceof NullContext) {
// The {@link NullContext} indicates that the amount of context has exceeded the threshold,
// so here init the entry only. No rule checking will be done.
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
// 若当前线程没有绑定Context,则创建一个Context并将其放到ThreadLocal里面
if (context == null) {
// Using default context.
context = InternalContextUtil.internalEnter(Constants.CONTEXT_DEFAULT_NAME);
}
// 若全局开关是关闭的,则直接返回一个无需做规则检测的资源对象
// Global switch is close, no rule checking will do.
if (!Constants.ON) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
// 查找SlotChain
ProcessorSlot<Object> chain = lookProcessChain(resourceWrapper);
/*
* Means amount of resources (slot chain) exceeds {@link Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE},
* so no rule checking will be done.
*/
// 若没有找到chain,则意味着chain数量超过了阈值,直接返回一个无需做规则检测的资源对象
if (chain == null) {
return new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, null, context);
}
// 创建一个资源操作对象
Entry e = new CtEntry(resourceWrapper, chain, context);
try {
//对资源进行操作
chain.entry(context, resourceWrapper, null, count, prioritized, args);
} catch (BlockException e1) {
e.exit(count, args);
throw e1;
} catch (Throwable e1) {
// This should not happen, unless there are errors existing in Sentinel internal.
RecordLog.info("Sentinel unexpected exception", e1);
}
return e;
}5. Context
要确定一个Context需要两个属性:名称和来源
protected static Context trueEnter(String name, String origin) {
// 尝试着从ThreadLocal中获取Context
Context context = contextHolder.get();
// 若ThreadLocal中没有Context,则尝试着从缓存map中获取
if (context == null) {
// 缓存map的key为Context名称,value为EntranceNode
Map<String, DefaultNode> localCacheNameMap = contextNameNodeMap;
// 获取EntranceNode【当然:目的是为了构建Context】
// 双重检测锁DCL,为了防止并发创建
DefaultNode node = localCacheNameMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
// 若缓存map的size 大于Context数量的最大阈值,则直接返回NULL_CONTEXT
if (localCacheNameMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
LOCK.lock();
try {
node = contextNameNodeMap.get(name);
if (node == null) {
if (contextNameNodeMap.size() > Constants.MAX_CONTEXT_NAME_SIZE) {
setNullContext();
return NULL_CONTEXT;
} else {
// 创建一个EntranceNode
node = new EntranceNode(new StringResourceWrapper(name, EntryType.IN), null);
// Add entrance node.
// 将新建的node添加到ROOT
Constants.ROOT.addChild(node);
// 将新建map写入到缓存map
// 为了防止"迭代稳定性问题" - iterator stable ,也叫写时复制(copy on write)
// 对于共享集合的写操作
// 如果不这样做的话,可能会引发读脏数据,这边没写完,那边已经走了
Map<String, DefaultNode> newMap = new HashMap<>(contextNameNodeMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(contextNameNodeMap);
newMap.put(name, node);
contextNameNodeMap = newMap;
}
}
} finally {
LOCK.unlock();
}
}
}
// 根据EntranceNode和name构建Context
context = new Context(node, name);
// 初始化Context的来源
context.setOrigin(origin);
// 将Context设置到ThreadLocal中去
contextHolder.set(context);
}
return context;
}6. lookProcessChain【这里得到的是一个链表】
ProcessorSlot<Object> lookProcessChain(ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper) {
// 从缓存map中获取当前资源的SlotChain
// 缓存map的key是资源,value为其相关的SlotChain
ProcessorSlotChain chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
// DCL 防止并发创建对象问题
// 若缓存中没有相关的SlotChain,则创建一个并放入缓存
if (chain == null) {
synchronized (LOCK) {
chain = chainMap.get(resourceWrapper);
if (chain == null) {
// Entry size limit.
