libuv是纯c编写的事件驱动的网络库, 它的定时器也是用最小堆实现(最小堆原理). 但是与java中的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor/Timer中的最小堆不同, libuv使用链表形式来存放结点, 而不是数组.
//节点信息
struct heap_node {
//分别为左子结点, 右子结点, 父结点的指针
struct heap_node* left;
struct heap_node* right;
struct heap_node* parent;
};
//堆
struct heap {
struct heap_node* min; //塔尖的位置的指针
unsigned int nelts; //节点的数量
};
它使用链表的原因可能有:
- c语言的对象/接口封装, 没有java/c++那样优雅, 不太好优雅地记录节点在数组中的索引位置.
- 不需要预先分配内存, 不需要中途扩充数组
负作用: 插入新节点时, 需要先从塔尖位置开始找出最末尾的位置, libuv的末节点搜索过程需要循环2倍的塔层数;
如果搜索末尾节点?
当以数组来存储最小堆时, 它有这样的性质(首位置索引定为1):
**第K个节点的左子节点位于2K的位置, 右子节点位于2K+1的位置, 父结点位于K/2的位置 **
左节点必定在偶数位置, 右节点必定在奇数位置.
然后根据上面的性质可以依次推算出它的各级父结点的位置以及左右属性
来看看libuv-1.x的入列过程
//使用一个int值来保存末节点的各级父节点的左右关系, 0表示在左边, 1表示在右边
//最后一个bit为金字塔第二级的左右关系
int path = 0;
//此处代码是以1作为首位置的索引, 那么左节点的索引为偶数, 右节点的索引为奇数
//父结点的索引为K/2
//1 + heap->nelts表示待填充的节点的索引.
for (k = 0, n = 1 + heap->nelts; n >= 2 /*跳过塔尖*/; k += 1, n /= 2/*父节点的索引*/)
//如果n为偶数(左节点), 那么(n & 1)值为0, 反之(右节点)为1; 然后将这个值存入path
//k用来记录path中的有效值的个数
path = (path << 1) | (n & 1);
/* Now traverse the heap using the path we calculated in the previous step. */
//从塔尖的位置一层一层的往下查找
parent = child = &heap->min;
while (k > 0) {
parent = child;
if (path & 1) //取出最后一个bit, 按照上面的推断, 1表示右边.
child = &(*child)->right;
else
child = &(*child)->left;
path >>= 1;
k -= 1;
}
/* Insert the new node. */
newnode->parent = *parent;
*child = newnode;
heap->nelts += 1;
/* Walk up the tree and check at each node if the heap property holds.
* It's a min heap so parent < child must be true.
*/
/** 如果父节点较大, 则执行上移过过程 */
while (newnode->parent != NULL && less_than(newnode, newnode->parent))
heap_node_swap(heap, newnode->parent, newnode);
heap_node_swap代码解析:
/* Swap parent with child. Child moves closer to the root, parent moves away. */
//为了方便说明, 本文只考虑一个比较简单的场景,如图1
static void heap_node_swap(struct heap* heap,
struct heap_node* parent,
struct heap_node* child) {
struct heap_node* sibling;
struct heap_node t;
//将child与parent指向的内容交换; 交换之后的关系, 如图2
t = *parent;
*parent = *child;
*child = t;
//开始修复各种指针的指向, 如图3
parent->parent = child; //见图3中的线(1),修复新子节点的parent
if (child->left == child) {
child->left = parent; 修复新有parent的左子节点
sibling = child->right;
} else {
child->right = parent; //见图3中的线(2), 修复新有parent的右子节点
sibling = child->left;
}
if (sibling != NULL)
sibling->parent = child; //见图3中的线(3)
//本文暂未考虑这种情况, 读者可以自己画一画
if (parent->left != NULL)
parent->left->parent = parent;
if (parent->right != NULL)
parent->right->parent = parent;
if (child->parent == NULL)
heap->min = child;
else if (child->parent->left == parent)
child->parent->left = child;
else
child->parent->right = child; //见图3中的线(4)
}
图1 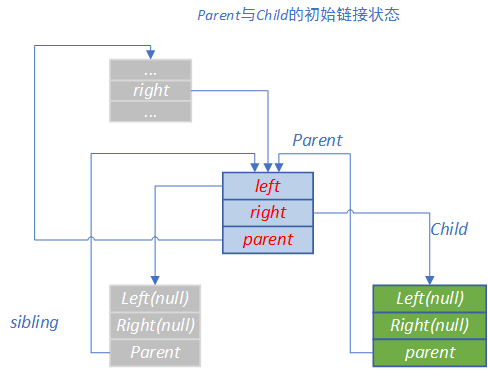
图2 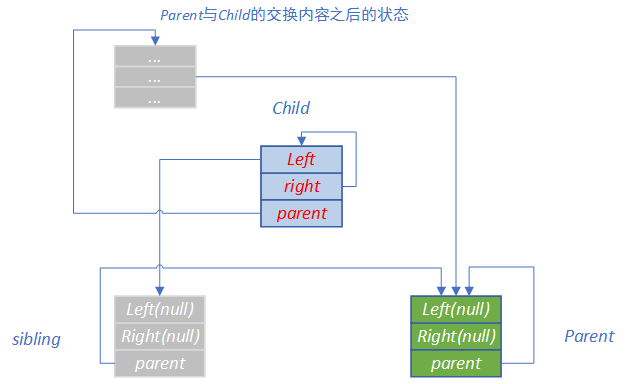
图3 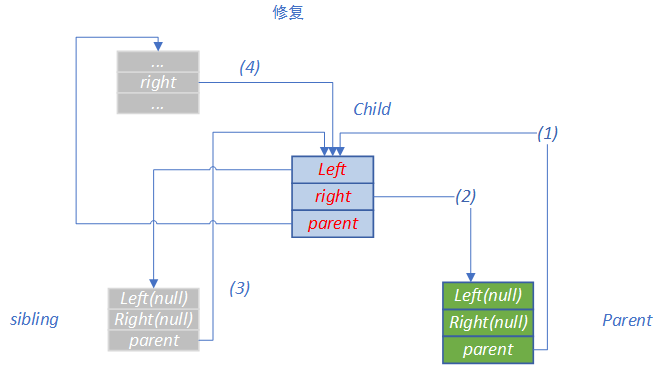







 本文详细介绍了libuv中使用的最小堆实现方法,并对比了Java中的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor/Timer。通过具体代码示例,解释了如何使用链表而非数组来实现最小堆,以及其在插入节点时的特殊处理。
本文详细介绍了libuv中使用的最小堆实现方法,并对比了Java中的ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor/Timer。通过具体代码示例,解释了如何使用链表而非数组来实现最小堆,以及其在插入节点时的特殊处理。

















 7840
7840

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








