Geometry Surface of OpenCascade BRep
摘要Abstract:几何曲面是参数表示的曲面 ,在边界表示中其数据存在于BRep_TFace中,BRep_TFace中不仅包括了几何曲线,还包含用于显示的离散几何信息,如三角剖分数据。本文主要对OpenCascade的BRep表示中几何曲面进行说明,将在后面分析Topology部分的读写程序时来说明包含几何数据的三种拓朴结构中分别包括哪些几何信息。
关键字Key Words:OpenCascade BRep, Geometry Surface, Topology
一、引言 Introduction
边界表示(Boundary Representation)也称为BRep表示,它是几何造型中最成熟、无二义的表示法。实体的边界通常是由面的并集来表示,而每个面又由它所在的曲面的定义加上其边界来表示,面的边界是边的并集,而边又是由点来表示的。
边界表示的一个重要特征是描述形体的信息包括几何信息(Geometry)和拓朴信息(Topology)两个方面。拓朴信息描述形体上的顶点、边、面的连接关系,它形成物体边界表示的“骨架”。形体的几何信息犹如附着在“骨架”上的肌肉。例如,形体的某个面位于某一个曲面上,定义这一曲面方程的数据就是几何信息。此外,边的形状、顶点在三维空间中的位置(点的坐标)等都是几何信息,一般来说,几何信息描述形体的大小、尺寸、位置和形状等。
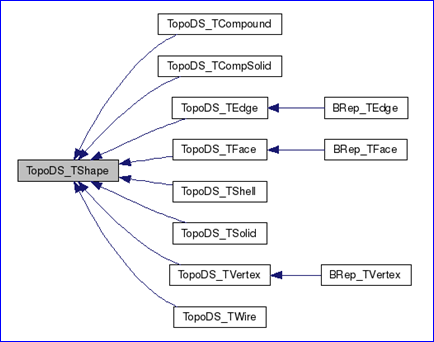
OpenCascade中几何(Geometry)与拓朴(Topology)的关系也是按上述方式组织的。即几何信息在BRep中并不是单独存在的,而是依附于拓朴存在的。通过继承TopoDS包中的抽象的拓朴类实现了边界表示(BRep)模型。如下图所示:
Figure 1.1 Topology data structure in OpenCascade
从上面的类图可以看出只有三种拓朴对象有几何数据:顶点(vertex)、边(edge)、面(face),分别为BRep_TVertex、BRep_TEdge、BRep_TFace。BRep_TVertex中主要包含一个空间点(x, y, z)数据;几何曲线数据主要存在于BRep_TEdge中,BRep_TEdge中不仅包括了几何曲线,还包含其他类型的几何信息;BRep_TFace中主要包含几何曲面及其他的几何数据,如面的三角剖分等。本文主要对OpenCascade的BRep表示中几何曲面进行说明,将在后面分析Topology部分的读写程序时来说明这三种拓朴结构中分别包括哪些几何信息。
Draw Test Harness是OpenCascade提供的一种灵活和简便的测试与演示OCCT造型库的工具。他不仅可以使用交互的方式来创建、显示和修改曲线、曲面和拓朴形状,还可以以脚本(script)的方式来使用,OpenCascade就是用脚本的方式来对其造型内核进行自动化测试(Tests)。本文将示例程序的几何曲面在Draw Test Harness进行创建与显示,结合图形的直观显示便于对抽象概念的理解。
二、示例程序 Example Code
在OpenCascade提供的文档《BRep Format Description White Paper》对其BRep文件数据进行了说明。BRep文件的几何部分包含了参数曲面,根据文档中提供的数据,利用其提供的类来将示例数据进行输出,再调试其相关代码来分析其实现。示例程序如下所示:
/* * Copyright (c) 2013 eryar All Rights Reserved. * * File : Main.cpp * Author : eryar@163.com * Date : 2013-12-01 12:18 * Version : 1.0v * * Description : Demonstrate the geometry surface section * of the BRep file of OpenCascade. * KeyWords : OpenCascade, BRep File, Geometry Surface * */ // OpenCascade library. #define WNT #include <Geom_Plane.hxx> #include <Geom_CylindricalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_ConicalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_SphericalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_ToroidalSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion.hxx> #include <Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution.hxx> #include <Geom_BezierSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_BSplineSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_RectangularTrimmedSurface.hxx> #include <Geom_OffsetSurface.hxx> #include <TColgp_Array2OfPnt.hxx> #include <TColStd_Array1OfReal.hxx> #include <TColStd_Array2OfReal.hxx> #include <TColStd_Array1OfInteger.hxx> #include <GeomTools.hxx> #include <Geom_Circle.hxx> #pragma comment(lib, "TKernel.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKMath.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKG3d.lib") #pragma comment(lib, "TKGeomBase.lib") int main(void) { gp_Ax2 axis(gp_Pnt(1, 2, 3), gp::DZ()); std::ofstream dumpFile("geometrySurface.txt"); // Surface record 1 - Plane. // Example: 1 0 0 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 Handle_Geom_Plane thePlane = new Geom_Plane(gp_Pnt(0, 0, 3), gp_Dir(0, 0, 1)); GeomTools::Write(thePlane, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(thePlane, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(thePlane, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(thePlane, std::cout); // Surface record 2 - Cylinder. // Example: 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4 Handle_Geom_CylindricalSurface theCylinder = new Geom_CylindricalSurface(axis, 4.0); GeomTools::Write(theCylinder, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theCylinder, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theCylinder, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theCylinder, std::cout); // Surface record 3 - Cone. // Example: 3 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 4 // 0.75 Handle_Geom_ConicalSurface theCone = new Geom_ConicalSurface(axis, 0.75, 4.0); GeomTools::Write(theCone, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theCone, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theCone, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theCone, std::cout); // Surface record 4 - Sphere. // Example: 4 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4 Handle_Geom_SphericalSurface theSphere = new Geom_SphericalSurface(axis, 4); GeomTools::Write(theSphere, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theSphere, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theSphere, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theSphere, std::cout); // Surface