// 缓存map的size >= chain数量的最大阈值,则直接返回null。不在创建chain
if (chainMap.size() >= Constants.MAX_SLOT_CHAIN_SIZE) {
return null;
}
// 创建新的chain
chain = SlotChainProvider.newSlotChain();
// 防止迭代稳定性问题
Map<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain> newMap = new HashMap<ResourceWrapper, ProcessorSlotChain>(
chainMap.size() + 1);
newMap.putAll(chainMap);
newMap.put(resourceWrapper, chain);
chainMap = newMap;
}
}
}
return chain;
}


@Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_NODE_SELECTOR_SLOT)
public class NodeSelectorSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object> {
@Spi(isSingleton = false, order = Constants.ORDER_CLUSTER_BUILDER_SLOT)
public class ClusterBuilderSlot extends AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<DefaultNode> {
从这里可以看出:order = Constants.ORDER_NODE_SELECTOR_SLOT 代表优先级,越小/优先级越高。且,如上这些都是系统已经定义好的,所以就会出现一个请求特定顺序经历Slot的顺序
public ProcessorSlotChain build() {
ProcessorSlotChain chain = new DefaultProcessorSlotChain();
// 通过SPI进行构建Slot,这里会构建较多,构建List
// 这里会加载所有的Slot
List<ProcessorSlot> sortedSlotList = SpiLoader.of(ProcessorSlot.class).loadInstanceListSorted();
for (ProcessorSlot slot : sortedSlotList) {
if (!(slot instanceof AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)) {
RecordLog.warn("The ProcessorSlot(" + slot.getClass().getCanonicalName() + ") is not an instance of AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot, can't be added into ProcessorSlotChain");
continue;
}
chain.addLast((AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?>) slot);
}
return chain;
}那么如何理解addLast?
@Override
public void addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor) {
end.setNext(protocolProcessor);
end = protocolProcessor;
}// 这是一个单向链表,默认包含一个节点,且有两个指针first end同时指向了这个节点
public class DefaultProcessorSlotChain extends ProcessorSlotChain {
AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> first = new AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<Object>() {
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
super.fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
super.fireExit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
}
};
AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> end = first;
@Override
public void addFirst(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor) {
protocolProcessor.setNext(first.getNext());
first.setNext(protocolProcessor);
if (end == first) {
end = protocolProcessor;
}
}
@Override
public void addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> protocolProcessor) {
end.setNext(protocolProcessor);
end = protocolProcessor;
}
/**
* Same as {@link #addLast(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot)}.
*
* @param next processor to be added.
*/
@Override
public void setNext(AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> next) {
addLast(next);
}
@Override
public AbstractLinkedProcessorSlot<?> getNext() {
return first.getNext();
}
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}
@Override
public void exit(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, int count, Object... args) {
first.exit(context, resourceWrapper, count, args);
}
}7. chain.entry 对资源操作
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object t, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
// 转向第一个节点,而非默认创建的
first.transformEntry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}void transformEntry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object o, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
T t = (T)o;
entry(context, resourceWrapper, t, count, prioritized, args);
}8. 来到NodeSelectorSlot【创建调用树】ROOT有,EntranceNode在Context里面,
所以这里核心是用来创建defaultNode的
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, Object obj, int count, boolean prioritized, Object... args)
throws Throwable {
/*
* It's interesting that we use context name rather resource name as the map key.
*
* Remember that same resource({@link ResourceWrapper#equals(Object)}) will share
* the same {@link ProcessorSlotChain} globally, no matter in which context. So if
* code goes into {@link #entry(Context, ResourceWrapper, DefaultNode, int, Object...)},
* the resource name must be same but context name may not.
*
* If we use {@link com.alibaba.csp.sentinel.SphU#entry(String resource)} to
* enter same resource in different context, using context name as map key can
* distinguish the same resource. In this case, multiple {@link DefaultNode}s will be created
* of the same resource name, for every distinct context (different context name) each.
*
* Consider another question. One resource may have multiple {@link DefaultNode},
* so what is the fastest way to get total statistics of the same resource?
* The answer is all {@link DefaultNode}s with same resource name share one
* {@link ClusterNode}. See {@link ClusterBuilderSlot} for detail.
