from
How it works
Consider a positive multiplier consisting of a block of 1s surrounded by 0s. For example, 00111110. The product is given by :
where M is the multiplicand. The number of operations can be reduced to two by rewriting the same as
In fact, it can be shown that any sequence of 1's in a binary number can be broken into the difference of two binary numbers:
Hence, we can actually replace the multiplication by the string of ones in the original number by simpler operations, adding the multiplier, shifting the partial product thus formed by appropriate places, and then finally subtracting the multiplier. It is making use of the fact that we do not have to do anything but shift while we are dealing with 0s in a binary multiplier, and is similar to using the mathematical property that 99 = 100 − 1 while multiplying by 99.
This scheme can be extended to any number of blocks of 1s in a multiplier (including the case of single 1 in a block). Thus,
Booth's algorithm follows this scheme by performing an addition when it encounters the first digit of a block of ones (0 1) and a subtraction when it encounters the end of the block (1 0). This works for a negative multiplier as well. When the ones in a multiplier are grouped into long blocks, Booth's algorithm performs fewer additions and subtractions than the normal multiplication algorithm.




 本文介绍了布斯乘法算法的工作原理,通过将乘数中的连续1替换为更简单的操作来减少乘法运算中的加法和减法次数。适用于正负乘数,尤其当乘数中的1成块出现时效率更高。
本文介绍了布斯乘法算法的工作原理,通过将乘数中的连续1替换为更简单的操作来减少乘法运算中的加法和减法次数。适用于正负乘数,尤其当乘数中的1成块出现时效率更高。

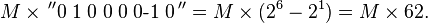

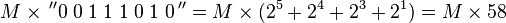

















 4176
4176

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








