solver 算是 Caffe 的核心的核心,它协调着整个模型的运作。Caffe 程序运行必带的一个参数就是solver 配置文件,solver.prototxt 文件是用来告诉 Caffe 如何训练网络的。
在Deep Learning中,往往loss function是非凸的,没有解析解,我们需要通过优化方法求解。solver的主要作用就是交替调用前向(forword)算法和后向(backward)算法来更新参数,从而最小化loss,实际上就是一种迭代的优化算法。
2. solver文件介绍
Solver的流程:
- 设计好需要优化的对象,以及用于学习的训练网络和用于评估的测试网络。(通过调用另外一个配置文件prototxt来进行)
- 通过forward和backward迭代的进行优化来跟新参数。
- 定期的评价测试网络。 (可设定多少次训练后,进行一次测试)
- 在优化过程中显示模型和solver的状态
在每一次的迭代过程中,solver做了这几步工作:
1、调用forward算法来计算最终的输出值,以及对应的loss
2、调用backward算法来计算每层的梯度
3、根据选用的slover方法,利用梯度进行参数更新
4、记录并保存每次迭代的学习率、快照,以及对应的状态。
solver.prototxt是caffe的配置文件。里面定义了网络训练时候的各种参数,比如学习率、权重衰减、迭代次数等等。
solver文件示例
solver文件是训练网络所必须要的文件,其中定义了诸如:求解器类型、学习率、学习率的变化策略等。其命令行调用方式模式一般为:
caffe train --solver=*_slover.prototxt
接下来看一个solver配置文件的例子:
train_net: "train.prototxt"
test_net: "val.prototxt"
test_iter: 100
test_interval: 938
base_lr: 0.00999999977648
display: 1000
max_iter: 9380
lr_policy: "step"
gamma: 0.10000000149
momentum: 0.899999976158
weight_decay: 0.000500000023749
stepsize: 3000
snapshot: 4000
snapshot_prefix: "./snapshot/"
solver_mode: GPU
type: "SGD"
下面的内容将会详细讲解其中的参数,并介绍其其使用方法。
3. solver文件参数详细解析
solver文件示例
下面以 Caffe 中的 mnist 实例进行简单明了的解释:
net: "examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt"
test_iter: 100
test_interval: 500
base_lr: 0.01
momentum: 0.9
weight_decay: 0.0005
lr_policy: "inv"
gamma: 0.0001
power: 0.75
display: 100
max_iter: 10000
snapshot: 5000
snapshot_prefix: "examples/mnist/lenet"
solver_mode: GPU
第1行:
net: "examples/mnist/lenet_train_test.prototxt"
用于设置深度网络模型,即指定网络配置文件(该实例中为 lenet_train_test.prototxt)的路径。
第2行,第3行以及第11行:
2. test_iter: 100
3. test_interval: 500
11. max_iter: 10000
test_iter 的大小为 test 数据集的总样本数与 batch_size 的比值,比如在 mnist 数据集中,有10000个测试样本,batch_size设为100的话,则 test_iter = 10000/100 = 100;
test_interval 表示测试间隔,例如,想要完成一次完整的 train 再测试,则 test_interval 的值为 50000/100 = 500,其中,50000为训练集数量,100为 batch_size 的大小;
max_iter 表示最大训练迭代次数,若 test_interval 测试间隔设为一次完整的 train,则 max_iter = test_interval * epoch,其中,epoch为训练的轮次。
第4-9行
1. base_lr: 0.01
2. momentum: 0.9
3. weight_decay: 0.0005
4. lr_policy: "inv"
5. gamma: 0.0001
6. power: 0.75
base_lr 用来表示网络的初始学习率;
momentum 表示动量大小,在新的计算中要保留的前面的权重数量,通常设置为0.9;
weight_decay 表示对较大权重的惩罚(正则化)因子,防止过拟合的一个参数;
lr_policy 表示训练过程中学习率的变化方式,有如下几种:
- fixed:保持 base_lr 不变.
