kubernetes
Vulnerabilities in open source are vital to a lot of organizations and developers are paying close attention to. Any little breach can be very bad, especially when it comes to container orchestration.
开源漏洞对于许多组织至关重要,开发人员正在密切关注。 任何小的违反都可能是非常糟糕的,尤其是在涉及容器编排时。
Kubernetes has become one of the leaders in the container market. Most companies are now employing the capabilities of Kubernetes to manage their container workloads.
Kubernetes已成为集装箱市场的领导者之一。 现在,大多数公司都在使用Kubernetes的功能来管理其容器工作负载。
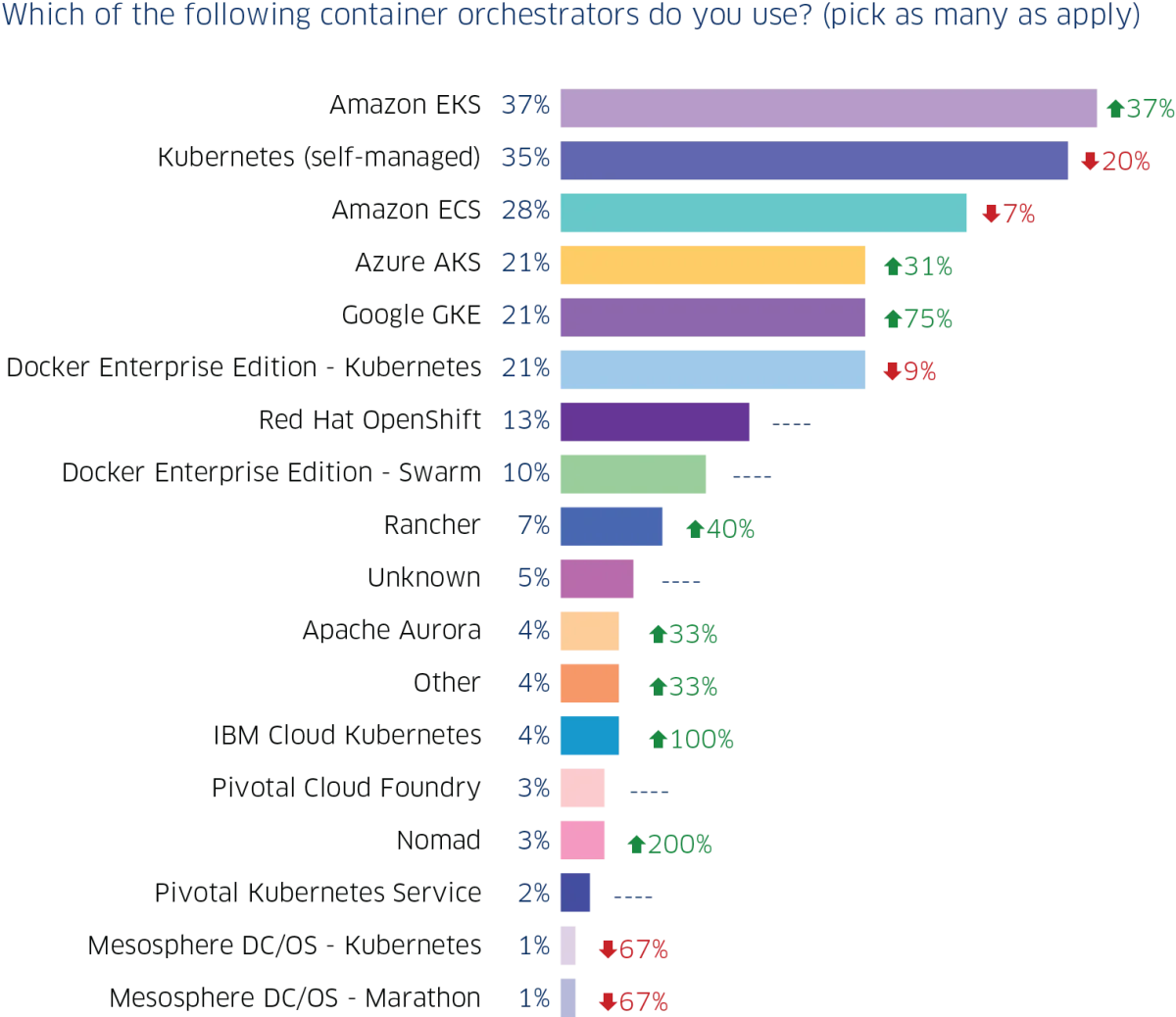
According to a survey, over 86% of companies are using Kubernetes for their container operations. Also, self-managed Kubernetes (35%) is now second to Amazon EKS (37%) with just a 2% difference after previously being the most used. Take a look at the figures below:
根据一项调查,超过86%的公司正在使用Kubernetes进行其容器运营。 此外,自我管理的Kubernetes(35%)现在仅次于Amazon EKS(37%),仅次于最常用的2%,仅次于Amazon EKS。 看一下下面的数字:
With all these, you should have guessed by now that there will be a lot of accompanying security vulnerabilities. For every version released, there’s a list of security vulnerabilities discovered and fixes released.
有了这些,您现在应该已经猜到会有很多伴随的安全漏洞。 对于每个发布的版本,都有一个发现的安全漏洞和发布的修复程序的列表。
In this article, we’ll be exploring the Kubernetes security vulnerabilities that have been found this year so far, and the security best practices to follow so you can avoid and fix them.
在本文中,我们将探索今年迄今为止发现的Kubernetes安全漏洞,以及遵循的最佳安全最佳实践 ,您可以避免和修复它们。
Kubernetes ContainerNetworking — CVE-2020–10749 (Kubernetes ContainerNetworking — CVE-2020–10749)
This was found in all versions of container networking/plugins before the version 0.8.6. It allowed containers in Kubernetes clusters to perform man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks.
在版本0.8.6之前的所有版本的容器网络/插件中都可以找到它。 它允许Kubernetes集群中的容器执行中间人(MitM)攻击。
A malicious container can send rogue IPv6 router advertisements to the host or other containers, to redirect traffic to the malicious








 本文翻译自Medium,探讨了2020年Kubernetes面临的安全漏洞,并详细介绍了针对这些漏洞的修复方法,以保障集群的安全运行。
本文翻译自Medium,探讨了2020年Kubernetes面临的安全漏洞,并详细介绍了针对这些漏洞的修复方法,以保障集群的安全运行。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 709
709

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








