day08-Stream
流只能用一次!!!!!
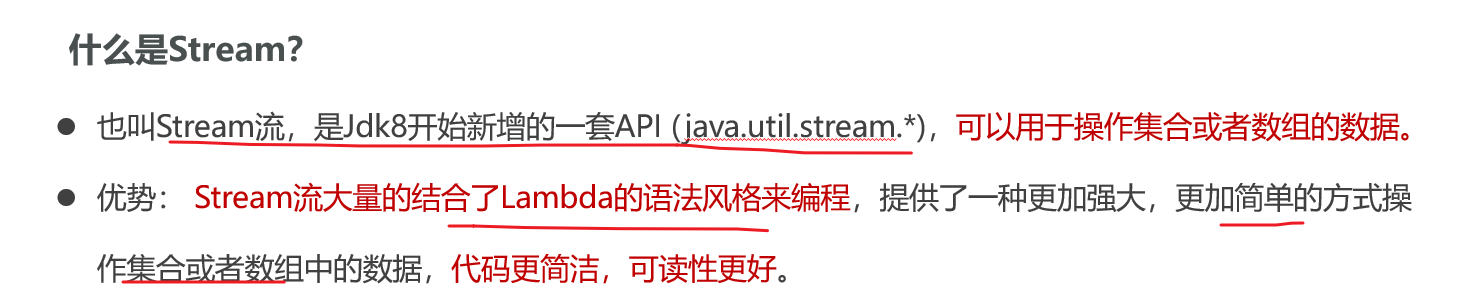
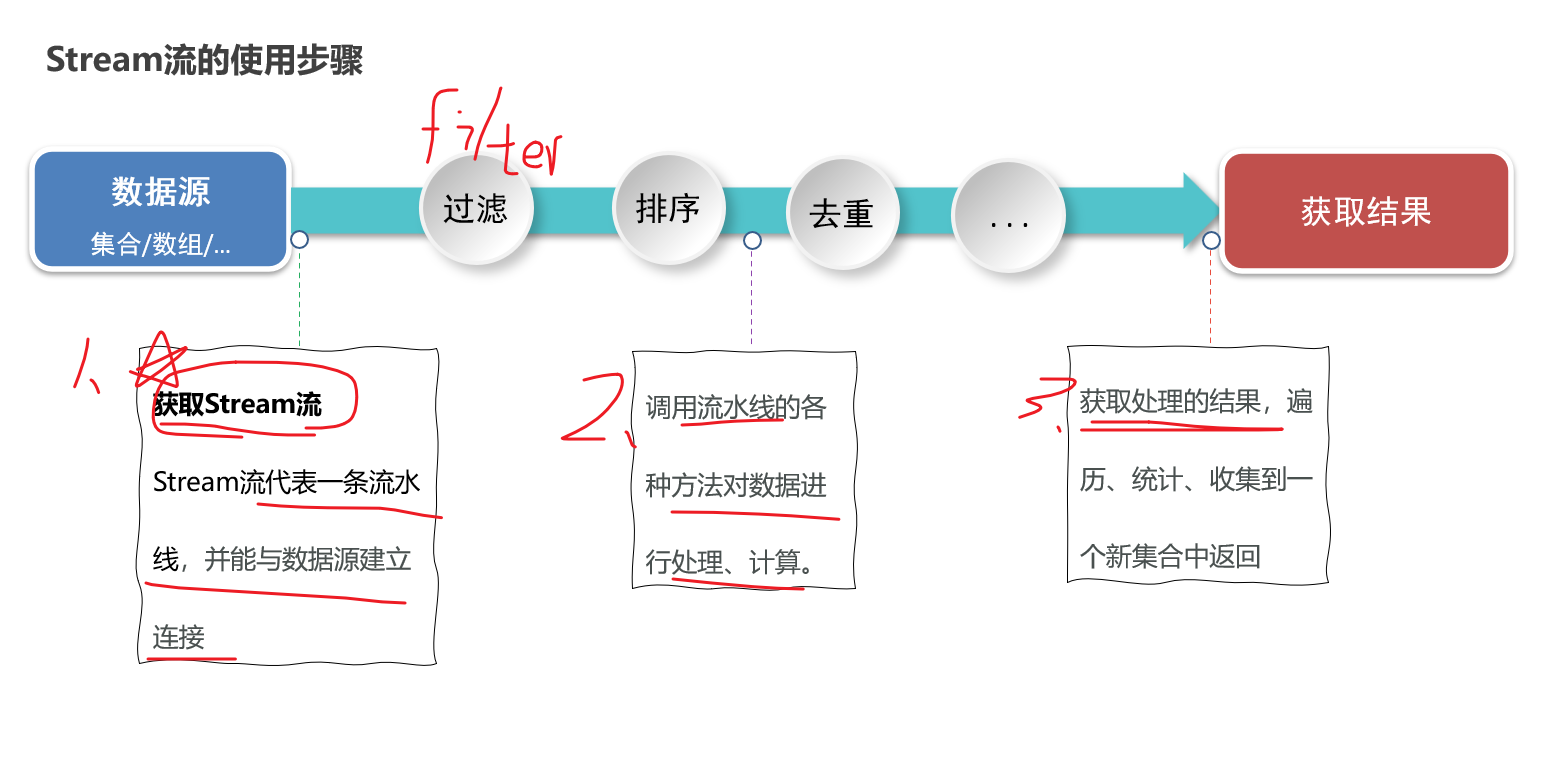
获取集合的Stream流

Stream流常见的中间方法

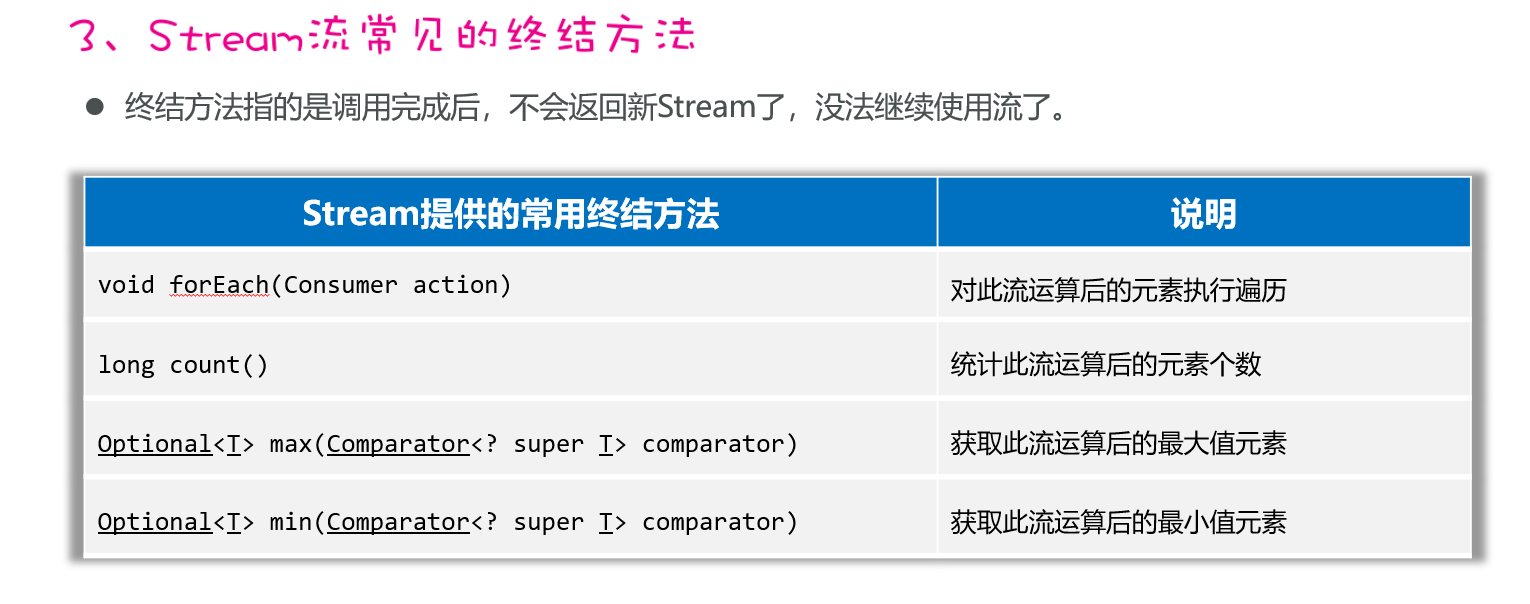
Stream流的常见终结方法
用完之后,不会再返回新流了
收集Stream流

day08-File,IO流
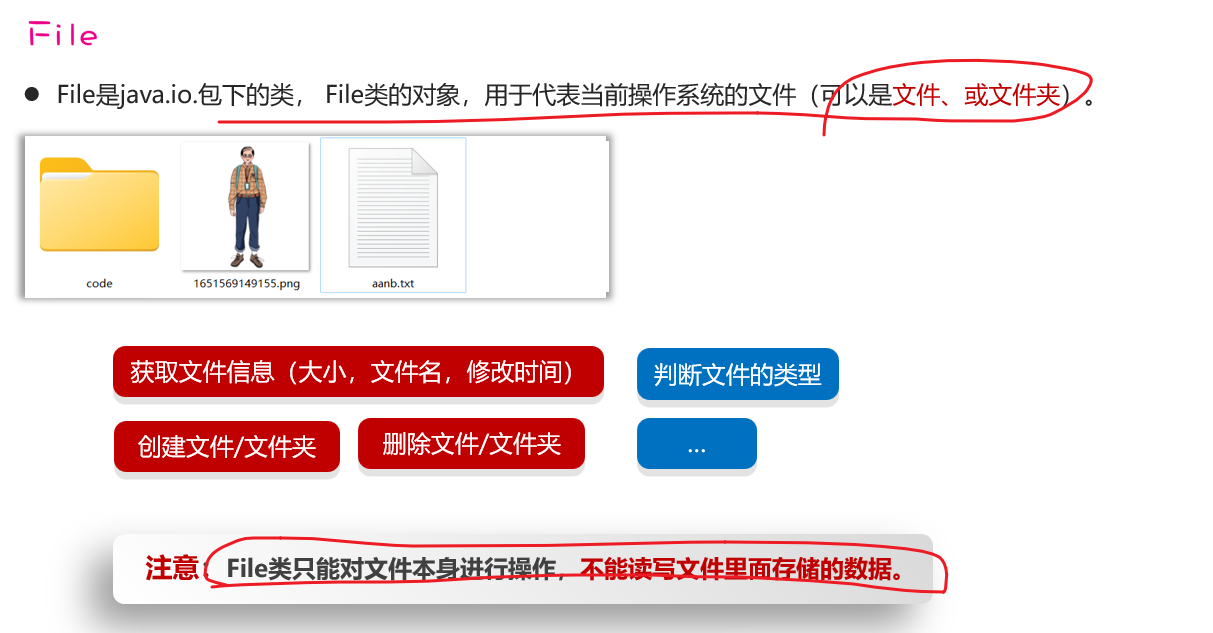