record 5 - Torus. // Example: 5 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 8 4 Handle_Geom_ToroidalSurface theTorus = new Geom_ToroidalSurface(axis, 8, 4); GeomTools::Write(theTorus, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theTorus, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theTorus, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theTorus, std::cout); // Surface record 6 - Linear Extrusion. // Example: 6 0 0.6 0.8 // 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4 Handle_Geom_Circle baseCurve = new Geom_Circle(axis, 4.0); Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion theExtrusion = new Geom_SurfaceOfLinearExtrusion(baseCurve, gp_Dir(0, 0.6, 0.8)); GeomTools::Write(theExtrusion, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theExtrusion, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theExtrusion, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theExtrusion, std::cout); // Surface record 7 - Revolution Surface. // Example: 7 -4 0 3 0 1 0 // 2 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 4 Handle_Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution theRevolution = new Geom_SurfaceOfRevolution(baseCurve, gp::OY()); theRevolution->SetLocation(gp_Pnt(-4, 0, 3)); GeomTools::Write(theRevolution, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theRevolution, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theRevolution, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theRevolution, std::cout); // Surface record 8 - Bezier Surface. // Example: 8 1 1 2 1 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10 // 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11 // 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12 TColgp_Array2OfPnt poles(1, 3, 1, 2); TColStd_Array2OfReal weights(1, 3, 1, 2); poles.SetValue(1, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 0, 1)); weights.SetValue(1, 1, 7.0); poles.SetValue(1, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 0, -4)); weights.SetValue(1, 2, 10.0); poles.SetValue(2, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 1, -2)); weights.SetValue(2, 1, 8.0); poles.SetValue(2, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 1, 5)); weights.SetValue(2, 2, 11.0); poles.SetValue(3, 1, gp_Pnt(0, 2, 3)); weights.SetValue(3, 1, 9.0); poles.SetValue(3, 2, gp_Pnt(1, 2, 6)); weights.SetValue(3, 2, 12.0); Handle_Geom_BezierSurface theBezierSurface = new Geom_BezierSurface(poles, weights); GeomTools::Write(theBezierSurface, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theBezierSurface, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theBezierSurface, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theBezierSurface, std::cout); // Surface record 9 - B-spline Surface. // Example: 9 1 1 0 0 1 1 3 2 5 4 0 0 1 7 1 0 -4 10 // 0 1 -2 8 1 1 5 11 // 0 2 3 9 1 2 6 12 // // 0 1 // 0.25 1 // 0.5 1 // 0.75 1 // 1 1 // // 0 1 // 0.3 1 // 0.7 1 // 1 1 Standard_Integer uDegree = 1; Standard_Integer vDegree = 1; Standard_Boolean uPeriodic = Standard_False; Standard_Boolean vPeriodic = Standard_False; TColStd_Array1OfReal uKnots(1, 5); TColStd_Array1OfReal vKnots(1, 4); TColStd_Array1OfInteger uMults(1, 5); TColStd_Array1OfInteger vMults(1, 4); uKnots.SetValue(1, 0); uKnots.SetValue(2, 0.25); uKnots.SetValue(3, 0.5); uKnots.SetValue(4, 0.75); uKnots.SetValue(5, 1.0); vKnots.SetValue(1, 0); vKnots.SetValue(2, 0.3); vKnots.SetValue(3, 0.7); vKnots.SetValue(4, 1.0); // Multiplicity of u and v are 1. uMults.Init(1); vMults.Init(1); Handle_Geom_BSplineSurface theBSplineSurface = new Geom_BSplineSurface(poles, weights, uKnots, vKnots, uMults, vMults, uDegree, vDegree, uPeriodic, vPeriodic); GeomTools::Write(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile); GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineSurface, dumpFile); GeomTools::Write(theBSplineSurface, std::cout); GeomTools::Dump(theBSplineSurface, std::cout); // Surface record 10 - Rectangular Trim Surface. // Example: 10 -1 2 -3 4 // 1 1 2 3 0 0 1 1 0 -0 -0 1 0 <





 本文深入探讨了OpenCascade的BRep表示中的几何曲面,包括平面、圆柱面、圆锥面、球面、圆环面、线性拉伸面、旋转面、Bezier曲面、B样条曲面、矩形裁剪曲面和偏移曲面。通过示例程序展示了如何在Draw Test Harness中创建和显示这些几何曲面,强调了多态在重构几何曲面读写代码中的重要性。
本文深入探讨了OpenCascade的BRep表示中的几何曲面,包括平面、圆柱面、圆锥面、球面、圆环面、线性拉伸面、旋转面、Bezier曲面、B样条曲面、矩形裁剪曲面和偏移曲面。通过示例程序展示了如何在Draw Test Harness中创建和显示这些几何曲面,强调了多态在重构几何曲面读写代码中的重要性。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 263
263

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








