二、同步器的实现(二)
3.ReentrantLock
ReentrantLock是个可重入的互斥锁,具有与使用synchronized同步代码访问monitor对象相同的一些基本行为和语义,但是ReentrantLock更加强大并且效率要高一些。下面看个示例:
/**
* ReentrantLock示例
* Created by bzhang on 2019/3/17.
*/
public class TestReentrantLock {
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public void m1(){
lock.lock(); //获取锁,若锁被别的线程占用则阻塞等待获取锁
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始占着茅坑了");
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(3);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"占了3小时的茅坑");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//lock.unlock(); //解锁,锁用完后一定要解锁,不然其他线程无法获取到锁,会一直阻塞
}
}
public void m2(){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"也想用茅坑,但被占着了");
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"终于等到了");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestReentrantLock test = new TestReentrantLock();
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
pool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
test.m1();
}
});
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
pool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
test.m2();
}
});
pool.shutdown();
}
}知道了简单的用法,我们来看看ReentrantLock,其继承关系如下图,实现了Lock接口。
Lock接口中有如下待实现方法:
public interface Lock {
//获取锁,若锁不可用(拿不到锁),就让当前线程休眠
void lock();
//获取锁,但是在等待获取时可被中断
void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException;
//尝试获取锁,即锁当前未被其它线程占用,则获取锁返回true,若锁被占用,不等待直接返回false
boolean tryLock();
//在一定时间内尝试获取锁,若在规定时间内成功获取就返回true,否则就返回false。
boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
//解锁/释放锁,持有锁的线程才能释放锁,因此使用完锁一定要释放,不然会造成死锁。
void unlock();
//返回绑定到此锁的condition实例
Condition newCondition();
}接口看完,来看看ReentrantLock是如何实现的,先看看构造方法:
private final Sync sync; //同步队列
//空构造
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync(); //创建一个非公平的同步队列,是AQS的子类实现
}
//根据fair构造
public ReentrantLock(boolean fair) {
//根据fair创建一个公平或非公平同步队列
sync = fair ? new FairSync() : new NonfairSync();
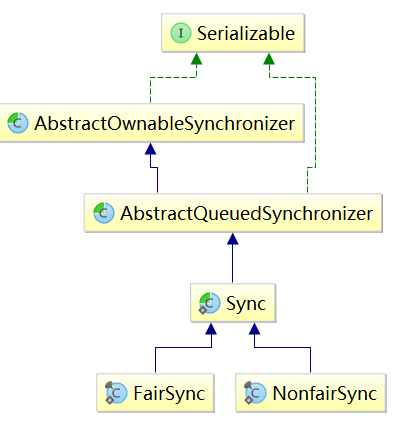
}由构造方法可知,ReentrantLock实际是创建了一个同步队列,NonfairSync或者FairSync。他们都是AQS的实现类,实现了AQS的独占模式,其中NonfairSync是非公平模式下竞争锁资源,即线程竞争锁资源时不以等待时间长短来决定。而FairSync则是公平模式下获取锁资源,即按照线程等待时间的长短来决定洗个获取锁资源的是谁,其继承关系如下图:
下面先看看公平同步队列及非公平同步队列的实现源码:
//ReentrantLock中FairSync的实现
//公平同步队列实现类
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
//尝试获取锁资源,若未获取成功则进入同步队列中等待
final void lock() {
//不可被中断的尝试获取锁方法
//前面分析AQS时已经分析过了,此处只要知道在进入等待队列之前acquire方法会调用
//tryAcquire方法先尝试获取锁即可,若获取锁失败则会加入同步队列中等待(因为acquire中调用了acquireQueued方法)
acquire(1);
}
//尝试获取锁,AQS实现类必须重写的方法。
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
//获取当前线程
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState(); //获取AQS同步队列状态值
//判断同步状态值是否为0,为0即锁资源当前处于释放状态,竞争锁
//不为0表示已经有线程获取到锁,直接去判断当前线程是否是拥有锁的线程
if (c == 0) {
//hasQueuedPredecessors是AQS中的方法,查询是否存在比当前线程等待时间更久的线程
//若不存在,表示当前线程的等待时间就是最长的,那么就尝试更新同步队列的状态值为acquires
//若当前线程是等待最久且同步队列状态值成功更新为acquires,那么就将当前线程设置为拥有独占访问的线程(即获取到锁资源)
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
//判断当前线程是否是拥有锁资源的线程
//该判断是用于判断是否是重入锁,若是重入直接获取锁。状态值也更新(代表重入的次数)
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
//非公平同步队列的实现类
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
//尝试获取锁资源,若未获取成功则进入同步队列中等待
final void lock() {
//直接尝试设置同步状态值,若成功表示获取到锁资源,直接将当前线程设为拥有锁资源的线程
//设置不成功在去尝试获取锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
//尝试获取锁操作,调用父类的nonfairTryAcquire方法
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
//NonfairSync及FairSync的公共父类
abstract static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
abstract void lock(); //抽象获取锁方法,子类实现,若为获取到锁,则进入同步队列等待
//非公平的尝试获取锁对象
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread(); //当前线程
