利用python完成课程作业ex3的第二部分,第二部分的要求如下:
In the previous part of this exercise, you implemented multi-class logistic regression to recognize handwritten digits. However, logistic regression cannotform more complex hypotheses as it is only a linear classier.3 In this part of the exercise, you will implement a neural network to recognize handwritten digits using the same training set as before. The neural network will be able to represent complex models that form non-linear hypotheses. For this week, you will be using parameters from a neural network
that we have already trained. Your goal is to implement the feedforward propagation algorithm to use our weights for prediction. In next week's exercise, you will write the backpropagation algorithm for learning the neural network parameters.
代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
Created on Sat Nov 23 10:55:24 2019
@author: Lonely_hanhan
"""
import scipy.io as sio
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.optimize as op
''' Setup the parameters you will use for this exercise '''
input_layer_size = 400; # 20x20 Input Images of Digits
hidden_layer_size = 25; # 25 hidden units
num_labels = 10; # 10 labels, from 1 to 10
# (note that we have mapped "0" to label 10)
'''=========== Part 1: Loading and Visualizing Data ============='''
print('Loading and Visualizing Data ...\n')
data = sio.loadmat('D:\exercise\machine-learning-ex3\machine-learning-ex3\ex3\ex3data1.mat')
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
m = X.shape[0]
#Randomly select 100 data points to display
def displayData(X):
#Compute rows, cols
[m, n] = X.shape
example_width = round(np.sqrt(n)).astype(int)
example_height = (n / example_width).astype(int)
#Compute number of items to display
display_rows = np.floor(np.sqrt(m)).astype(int)
display_cols = np.ceil(m / display_rows).astype(int)
#Between images padding
pad = 1
#Setup blank display
display_array = - np.ones((display_rows * (example_height + pad), \
display_cols * (example_width + pad)))
# Copy each example into a patch on the display array
curr_ex = 0
for j in range(display_rows):
for i in range(display_cols):
if curr_ex > m-1:
break
#Copy the patch
#Get the max value of the patch
max_val = np.max(np.abs(X[curr_ex]))
display_array[j * (example_height + pad) + np.arange(example_height),\
i * (example_width + pad) + np.arange(example_width)[:, np.newaxis]] = \
X[curr_ex].reshape((example_height, example_width)) / max_val
curr_ex += 1
if curr_ex > m-1:
break
plt.figure()
plt.imshow(display_array, cmap='gray', extent=[-1, 1, -1, 1])
plt.axis('off')
return
rand_indices = np.random.permutation(range(m)) #获取0-4999 5000个无序随机索引
selected = X[rand_indices[0:100], :] #获取前100个随机索引对应的整条数据的输入特征
displayData(selected) #调用可视化函数 进行可视化
#input('Program paused. Press ENTER to continue')
# In this part of the exercise, we load some pre-initialized
# neural network parameters.
print('\nLoading Saved Neural Network Parameters ...\n')
weight = sio.loadmat('D:\exercise\machine-learning-ex3\machine-learning-ex3\ex3\ex3weights.mat')
Theta1 = weight['Theta1'] # first layer sigmoid
Theta2 = weight['Theta2'] # second layer sigmnid
'''================= Part 3: Implement Predict ================='''
# After training the neural network, we would like to use it to predict
# the labels. You will now implement the "predict" function to use the
# neural network to predict the labels of the training set. This lets
# you compute the training set accuracy.
def sigmond(z):
return 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
def predict(Theta1, Theta2, X):
# Useful values
m = X.shape[0]
#num_labels = Theta2.shape[0]
X = np.c_[np.ones(m), X]
# You need to return the following variables correctly
p = np.zeros((m, 1))
# ====================== YOUR CODE HERE ======================
# Instructions: Complete the following code to make predictions using
# your learned neural network. You should set p to a
# vector containing labels between 1 to num_labels.
#
# Hint: The max function might come in useful. In particular, the max
# function can also return the index of the max element, for more
# information see 'help max'. If your examples are in rows, then, you
# can use max(A, [], 2) to obtain the max for each row.
#计算第二层
z2 = np.dot(X, (Theta1.T))
a2 = sigmond(z2)
n2 = a2.shape[0]
a2 = np.c_[np.ones(n2), a2] #第二层列加一
#计算输出层
z3 = np.dot(a2, Theta2.T)
out = sigmond(z3)
p = np.argmax(out, axis=1)
return p+1
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, X)
print('Training set accuracy:',sum(pred[:, np.newaxis] == y)[0] /5000 * 100,"%")
# To give you an idea of the network's output, you can also run
# through the examples one at the a time to see what it is predicting.
# Randomly permute examples
rp = np.random.permutation(range(m))
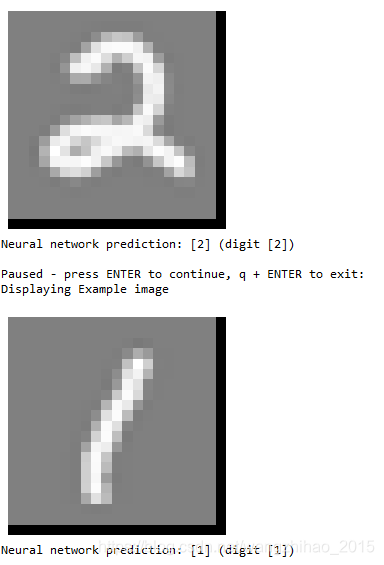
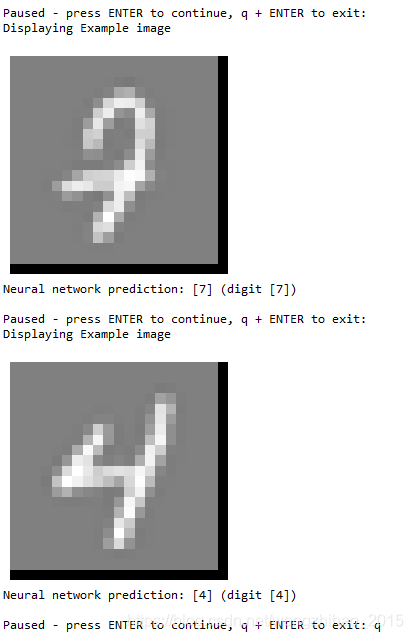
for i in range(m):
print('Displaying Example image')
example = X[rp[i]]
example = example.reshape((1, example.size))
displayData(example)
plt.show()
pred = predict(Theta1, Theta2, example)
print('Neural network prediction: {} (digit {})'.format(pred, np.mod(pred, 10)))
s = input('Paused - press ENTER to continue, q + ENTER to exit: ')
if s == 'q':
break结果如下:

