本文记录koa 用法,及 源码中用到的三方库。 备忘。
目录
statuses http code <--> message
koa
安装
npm i koa -sts的话再装2个 开发依赖, 方便跳转
npm i @types/node -d
npm i @types/koa -d
delegates 简化嵌套对象访问
const animal = {
dog: {
name: '旺财',
talk() {
console.log('wang!');
}
},
}animal.dog.name 可以访问嵌套对象中的属性。
能不能 animal.name 就直接访问了 animal.dog.name
能!, 用 https://github.com/tj/node-delegates
const delegate = require('delegates');
// animal 的定义, 不再重复
delegate(animal, 'dog')
.access('name')
.method('talk')
animal.talk(); // 输出 wang!
console.log(animal.name); // 输出 旺财用法
.access('name')
animal.name = 'dog2'; // 即可以set
console.log(animal.name); // 又可以get
.getter('name')
console.log(animal.name); // 可以get
animal.name = 'dog2'; // 不可以!!! 实际上会设置了 animal 的name属性 而不是 dog.name
.setter('name')
console.log(animal.name); // 不可以!!!
animal.name = 'dog2'; // 相当于设置 dog.dog.name
.fluent('name')
animal.name('name') // 设置 animal.dog.name
console.log(animal.name()) // 获取 animal.dog.name
koa 的 context 就是借助了 delegate 来方便访问 嵌套的 request 和 response 对象
depd 漂亮的deprecate信息
输出 deprecate 信息, 五颜六色的,蛮漂亮的
const deprecate = require('depd')('wjs');
deprecate('i am a deprecate info');
输出结果
![]()
cookies
cookie 是 服务器返回给客户端的一些 key-value 对
比如下面这个例子。 服务器返回 了 4个 key-value 对。 分别是
LastVisit 当前时间
k1 v1
k2 v2
k3 v3
客户端下次访问会携带上这些 key-value. 服务器存啥,客户端返回啥。
还可以指定这些key 的过期时间, 是否验证, 详细见下面的例子
const http = require('http');
const Cookies = require('cookies');
const moment = require('moment');
//cookies进行签名(加密)
var keys = ['keyboard cat'];
var server = http.createServer(function (req, res) {
if (req.url == '/favicon.ico')
return
//创建cookie对象
var cookies = new Cookies(req, res, { keys: keys })
// 获取cookie,new Cookies时设置了签名,获取时也要进行签名认证
var lastVisit = cookies.get('LastVisit', { signed: true });
// 设置cookie('键名','值','有效期')
const now = new Date().getTime();
cookies.set('LastVisit', now,{ signed: true });
cookies.set('k1', 'v1', { signed: true,maxAge:0 }); //永久有效
cookies.set('k3', 'v3', { signed: true,maxAge:-1 }); //删除cookie
cookies.set('k2', 'v2',{ signed: true,maxAge:60000*60*24*7 }); //单位毫秒,有效期为7天
if (!lastVisit) {
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain;charset=utf8')
res.end('你好,你这是首次访问!')
} else {
console.log(cookies.get('k1', { signed: true })); // v1
console.log(cookies.get('k2', { signed: true })); // v2
console.log(cookies.get('k3', { signed: true })); // undefined 马上就被删了 所以没有传回来
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain;charset=utf8')
res.write('当前时间 ' + moment(now).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS"));
res.end('\n上次时间 ' + moment(parseInt(lastVisit)).format("YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss.SSS") + '.')
}
})
server.listen(3000, function () {
console.log('Visit us at http://127.0.0.1:3000/ !')