int c = getState(); //获取同步队列的状态值
//判断状态值是否为0,即锁是否未被其他线程获取
if (c == 0) {
//直接尝试更新状态值,若是成功(即获取到锁)直接返回
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
//若锁资源处于被占用状态,就判断当前线程是否是拥有锁的线程,重入锁直接获取锁资源
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
//尝试释放锁资源
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases; //获取当前队列的状态值,并得到想要更新的状态值
//判断当前线程是否是拥有锁资源的线程,不是抛异常
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false; //释放锁是否成功的标识
//若更新的状态值为0,表示线程将释放锁
//不为0,表示是重入锁,尚未到达释放状态
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c); //更新状态
return free;
}
//判断当前线程是否是拥有锁资源的额线程
protected final boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getExclusiveOwnerThread() == Thread.currentThread();
}
//新建条件队列
final ConditionObject newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
//返回当前独占锁资源的线程,若锁已被释放则返回null
final Thread getOwner() {
return getState() == 0 ? null : getExclusiveOwnerThread();
}
//返回同步状态值,若大于0锁资源处于独占状态,且可表示重入的次数。
//返回为0表示处于释放状态
final int getHoldCount() {
return isHeldExclusively() ? getState() : 0;
}
//判断锁资源是否处于占用状态
final boolean isLocked() {
return getState() != 0;
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}以上就是ReentrantLock中公平锁及非公平锁底层的同步队列的实现,下面看看ReentrantLock的源码:
public class ReentrantLock implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
//尝试获取锁方法,锁锁资源已被其他线程占用,则阻塞当前线程以等待获取锁
//实际是调用底层同步队列的lock方法
public void lock() {
sync.lock(); //实际调用的获取锁方法
}
//可被中断的尝试获取锁的方法
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1); //调用AQS中的方法实现
}
//尝试获取锁,以非公平方式尝试获取锁,只尝试一次,获取不到不会等待直接返回
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.nonfairTryAcquire(1);
}
//在一定时间内尝试获取锁,若在timeout时间内成功获取,返回true,超时则返回false
public boolean tryLock(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(timeout));
}
//释放锁,必须要拥有锁才能释放,不然抛异常
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
//返回与当前锁资源相关的条件队列
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition(); //实际是新建一个条件等待队列
}
//查看拥有锁的线程的重入次数
public int getHoldCount() {
return sync.getHoldCount();
}
//判断当前线程是否是拥有锁的线程
public boolean isHeldByCurrentThread() {
return sync.isHeldExclusively();
}
//查看锁是否被占用(即被某一线程使用)
public boolean isLocked() {
return sync.isLocked();
}
//查看是否是公平锁
public final boolean isFair() {
return sync instanceof FairSync;
}
//获取当前拥有锁的线程,若锁资源处于释放状态,则返回null
protected Thread getOwner() {
return sync.getOwner();
}
//查看是否有线程等待获取锁,即同步队列是否为空
public final boolean hasQueuedThreads() {
return sync.hasQueuedThreads();
}
//查看thread线程是否是等待获取锁的一员
public final boolean hasQueuedThread(Thread thread) {
return sync.isQueued(thread);
}
//查看等待获取锁的线程数的估计值
public final int getQueueLength() {
return sync.getQueueLength();
}
//获取同步队列中等待获取锁的线程列表
protected Collection<Thread> getQueuedThreads() {
return sync.getQueuedThreads();
}
//condition等待队列中是否有等待条件的结点
public boolean hasWaiters(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.hasWaiters((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}
//获取给定的condition中等待队列的长度的估计值
public int getWaitQueueLength(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.getWaitQueueLength((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}
//获取给定condition条件队列中等待线程的线程列表
protected Collection<Thread> getWaitingThreads(Condition condition) {
if (condition == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
if (!(condition instanceof AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject))
throw new IllegalArgumentException("not owner");
return sync.getWaitingThreads((AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.ConditionObject)condition);
}
}





















 1329
1329

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








