在Linux系统下,获取毫秒级的系统时间,使用毫秒级的定时器,修改文件访问时间等,用sys/time.h下的方法会很方便
数据结构:
timeval:time value 存储时间格式
struct timeval {
long tv_sec; //秒
long tv_usec; //毫秒
}
itimerval:
struct itimerval {
struct timerval it_value; //从设定定时器开始计算,到第一次定时器生效的时间
struct timerval it_interval; //每两次定时器生效的时间间隔
};
特别说明:
l 如果it_value被设为0,系统无视it_interval的值并且终止timer,所以可以通过这种方式来使timer失效
l 如果it_interval被设为0,则timer在执行一次之后失效
方法:
1. int getitimer(int, struct itimerval *);
获取定时器,一般会有三种类型的定时器:
ITIMER_REAL:
Decrements in real time. A SIGALRM signal is delivered when this timer expires.
ITIMER_VIRTUAL:
Decrements in process virtual time. It runs only when the process is executing. A SIGVTALRM signal is delivered when it expires.
ITIMER_PROF:
Decrements both in process virtual time and when the system is running on behalf of the process. It is designed to be used by interpreters in statistically profiling the execution of interpreted programs. Each time the ITIMER_PROF timer expires, the SIGPROF signal is delivered.
例如:
如果要获得real time类型的定时器,则调用
getitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &value);
2. int setitimer(int, const struct itimerval *, struct itimerval *);
设置定时器
第一个参数:定时器类型
第二个参数:指定的定时器
第三个参数:调用setitimer之前的旧定时器
3. int gettimeofday(struct timeval *, void *);
获取毫秒级别的系统时间
如果第二个参数不为NULL,结果不可预料(If tzp is not a null pointer, the behaviour is unspecified.)
4. int utimes(const char *, const struct timeval [2]);
用来设定Linux系统下文件的最后访问时间和最后修改时间
第一个参数:文件路径
第二个参数:timeval[0]指的是最后访问时间
timeval[1]指的是最后修改时间
用法详解:
1.用来获取毫秒级的系统时间(从1970年1月1日开始算起)
int gettimeofday(struct timeval *, void *);
例子:gettimeofday.cpp
#include <sys/time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { struct timeval curtime; gettimeofday(&curtime, NULL); printf("curtime.tv_sec:%d\n", curtime.tv_sec); printf("curtime.tv_usec:%d\n", curtime.tv_usec); return 0; }
2.使用定时器
例子:timer.cpp
#include <sys/time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <signal.h> #include <string.h> #include <unistd.h> void sayHello(int); int main() { signal(SIGALRM, sayHello); struct itimerval timer; memset(&timer, 0, sizeof(timer)); timer.it_value.tv_sec = 5; timer.it_value.tv_usec = 0; timer.it_interval.tv_sec = 3; timer.it_interval.tv_usec = 0; setitimer(ITIMER_REAL, &timer, NULL); while(true) { pause(); } return 0; } void sayHello(int temp) { printf("hello world!\n"); }
代码详解:
使用settimer设定的timer时间到的时候,会发出SIGALRM信号,通过signal(SIGALRM, sayHello)方法指定在收到信号时的动作。
按照代码中的设定,从settimer方法被调用开始算起,经过5秒钟第一次执行sayHello方
法,之后每3秒钟执行一次sayHello
通过while(true)死循环保证进程不会终止,如果没有这个死循环,timer只会在5秒钟后响 应一次
3.修改文件最后访问时间和最后修改时间
#include <sys/time.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int main() { char path[] = "/home/mqq/jordan/try/test"; struct timeval times[2]; for(int i=0; i<2; i++) { memset(×[i], 0, sizeof(timeval)); } times[0].tv_sec = 123; times[0].tv_usec = 0; times[1].tv_sec = 456; times[1].tv_usec = 0; utimes(path, times); perror("error info:"); return 0; }
用stat + filename 可以查看文件上次访问时间等信息
程序执行前:
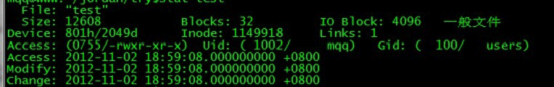
执行后:
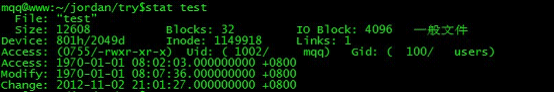




















 538
538

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