File代表文件本身(File只能对文件本身操作,不能读写文件里存储的数据)
IO流用于读写数据


File
File封装的对象仅仅是一个路径名,这个路径可以是存在的,也允许是不存在的。

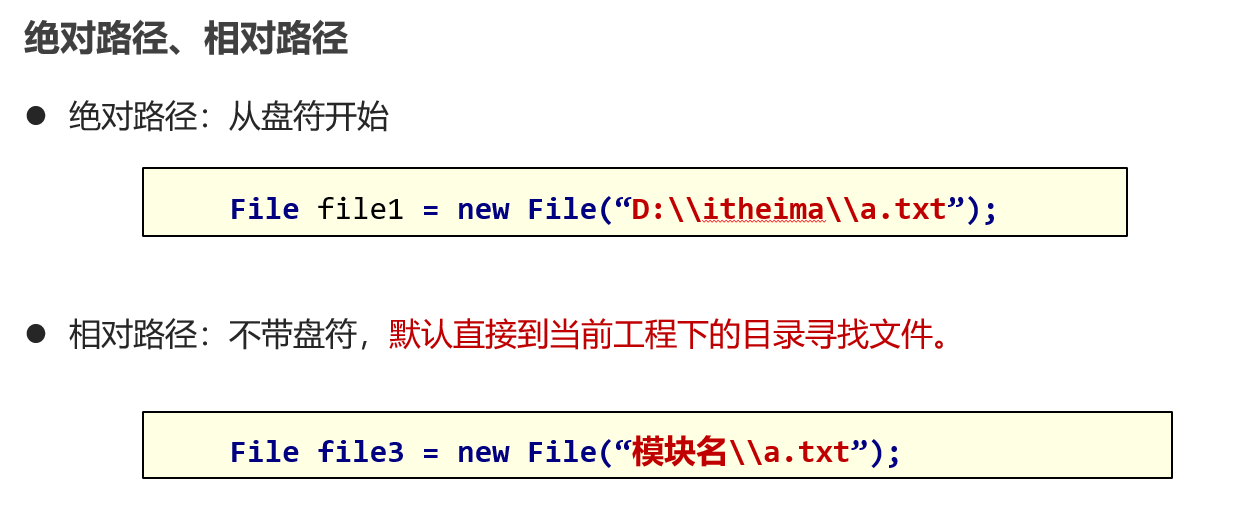
常用方法1:判断文件类型、获取文件信息
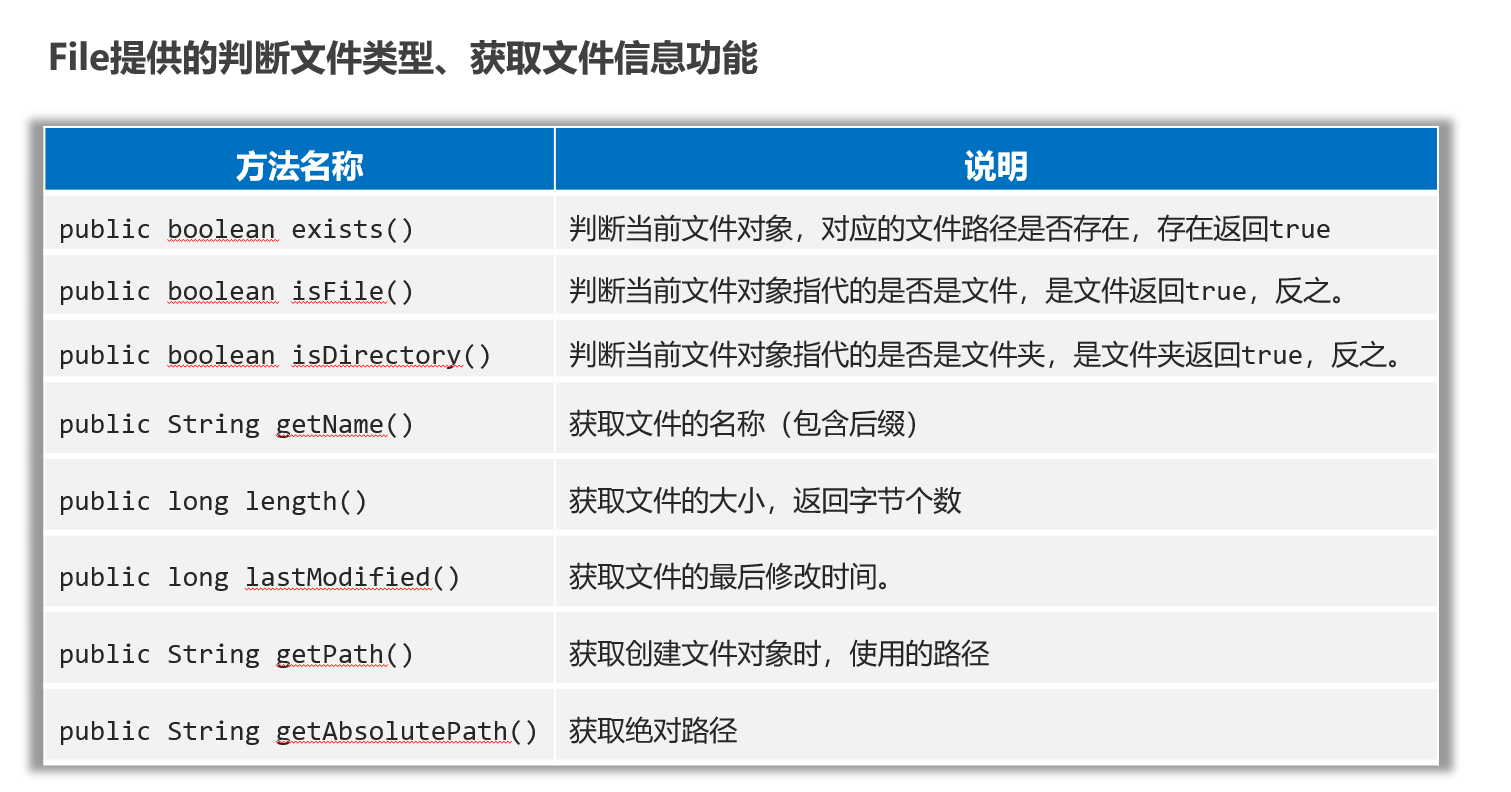
常用方法2:创建文件、删除文件

删除功能只能删除文件和空文件夹,不能删除非空文件夹
常用方法3:遍历文件夹


递归

猴子吃桃问题