})
statuses http code <--> message
http code <--> message 相互转换
npm 周下载 1700多w, https://github.com/jshttp/statuses 204赞
很多人用, 却不给人家点个赞。
koa 用的是 "statuses": "^1.5.0" ,已经和最新的版本不兼容了
const status = require('statuses');
console.log(status[500]); // Internal Server Error
console.log(status["forbidden"]); // 403最新版本 "statuses": "^2.0.0" 要这样
const status = require('statuses');
console.log(status.message[500]); // Internal Server Error
console.log(status.code["forbidden"]); // 403
// 调用 函数 返回 string 对应的 code
status('forbidden') // => 403
// 如果是 retry 的 code 返回 true, 否则返回 undefined
status.retry[501] // => undefined
status.retry[503] // => true
// 如果 code 期望 body 是 empty的 返回 true
status.empty[200] // => undefined
status.empty[204] // => true
status.empty[304] // => true
// 如果是重定向的code, 返回 true
status.redirect[200] // => undefined
status.redirect[301] // => truestatus.message code --> messgae string
status.code messgae string --> code
确实要更直观些~~~~
accepts http headers解析
负责处理http 捎带的 headers 信息
即 req.headers 中的信息
var accepts = require('accepts')
var http = require('http')
function app (req, res) {
var accept = accepts(req)
// 数组里的顺序是有意义的,出现在前面的将被优先选择
switch (accept.type(['json', 'html'])) {
case 'json':
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'application/json')
res.write('{"hello":"world!"}')
break
case 'html':
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/html')
res.write('<b>hello, world!</b>')
break
default:
// 指定了head 又不是json和html 的 就到这里
res.setHeader('Content-Type', 'text/plain')
res.write('hello, world!')
break
}
res.end()
}
http.createServer(app).listen(3000)
// 没指定 就采用 type() 数组第一个 即 json
curl http://localhost:3000
// json
curl -H'Accept: application/json' http://localhost:3000
// html
curl -H'Accept: text/html' http://localhost:3000
// 下面两个 accept.type(['json', 'html']) 找不到合适的,返回false
// 采用 default 分支
curl -H'Accept: text/plain' http://localhost:3000
curl -H'Accept: application/mathml+xml' http://localhost:3000
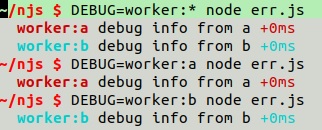
debug 控制调试日志
// err.js
const Debugger = require('debug');
const a = Debugger('worker:a');
const b = Debugger('worker:b');
a('debug info from a')
b('debug info from b')DEBUG=worker:* node err.js 显示 worker下所有的日志
DEBUG=worker:a node err.js 只显示 woker:a 的日志
docker 下开启 -e DEBUG=koa:*
docker run -e DEBUG=koa:* -p 8000:8000 -d 镜像名字
http-assert
assert(name === 'wjs', 401, 'authentication failed')如果name 不是 wjs, throw http-errors 异常,
err.status = 401
err.message = 'authentication failed'
err.expose = true
源码
var createError = require('http-errors')
function assert (value, status, msg, opts) {
if (value) return
throw createError(status, msg, opts)
}
http-errors
var createError = require('http-errors')
createError(401, 'Please login to view this page.') // 状态码 错误消息
methods
返回http的所有方法,返回的均为小写,字符串数组
比如我当前返回的是
const methods = require('methods')
console.log(methods);
[
'acl', 'bind', 'checkout',
'connect', 'copy', 'delete',
'get', 'head', 'link',
'lock', 'm-search', 'merge',
'mkactivity', 'mkcalendar', 'mkcol',
'move', 'notify', 'options',
'patch', 'post', 'propfind',
'proppatch', 'purge', 'put',
'rebind', 'report', 'search',
'source', 'subscribe', 'trace',
'unbind', 'unlink', 'unlock',
'unsubscribe'
]
koa-router
koa 路由器中间件, 解析
下面是增、删、改、查的 示例
"use strict";
const Koa = require("koa");
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const Router = require('koa-router');
const only = require("only");
// koa-router 可以把参数解析到 ctx.params 中
// path '/user/:id' 中存在 :id 时, /user/223oo 的 223oo就被存放到 ctx.params.id 中
// path '/user/:id/:name' /user/223oo/wjs 的 ctx.params 会有 {id:'223oo', name:'wjs'}
const app = new Koa();
let router = new Router();
let users = new Map([
['1', {id:'1', name:'wjs', age:22}],
['2', {id:'2', name:'wjs2', age:22}],
['3', {id:'3', name:'wjs3', age:22}],
]);
// curl localhost:3000/user/3
async function getUser(ctx, next) {
let u = users.get(ctx.params.id) || {};
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(u);
await next();
}
// curl -X DELETE localhost:3000/user/2