- step:如果设置为 step,则还需要设置一个 stepsize, 返回 base_lr *
gamma ^ (floor(iter / stepsize)),其中 iter 表示当前的迭代次数 - exp:返回 base_lr * gamma ^ iter,iter 为当前迭代次数
- inv:如果设置为 inv,还需要设置一个 power, 返回 base_lr * (1 + gamma * iter) ^ (- power)
- multistep:如果设置为 multistep,则还需要设置一个 stepvalue。这个参数和 step 很相似,step 是均匀等间隔变化,而 multistep 则是根据 stepvalue 值变化
- poly:学习率进行多项式误差, 返回 base_lr (1 - iter/max_iter) ^ (power)
- sigmoid:学习率进行sigmod衰减,返回 base_lr ( 1/(1 + exp(-gamma * (iter - stepsize))))
以为此处设置为 “inv”,所以需要设置 gamma 和 power 值。
以为此处设置为 “inv”,所以需要设置 gamma 和 power 值。
第10行
10. display: 100
表示每训练100次,在屏幕上显示一次。如果设置为0,则不显示。
第12,13行
12. snapshot: 5000
13. snapshot_prefix: “examples/mnist/lenet”
将训练出来的 model 和 solver 状态进行保存,snapshot 用于设置训练多少次后进行保存,默认为0,不保存。snapshot_prefix 为设置保存路径。也可以设置 snapshot_format,保存的类型。有两种选择:HDF5 和 BINARYPROTO ,默认为 BINARYPROTO。
第14行
14. solver_mode: GPU
设置运行模式。默认为GPU,如果没有GPU,则需要改成CPU,否则会出错。
4. 参数补充说明
1.test_iter计算
test_iter: 100
该参数需要训练的总文件个数N和训练网络模型文件中定义的batch_size相结合,在test_iter指定的迭代次数中需要跑完所有的训练数据,这里称之为一个epoch。那么其取值可以表述为下面的公式:
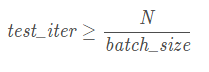
2.test_interval计算
参数test_interval,既是测试间隔,就是规定迭代多少次之后才开始进行测试
test_interval: 938
该参数的值也是与测试的总文件个数M和测试网络模型文件中定义的batch_size相结合确定的。其取值公式为:
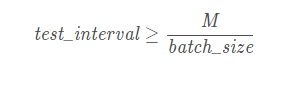
3.学习率的设置及其变化策略
base_lr: 0.00999999977648 # 基础学习率
lr_policy: "step" # 学习率变化的策略
gamma: 0.10000000149 # 学习速率衰减常数,每次更新学习速率都是乘上这个固定常数
momentum: 0.899999976158 # 动量,遗忘因子
weight_decay: 0.000500000023749 # 用于防止过拟合,乘以权值惩罚项
stepsize: 3000 # 学习率变化的步长,不能太小,如果太小会导致学习率再后来越来越小,达不到充分收敛的效果。
4.求解器的类型选择
求解器的类型选择,默认就是SGD
type: "SGD"
可供选择的求解器类型:
enum SolverType {
SGD = 0;
NESTEROV = 1;
ADAGRAD = 2;
RMSPROP = 3;
ADADELTA = 4;
ADAM = 5;
}
5. SolverParameter定义
这里提出完整的SolverParameter的定义,以供查阅…
// Update the next available ID when you add a new SolverParameter field.
//
// SolverParameter next available ID: 42 (last added: layer_wise_reduce)
message SolverParameter {
//
// Specifying the train and test networks
//
// Exactly one train net must be specified using one of the following fields:
// train_net_param, train_net, net_param, net
// One or more test nets may be specified using any of the following fields:
// test_net_param, test_net, net_param, net
// If more than one test net field is specified (e.g., both net and
// test_net are specified), they will be evaluated in the field order given
// above: (1) test_net_param, (2) test_net, (3) net_param/net.
// A test_iter must be specified for each test_net.
// A test_level and/or a test_stage may also be specified for each test_net.
//
// Proto filename for the train net, possibly combined with one or more
// test nets.
optional string net = 24;
// Inline train net param, possibly combined with one or more test nets.
optional NetParameter net_param = 25;
optional string train_net = 1; // Proto filename for the train net.
repeated string test_net = 2; // Proto filenames for the test nets.
optional NetParameter train_net_param = 21; // Inline train net params.
repeated NetParameter test_net_param = 22; // Inline test net params.
// The states for the train/test nets. Must be unspecified or
// specified once per net.
//
// By default, train_state will have phase = TRAIN,
// and all test_state's will have phase = TEST.
// Other defaults are set according to the NetState defaults.
optional NetState train_state = 26;
repeated NetState test_state = 27;
// The number of iterations for each test net.
repeated int32 test_iter = 3;
// The number of iterations between two testing phases.
optional int32 test_interval = 4 [default = 0];
optional bool test_compute_loss = 19 [default = false];
// If true, run an initial test pass before the first iteration,
// ensuring memory availability and printing the starting value of the loss.
optional bool test_initialization = 32 [default = true];
optional float base_lr = 5; // The base learning rate
// the number of iterations between displaying info. If display = 0, no info
// will be displayed.
optional int32 display = 6;
// Display the loss averaged over the last average_loss iterations
optional int32 average_loss = 33 [default = 1];
optional int32 max_iter = 7; // the maximum number of iterations
// accumulate gradients over `iter_size` x `batch_size` instances
optional int32 iter_size = 36 [default = 1];
// The learning rate decay policy. The currently implemented learning rate
// policies are as follows:
// - fixed: always return base_lr.