文件搜索
需求:从D:盘中,搜索“QQ.exe” 这个文件,找到后直接输出其位置。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
File f = new File("D:\\");
test(f);
}
//处理文件对象
public static void test(File f){
if(f.isFile()){
if ("QQ.exe".equals(f.getName())){
System.out.println(f.getAbsolutePath());
return;
}
}
else if(f.isDirectory()){
File[] files = f.listFiles();//获取文件对象数组
if(files == null){
return;
}
for (File file : files) {//遍历文件对象数组
test(file);
}
}
}
}
字符集
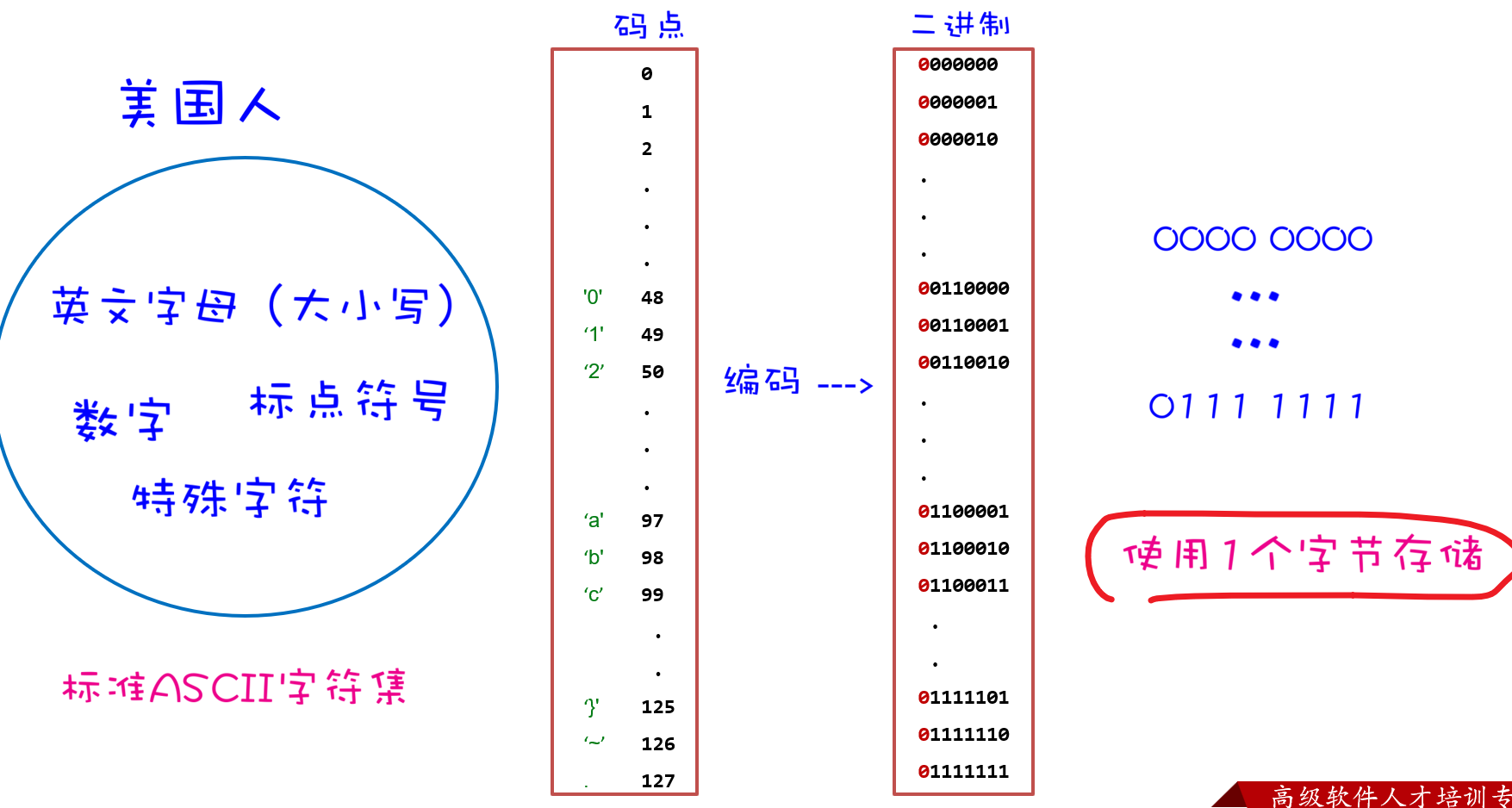
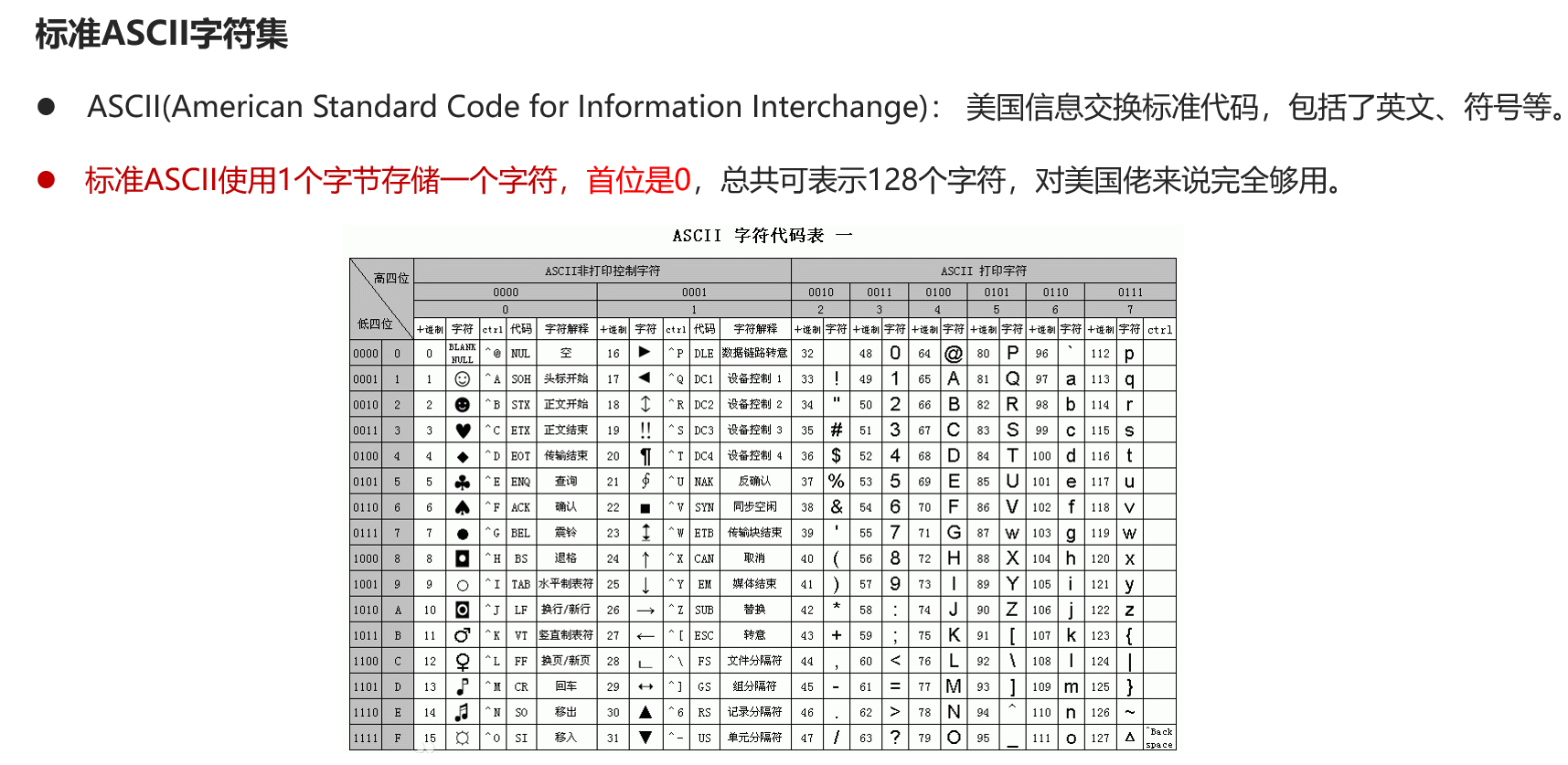
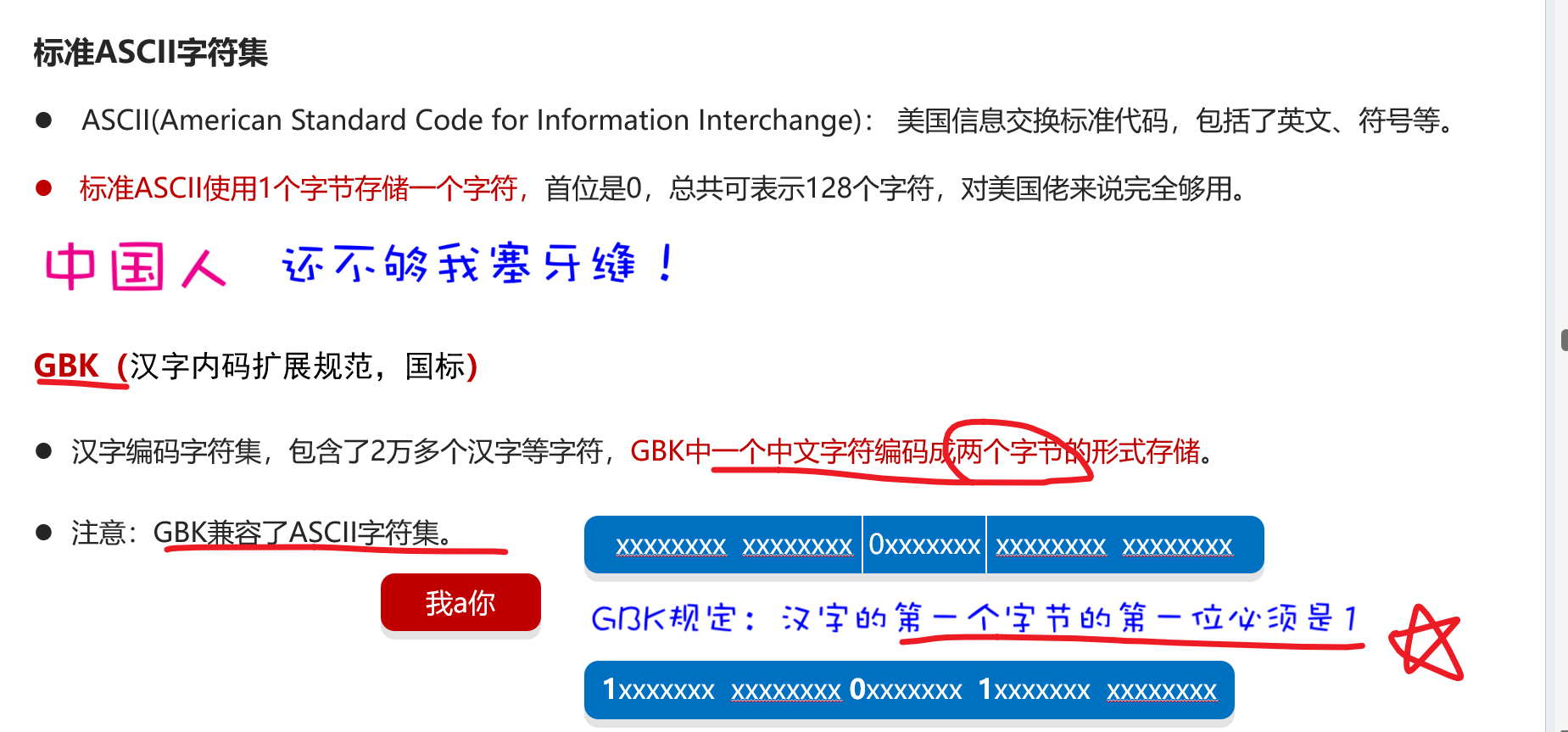


