迭代器模式 出处 图解设计模式 结城浩著
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:57
*/
public interface Iterator {
public abstract boolean hasNext();
public abstract Object next();
}
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:56
*/
public class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator {
private BookShelf bookShelf_;
private int index;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf){
this.bookShelf_ = bookShelf;
this.index = 0;
}
public void finalize() throws Throwable {
}
public boolean hasNext(){
if (index < bookShelf_.getLength()) {
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public Object next(){
Book book = bookShelf_.getBookAt(index);
index++;
return book;
}
}
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:53
*/
public interface Aggregate {
public abstract Iterator iterator();
}
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:55
*/
public class BookShelf implements Aggregate {
private Book[] books;
private int last = 0;
public BookShelf(int maxsize){
this.books = new Book[maxsize];
}
public void finalize() throws Throwable {
}
public void appendBook(Book book){
this.books[last] = book;
last++;
}
public Book getBookAt(int index){
return books[index];
}
public int getLength(){
return last;
}
public Iterator iterator() {
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:55
*/
public class Book {
private String name;
public Book(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void finalize() throws Throwable {
}
}
/**
* @author linx
* @version 1.0
* @created 19-十二月-2017 13:08:55
*/
/* The test class or client */
class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(4);
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("A"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("B"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("C"));
bookShelf.appendBook(new Book("D"));
Iterator it = bookShelf.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) {
Book book = (Book)it.next();
System.out.println(book.getName());
}
}
}




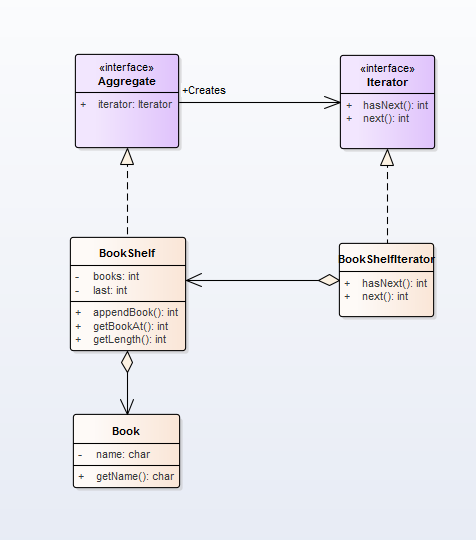
 本文介绍了一种使用Java实现的迭代器模式,通过BookShelf类作为聚合类,BookShelfIterator类作为具体迭代器,实现了对书籍集合的遍历。该模式分离了遍历行为与聚合对象,使得增加新的遍历方式更为灵活。
本文介绍了一种使用Java实现的迭代器模式,通过BookShelf类作为聚合类,BookShelfIterator类作为具体迭代器,实现了对书籍集合的遍历。该模式分离了遍历行为与聚合对象,使得增加新的遍历方式更为灵活。

















 177
177

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