// - step: return base_lr * gamma ^ (floor(iter / step))
// - exp: return base_lr * gamma ^ iter
// - inv: return base_lr * (1 + gamma * iter) ^ (- power)
// - multistep: similar to step but it allows non uniform steps defined by
// stepvalue
// - poly: the effective learning rate follows a polynomial decay, to be
// zero by the max_iter. return base_lr (1 - iter/max_iter) ^ (power)
// - sigmoid: the effective learning rate follows a sigmod decay
// return base_lr ( 1/(1 + exp(-gamma * (iter - stepsize))))
//
// where base_lr, max_iter, gamma, step, stepvalue and power are defined
// in the solver parameter protocol buffer, and iter is the current iteration.
optional string lr_policy = 8;
optional float gamma = 9; // The parameter to compute the learning rate.
optional float power = 10; // The parameter to compute the learning rate.
optional float momentum = 11; // The momentum value.
optional float weight_decay = 12; // The weight decay.
// regularization types supported: L1 and L2
// controlled by weight_decay
optional string regularization_type = 29 [default = "L2"];
// the stepsize for learning rate policy "step"
optional int32 stepsize = 13;
// the stepsize for learning rate policy "multistep"
repeated int32 stepvalue = 34;
// Set clip_gradients to >= 0 to clip parameter gradients to that L2 norm,
// whenever their actual L2 norm is larger.
optional float clip_gradients = 35 [default = -1];
optional int32 snapshot = 14 [default = 0]; // The snapshot interval
optional string snapshot_prefix = 15; // The prefix for the snapshot.
// whether to snapshot diff in the results or not. Snapshotting diff will help
// debugging but the final protocol buffer size will be much larger.
optional bool snapshot_diff = 16 [default = false];
enum SnapshotFormat {
HDF5 = 0;
BINARYPROTO = 1;
}
optional SnapshotFormat snapshot_format = 37 [default = BINARYPROTO];
// the mode solver will use: 0 for CPU and 1 for GPU. Use GPU in default.
enum SolverMode {
CPU = 0;
GPU = 1;
}
optional SolverMode solver_mode = 17 [default = GPU];
// the device_id will that be used in GPU mode. Use device_id = 0 in default.
optional int32 device_id = 18 [default = 0];
// If non-negative, the seed with which the Solver will initialize the Caffe
// random number generator -- useful for reproducible results. Otherwise,
// (and by default) initialize using a seed derived from the system clock.
optional int64 random_seed = 20 [default = -1];
// type of the solver
optional string type = 40 [default = "SGD"];
// numerical stability for RMSProp, AdaGrad and AdaDelta and Adam
optional float delta = 31 [default = 1e-8];
// parameters for the Adam solver
optional float momentum2 = 39 [default = 0.999];
// RMSProp decay value
// MeanSquare(t) = rms_decay*MeanSquare(t-1) + (1-rms_decay)*SquareGradient(t)
optional float rms_decay = 38 [default = 0.99];
// If true, print information about the state of the net that may help with
// debugging learning problems.
optional bool debug_info = 23 [default = false];
// If false, don't save a snapshot after training finishes.
optional bool snapshot_after_train = 28 [default = true];
// DEPRECATED: old solver enum types, use string instead
enum SolverType {
SGD = 0;
NESTEROV = 1;
ADAGRAD = 2;
RMSPROP = 3;
ADADELTA = 4;
ADAM = 5;
}
// DEPRECATED: use type instead of solver_type
optional SolverType solver_type = 30 [default = SGD];
// Overlap compute and communication for data parallel training
optional bool layer_wise_reduce = 41 [default = true];
}
<div class="hljs-button {2}" data-title="复制" data-report-click="{"spm":"1001.2101.3001.4259"}"></div>`





 本文详细介绍了Caffe中Solver的重要作用,它是训练神经网络过程中的核心,负责协调网络的前向传播和反向传播,通过优化算法更新参数以最小化损失。Solver配置文件solver.prototxt定义了训练参数,如学习率、优化策略和迭代次数等。文中还举例说明了各参数的具体含义和计算方法,包括学习率衰减策略、测试间隔和动量等,并提供了MNIST实例进行解析。
本文详细介绍了Caffe中Solver的重要作用,它是训练神经网络过程中的核心,负责协调网络的前向传播和反向传播,通过优化算法更新参数以最小化损失。Solver配置文件solver.prototxt定义了训练参数,如学习率、优化策略和迭代次数等。文中还举例说明了各参数的具体含义和计算方法,包括学习率衰减策略、测试间隔和动量等,并提供了MNIST实例进行解析。
















 611
611

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