*/
// 从缓存中获取DefaultNode
DefaultNode node = map.get(context.getName());
//DCL
if (node == null) {
synchronized (this) {
node = map.get(context.getName());
if (node == null) {
// 创建一个DefaultNode,并且放入缓存中
node = new DefaultNode(resourceWrapper, null);
HashMap<String, DefaultNode> cacheMap = new HashMap<String, DefaultNode>(map.size());
cacheMap.putAll(map);
cacheMap.put(context.getName(), node);
map = cacheMap;
// Build invocation tree
//将新建Node添加到调用树中
((DefaultNode) context.getLastNode()).addChild(node);
}
}
}
context.setCurNode(node);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}9. 来到ClusterBuilderSlot
构建ClusterBuilderSlot阶段
10. 来到StatisticSlot
11. 来到FlowSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 检测并应用流控规则
checkFlow(resourceWrapper, context, node, count, prioritized);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
void checkFlow(ResourceWrapper resource, Context context, DefaultNode node, int count, boolean prioritized)
throws BlockException {
checker.checkFlow(ruleProvider, resource, context, node, count, prioritized);
}public abstract class AbstractRule implements Rule {
/**
* Resource name.
*/
// 资源名称
private String resource;
/**
* <p>
* Application name that will be limited by origin.
* The default limitApp is {@code default}, which means allowing all origin apps.
* </p>
* <p>
* For authority rules, multiple origin name can be separated with comma (',').
* </p>
*/
// 请求来源
private String limitApp;
public class FlowRule extends AbstractRule {
public FlowRule() {
super();
setLimitApp(RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT);
}
public FlowRule(String resourceName) {
super();
setResource(resourceName);
setLimitApp(RuleConstant.LIMIT_APP_DEFAULT);
}
/**
* The threshold type of flow control (0: thread count, 1: QPS).
*/
// 阈值类型 0 线程数 1 QPS
private int grade = RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS;
/**
* Flow control threshold count.
*/
private double count;
/**
* Flow control strategy based on invocation chain.
*
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_DIRECT} for direct flow control (by origin);
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_RELATE} for relevant flow control (with relevant resource);
* {@link RuleConstant#STRATEGY_CHAIN} for chain flow control (by entrance resource).
*/
// 流控模式 直接、关联、链路
private int strategy = RuleConstant.STRATEGY_DIRECT;
/**
* Reference resource in flow control with relevant resource or context.
*/
// 关联流控模式下,关联的资源
private String refResource;
/**
* Rate limiter control behavior.
* 0. default(reject directly), 1. warm up, 2. rate limiter, 3. warm up + rate limiter
*/
// 流控效果 0 快速失败 1 warm up(令牌桶算法) 2 rate limiter(漏斗算法) 3 1+2
private int controlBehavior = RuleConstant.CONTROL_BEHAVIOR_DEFAULT;
// warm up 预热时长
private int warmUpPeriodSec = 10;
// 排队等待超时时长
/**
* Max queueing time in rate limiter behavior.
*/
private int maxQueueingTimeMs = 500;
// 是否是集群模式
private boolean clusterMode;
/**
* Flow rule config for cluster mode.
*/
private ClusterFlowConfig clusterConfig;12. ruleProvider.apply
private final Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>> ruleProvider = new Function<String, Collection<FlowRule>>() {
@Override
public Collection<FlowRule> apply(String resource) {
// Flow rule map should not be null.