❌ 注意:Unicode只是字符集标准,需要配合编码方案,如 UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32 才能在计算机中使用。


字符集的编码、解码操作
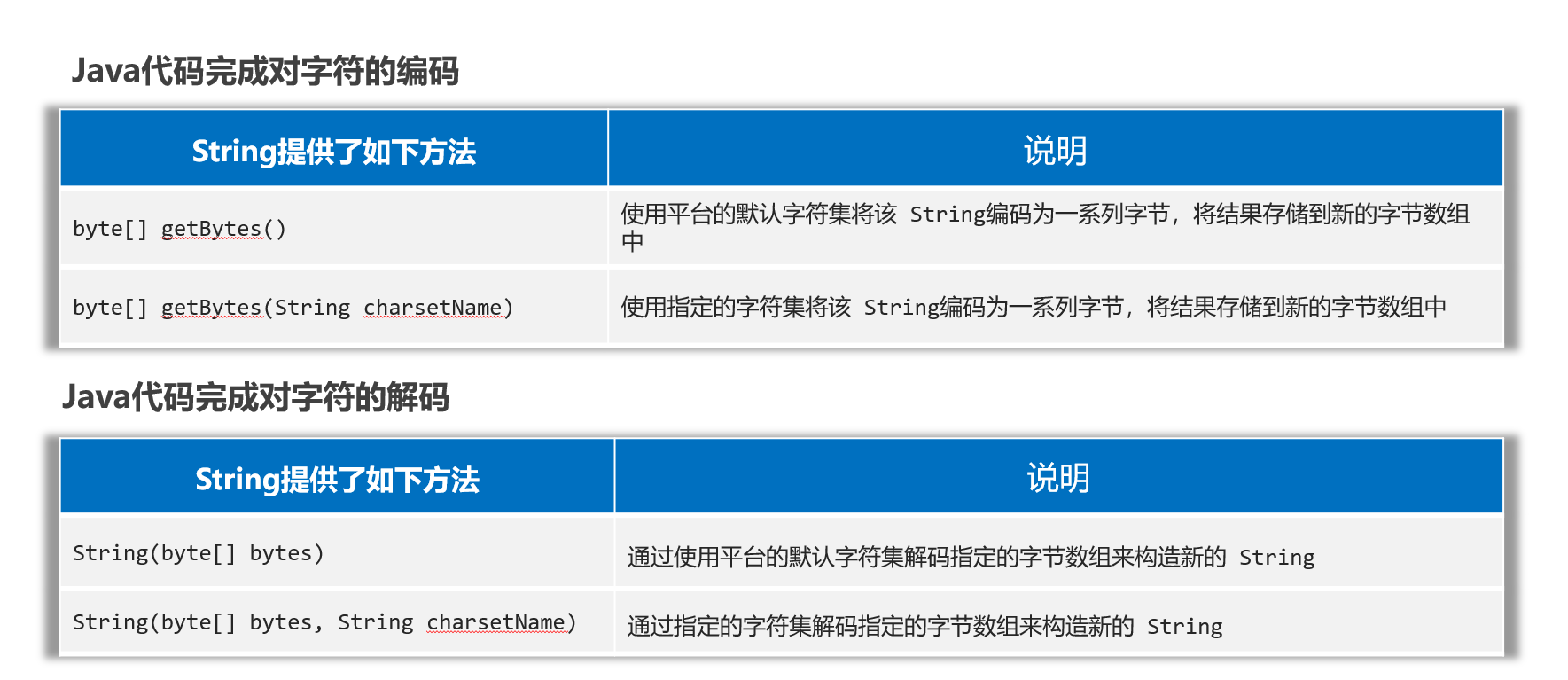
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "我a你";//默认utf-8编码
byte[] bytes = s.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));//[-26, -120, -111, 97, -28, -67, -96]
String s1 = new String(bytes);
System.out.println(s1);//我a你
String s2 = new String(bytes,0,4);//解码数组的一部分
System.out.println(s2);//我a
}
之前迷惑的地方:
Java 中的 char 本质上是一个 无符号的 16 位整数,它可以表示 Unicode 编码值(0~65535),所以它可以直接参与数值运算。
**Java 中的 char 是 UTF-16 编码表示的 Unicode 字符单元,占用 **固定2个字节(16位)。
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = new String(new char[]{'中'});//可以通过char数组创建字符串
byte[] bytes1 = s1.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));//[-28, -72, -83],每个中文占用3字节
String s2 = new String(new char[]{'a'});
byte[] bytes2 = s2.getBytes();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes2));//[97],每个英文占用1字节
}





















 819
819

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