对于这段代码中的第三部分:Implement Predict中类别的预测概率(这部分需要跟练习ex3_1进行对比)的自己理解:
首先一直认为和第一部分输出类别计算结果一样,即第0类代表数字10,然而输出的结果:
![]()
之后一直在找错误,例如是否公式写错,是否缺少东西,直到找到了这篇文章,文章链接:https://towardsdatascience.com/andrew-ngs-machine-learning-course-in-python-neural-networks-e526b41fdcd9
发现第二部分跟第一部分不同的是,最优的theta是已经给出的,并且输出单元的索引0~9应该是对应着的是1~10,matlab应该没有这种情况,因为他们输出单元位置的索引直接返回的是1~10,所以在python中需要对输出的p进行加一。
以上是自己的理解,如果有什么地方理解不对,希望各位大佬可以批评指正!
为了记录自己的学习进度同时也加深自己对知识的认知,刚刚开始写博客,如有错误或者不妥之处,请大家给予指正。





 本文详细介绍了利用预训练的神经网络参数进行手写数字识别的过程。通过实施前向传播算法,实现了对训练集的手写数字预测,提高了模型的准确性。文章对比了神经网络与逻辑回归在复杂假设形成上的差异,强调了神经网络处理非线性问题的能力。
本文详细介绍了利用预训练的神经网络参数进行手写数字识别的过程。通过实施前向传播算法,实现了对训练集的手写数字预测,提高了模型的准确性。文章对比了神经网络与逻辑回归在复杂假设形成上的差异,强调了神经网络处理非线性问题的能力。
















 301
301

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