// 获取到所有资源的流控规则
// map的key为资源名称,value为该资源上加载的所有流控规则
Map<String, List<FlowRule>> flowRules = FlowRuleManager.getFlowRuleMap();
// 获取指定资源的所有流控规则
return flowRules.get(resource);
}
};13. canPassCheck
public boolean canPassCheck(/*@NonNull*/ FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized) {
// 从规则中获取限定的来源
String limitApp = rule.getLimitApp();
// 若限流的来源为null,则请求直接通过
if (limitApp == null) {
return true;
}
// 使用流控处理集群
if (rule.isClusterMode()) {
return passClusterCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}
// 使用规则处理单机流控
return passLocalCheck(rule, context, node, acquireCount, prioritized);
}private static boolean passLocalCheck(FlowRule rule, Context context, DefaultNode node, int acquireCount,
boolean prioritized) {
// 选择出合适的规则Node
Node selectedNode = selectNodeByRequesterAndStrategy(rule, context, node);
// 若没有选择出node,说明没有规则,则直接返回true,表示检测通过
if (selectedNode == null) {
return true;
}
// 使用规则进行逐项检测
return rule.getRater().canPass(selectedNode, acquireCount, prioritized);
}public boolean canPass(Node node, int acquireCount, boolean prioritized) {
// 获取当前时间窗中已经统计的数据
int curCount = avgUsedTokens(node);
// 若总数据量大于count,那么返回false,代表没有通过检测
// 若小于等于阈值,则返回true,表示通过检测
if (curCount + acquireCount > count) {
if (prioritized && grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_QPS) {
long currentTime;
long waitInMs;
currentTime = TimeUtil.currentTimeMillis();
waitInMs = node.tryOccupyNext(currentTime, acquireCount, count);
if (waitInMs < OccupyTimeoutProperty.getOccupyTimeout()) {
node.addWaitingRequest(currentTime + waitInMs, acquireCount);
node.addOccupiedPass(acquireCount);
sleep(waitInMs);
// PriorityWaitException indicates that the request will pass after waiting for {@link @waitInMs}.
throw new PriorityWaitException(waitInMs);
}
}
return false;
}
return true;
} private int avgUsedTokens(Node node) {
// 若没有选择出Node,则代表不需要统计数据,直接返回0
if (node == null) {
return DEFAULT_AVG_USED_TOKENS;
}
// 若阈值类型是线程数,则直接返回当前的线程数量
// 若阈值类型为qps,则直接返回当前的qps
return grade == RuleConstant.FLOW_GRADE_THREAD ? node.curThreadNum() : (int)(node.passQps());
}14. DegradeSlot
@Override
public void entry(Context context, ResourceWrapper resourceWrapper, DefaultNode node, int count,
boolean prioritized, Object... args) throws Throwable {
// 触发熔断降级检测
performChecking(context, resourceWrapper);
fireEntry(context, resourceWrapper, node, count, prioritized, args);
}
// Sentinel1.8 中, 将三种熔断策略(慢调用、异常比、异常数) 封装为两种熔断器
public interface CircuitBreaker {
/**
* Get the associated circuit breaking rule.
*
* @return associated circuit breaking rule
*/
// 获取降级规则
DegradeRule getRule();
/**
* Acquires permission of an invocation only if it is available at the time of invoking.
*
* @param context context of current invocation
* @return {@code true} if permission was acquired and {@code false} otherwise
*/
// 判断请求是否可以通过
// 返回true表示不用降级
boolean tryPass(Context context);
/**
* Get current state of the circuit breaker.
*
* @return current state of the circuit breaker
*/
// 熔断器状态
State currentState();
/**
* <p>Record a completed request with the context and handle state transformation of the circuit breaker.</p>
* <p>Called when a <strong>passed</strong> invocation finished.</p>
*
* @param context context of current invocation
*/
// on开头的一般是回调 当请求通过并完成后会触发
void onRequestComplete(Context context);
/**
* Circuit breaker state.
*/
enum State {
/**
* In {@code OPEN} state, all requests will be rejected until the next recovery time point.
*/
// 打开状态,会拒绝所有的请求
OPEN,
/**
* In {@code HALF_OPEN} state, the circuit breaker will allow a "probe" invocation.
* If the invocation is abnormal according to the strategy (e.g. it's slow), the circuit breaker
* will re-transform to the {@code OPEN} state and wait for the next recovery time point;
* otherwise the resource will be regarded as "recovered" and the circuit breaker
* will cease cutting off requests and transform to {@code CLOSED} state.
*/
// 过度状态
HALF_OPEN,
/**
* In {@code CLOSED} state, all requests are permitted. When current metric value exceeds the threshold,
* the circuit breaker will transform to {@code OPEN} state.
