以下主要是面向实验二和实验三的笔记:
2015年04月13日
P11
1.arr,&arr
(arr+1),(&arr+1)
区别:
一个变量对应一个内存
eg. 地址:0x10000 ->&arr
内容:0x20000 ->arr
数组是例外的:
1)数组名arr ->&arr[0] arr[0]->int (数组的首地址)
int *
2)typedef int ARRAY[10]
ARRAY a;//sizeof(a) ->40
&arr ->ARRAY*
sizeof(arr); ->40
3)所以:arr//10000
(arr+1)//10004
(&arr+1)//10040
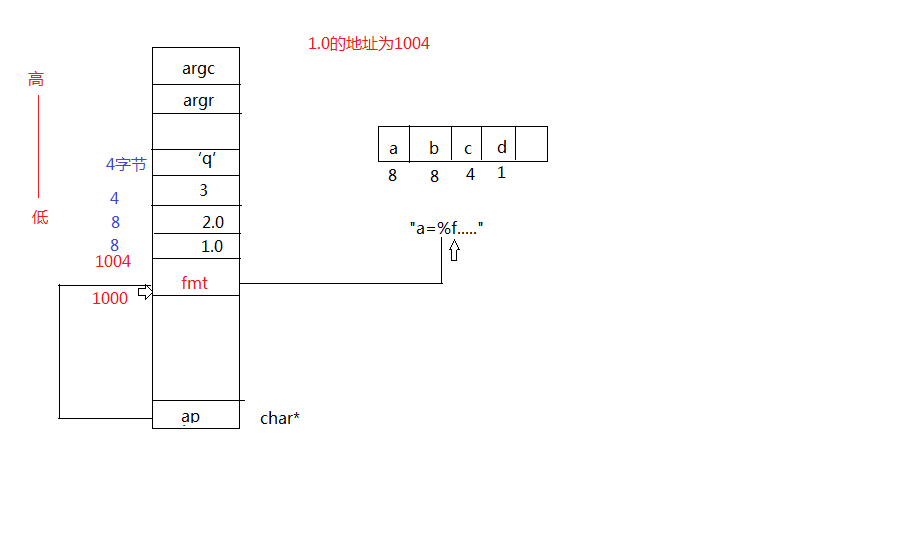
2.P395源代码
C语言约定,从右到左
“实参提升”
int printf(char *fmt,...){
usigned int addr = (usigned int)(&fmt);
addr += sizeof(char*);//1004
double *prt = (double*)addr;
*prt
double h = *((double *)addr);
addr += sizeof(double);
}
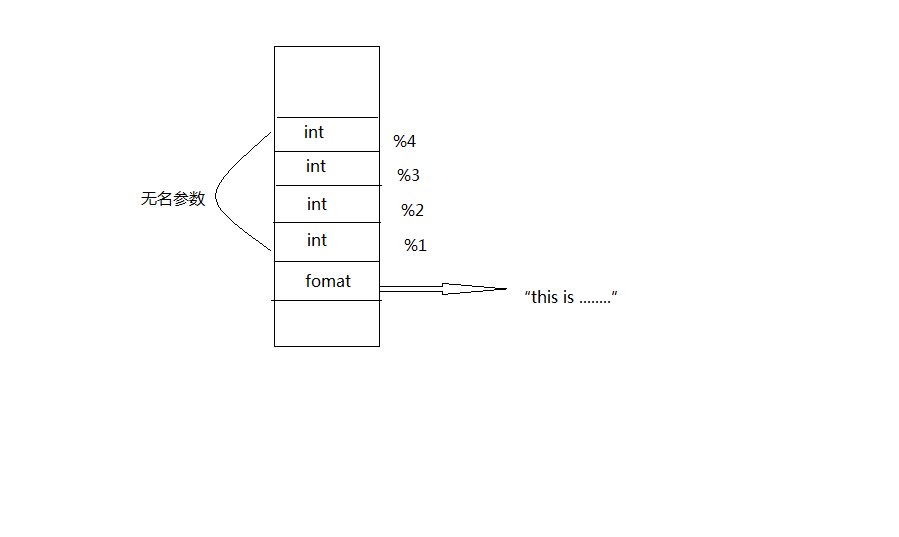
3.实验二
variable argument va_arg 变参
ptr //1
iptr //4
做 int myprintf(const char,...){
*format
}
2015年4月27日
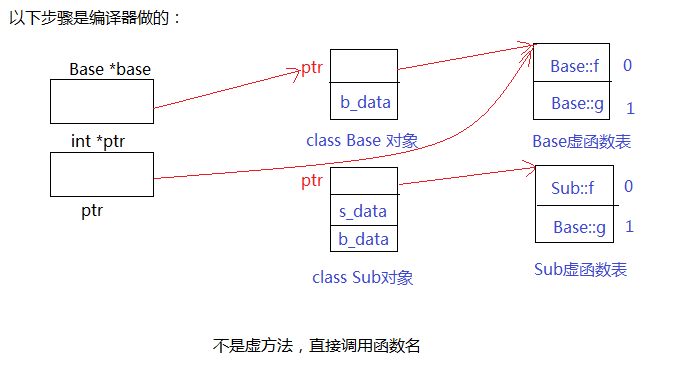
1.不是虚方法 Base::h(...); //静态绑定 编译前
base ->f(10,20);//动态绑定 运行时
2.
全局变量
int c_data;
class Base{
int b_data;
static int c_data;
void h(int a, int b){}
virtual void f(int a, int b){}
}
->
struct Base{
int b_data;
};
void Base_h(Base* this/*非静态,要指向某方法*/,int a, int b)
void Base_f(Base* this/*非静态,要指向某方法*/,int a, int b)
3.
void f(void){}
void g(void){}
typedef void (*FUNC_PTR)(void);
void test(FUNC_PTR ptr){ptr();
int main(){
test(f);
test(g);
}
2015年05月03日
第6章 中间代码生成
1.目标代码生成(汇编)
”龙书“P2
语法分析->语法树 .ast
^
|
语义检查
IR 中间代码
ast 抽象语法树
2.编译器驱动(ucc.exe) 封装了:
cpp.exe 预处理器
cl.exe 编译器
as.exe 汇编器
link.exe 连接器
C Preprocessor Makefile /usr/bin/as link.exe
3.ucc/driver ucc.exe Driver
ucc/ucl ucl.exe Compiler
寄存器x86: eax-movl->a b-??->eax
eax,elx,ecx,edx
esp,ebp,es,eal




















 2045
2045

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








