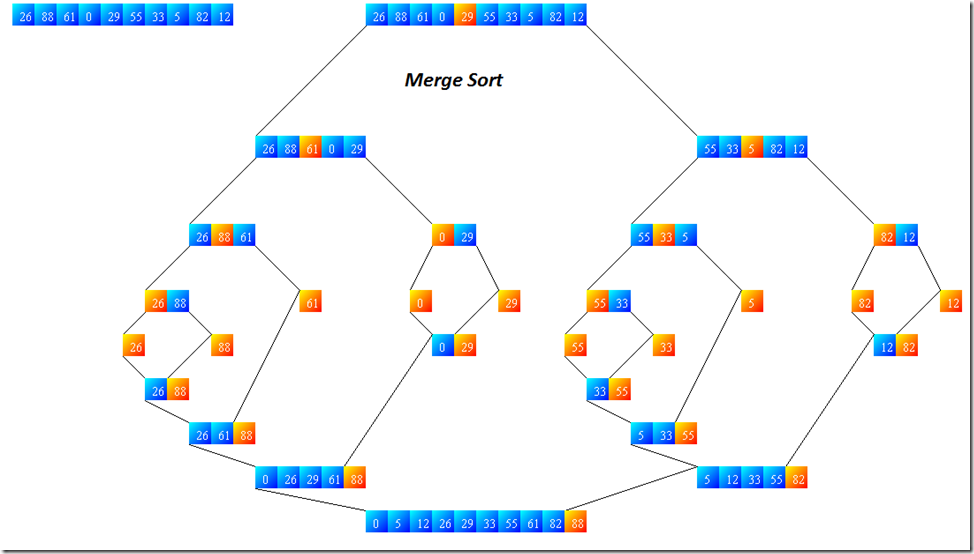
Merge sort is based on Divide and conquer method. It takes the list to be sorted and divide it in half to create two unsorted lists. The two unsorted lists are then sorted and merged to get a sorted list. The two unsorted lists are sorted by continually calling the merge-sort algorithm; we eventually get a list of size 1 which is already sorted. The two lists of size 1 are then merged.
/* Logic: This is divide and conquer algorithm. This works as follows.
(1) Divide the input which we have to sort into two parts in the middle. Call it the left part and right part.
Example: Say the input is -10 32 45 -78 91 1 0 -16 then the left part will be -10 32 45 -78 and the right part will be 91 1 0 6.
(2) Sort Each of them seperately. Note that here sort does not mean to sort it using some other
method. We already wrote fucntion to sort it. Use the same.
(3) Then merge the two sorted parts.*/
/*This function Sorts the array in the range [left,right]. That is from index left to index right inclusive */ void MergeSort(int *array, int left, int right){ int mid = (left+right)/2; /* We have to sort only when left<right because when left=right it is anyhow sorted*/ if(left<right) { /* Sort the left part */ MergeSort(array,left,mid); /* Sort the right part */ MergeSort(array,mid+1,right); /* Merge the two sorted parts */ Merge(array,left,mid,right); } } /* Merge functions merges the two sorted parts. Sorted parts will be from [left, mid] and [mid+1, right]. */ void Merge(int *array, int left, int mid, int right) { /*We need a Temporary array to store the new sorted part*/ int tempArray[right-left+1]; int pos=0,lpos = left,rpos = mid + 1; while(lpos <= mid && rpos <= right) { if(array[lpos] < array[rpos]) { tempArray[pos++] = array[lpos++]; } else { tempArray[pos++] = array[rpos++]; } } while(lpos <= mid) tempArray[pos++] = array[lpos++]; while(rpos <= right) tempArray[pos++] = array[rpos++]; int iter; /* Copy back the sorted array to the original array */ for(iter = 0;iter < pos; iter++) { array[iter+left] = tempArray[iter]; } return; }
Best case – When the array is already sorted O(nlogn).
Worst case – When the array is sorted in reverse order O(nlogn).
Average case – O(nlogn).
Extra space is required, so space complexity is O(n) for arrays and O(logn) for linked lists.







 本文详细介绍了一种基于分治策略的高效排序算法——归并排序。该算法通过不断将待排序的序列分成两部分,直至每个子序列只有一个元素,然后合并这些已排序的子序列来完成排序过程。文章给出了归并排序的具体实现步骤,并分析了其时间复杂度为O(nlogn),空间复杂度为O(n)。
本文详细介绍了一种基于分治策略的高效排序算法——归并排序。该算法通过不断将待排序的序列分成两部分,直至每个子序列只有一个元素,然后合并这些已排序的子序列来完成排序过程。文章给出了归并排序的具体实现步骤,并分析了其时间复杂度为O(nlogn),空间复杂度为O(n)。
















 348
348

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