*/
// 关闭状态,所有请求可以关闭
CLOSED
}
}
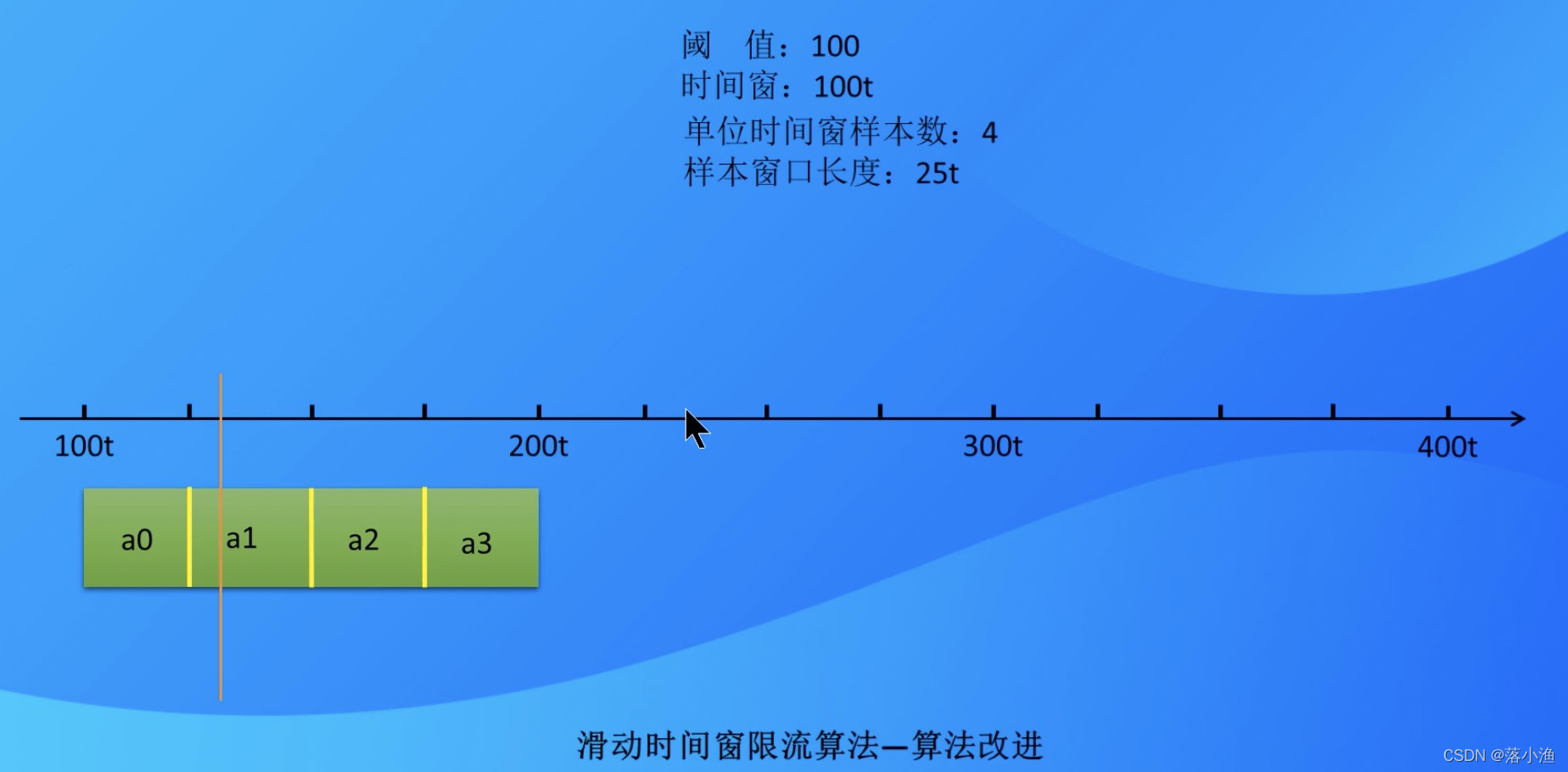
15. 时间窗限流算法

并不能保证任一时间段都是合理的,然后引入了滑动时间窗算法
 会浪费统计资源,影响效率,因为有大量重复统计数据
会浪费统计资源,影响效率,因为有大量重复统计数据























 339
339

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








