题意:给你一个函数f[x],问你是否存在满足 g(h(x)) = x for all 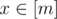 , and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all
, and h(g(x)) = f(x) for all  , 的两个函数
, 的两个函数
题解:先化简公式得到一个构造g(x)的公式,g(x)=g(f(x)),并查集将x和f(x)捆绑起来,然后for一遍g(x)这个函数,将属于同一个集团里面的编上相同的号码,然后推出公式h(x)=f(h(x))得到h(x)函数的值,最后用题目条件分别check一下生成的函数
#include <iostream> #include <cstdio> #include <cmath> #include <algorithm> #include <map> #include <queue> #include <vector> #include <cstring> #include <iomanip> #include <set> #include<ctime> #include<unordered_map> //CLOCKS_PER_SEC #define se second #define fi first #define ll long long #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 #define Pii pair<int,int> #define Pli pair<ll,int> #define ull unsigned long long #define pb push_back #define fio ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0) const int N=1e6+10; const ull base=163; const int INF=0x3f3f3f3f; using namespace std; int f[N],g[N],h[N]; int fa[N]; int F(int x){ return fa[x]==x?x:fa[x]=F(fa[x]); } map<int,int>mp; int main(){ fio; int n; cin>>n; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) { cin>>f[i]; } for(int i=1;i<=N-5;i++)fa[i]=i; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ int u=i,v=f[i]; u=F(i),v=F(v); if(u!=v){ fa[u]=v; } } int m=0; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(!mp[F(f[i])]){ mp[F(f[i])]=++m; } g[i]=mp[F(f[i])]; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ h[g[i]]=f[i]; } for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ if(h[g[i]]!=f[i]){ return cout<<-1,0; } } for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ if(g[h[i]]!=i){ return cout<<-1,0; } } cout<<m<<endl; for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){ cout<<g[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl;; for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){ cout<<h[i]<<" "; } return 0; }







 本文探讨了一道关于函数构造的问题,通过分析给定函数f[x],寻找满足特定条件的函数g(x)和h(x)。利用并查集算法进行节点连接,确保函数的正确构造,并检查生成的函数是否符合题目要求。
本文探讨了一道关于函数构造的问题,通过分析给定函数f[x],寻找满足特定条件的函数g(x)和h(x)。利用并查集算法进行节点连接,确保函数的正确构造,并检查生成的函数是否符合题目要求。
















 558
558

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