async function delUser(ctx, next) {
let result = users.delete(ctx.params.id);
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
// curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type:application/json" localhost:3000/user/2 -d '{"id":"2", "name":"222", "age":33}'
async function updateUser(ctx, next) {
const id = ctx.params.id;
const u = ctx.request.body;
console.log(u);
let result = false;
if (typeof id === "string" && users.has(id)) {
users.set(id, only(u, ['id', 'name', 'age']))
result = true;
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
// curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"id":"4","name":"wjs4","age":22, "gender":"male"}' http://localhost:3000/user
async function addUser(ctx, next) {
const u = ctx.request.body;
let result = false;
if (u && typeof u.id === "string") {
let oldSize = users.size;
// 只选取了 id ,name ,age 3个属性,其它属性忽略,比如上面例子中的 "gender":"male"
users.set(u.id, only(u, ['id', 'name', 'age']));
if (oldSize+1 === users.size)
result = true
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
router
.post('/user', addUser)
.del('/user/:id', delUser)
.put('/user/:id', updateUser)
.get('/user/:id', getUser)
app
.use(koaBody()) // 把数据填充到 ctx.request.body 中
.use(router.routes())
.use(router.allowedMethods());
app.listen(3000);
koa-rapid-router
koa-router好是好,就是路由效率很低,所有的middleware callback 都存在一个数组里,path来了得全数组匹配,且是 正则匹配。匹配过的也没有做缓存优化。如果想要效率高些的,也许可以试试 koa-rapid-router
| command | architecture | Latency | Req/Sec | Bytes/Sec |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| test:koa | koa + koa-router | 220.29 ms | 441.75 | 62.7 kB |
| test:fast | fastify | 1.9 ms | 50988.65 | 7.24 MB |
| test:rapid | koa + koa-rapid-router | 2.32 ms | 41961.6 | 5.96 MB |
| test:http | http + koa-rapid-router | 1.82 ms | 53160.8 | 5.37 MB |
开启匹配缓存(默认没开启)
// 开启并设置缓存尺寸 为10
const routerContainer = require('koa-rapid-router');
let rc = new routerContainer({cache:10});缓存只对 动态路径起作用,静态路径没有缓存。
用法
"use strict";
const Koa = require('koa');
const koaBody = require('koa-body');
const only = require("only");
const routerContainer = require('koa-rapid-router');
let rc = new routerContainer({cache:10}); // 缓存尺寸设置为10,默认没开启
let router = rc.create();
// koa-rapid-router 可以把参数解析到 ctx.params 中
// path '/user/{id:number}' 中存在 :id 时, /user/223oo 的 223oo就被存放到 ctx.params.id 中
let users = new Map([
['1', {id:'1', name:'wjs', age:22}],
['2', {id:'2', name:'wjs2', age:22}],
['3', {id:'3', name:'wjs3', age:22}],
]);
// curl localhost:3000/user/3
async function getUser(ctx, next) {
let u = users.get(ctx.params.id) || {};
ctx.body = JSON.stringify(u);
await next();
}
// curl -X DELETE localhost:3000/user/2
async function delUser(ctx, next) {
let result = users.delete(ctx.params.id);
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
// curl -X PUT -H "Content-Type:application/json" localhost:3000/user/2 -d '{"id":"2", "name":"222", "age":33}'
async function updateUser(ctx, next) {
const id = ctx.params.id;
const u = ctx.request.body;
console.log(u);
let result = false;
if (typeof id === "string" && users.has(id)) {
users.set(id, only(u, ['id', 'name', 'age']))
result = true;
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
// curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -d '{"id":"4","name":"wjs4","age":22, "gender":"male"}' http://localhost:3000/user
async function addUser(ctx, next) {
const u = ctx.request.body;
let result = false;
if (u && typeof u.id === "string") {
let oldSize = users.size;
// 只选取了 id ,name ,age 3个属性,其它属性忽略,比如上面例子中的 "gender":"male"
users.set(u.id, only(u, ['id', 'name', 'age']));
if (oldSize+1 === users.size)
result = true
}
ctx.body = JSON.stringify({result});
await next();
}
router
.post('/user', addUser)
.delete('/user/{id:number}', delUser)
.put('/user/{id:number}', updateUser)
.get('/user/{id:number}', getUser)
const app = new Koa();
app
.use(koaBody()) // 把数据填充到 ctx.request.body 中
.use(rc.Koa())
.listen(3000);
原理
rapid 把路径分为静态的和动态的。含有正则的路径为动态路径,否则为静态。
/zzz/{a:number} 是动态路径,它可以匹配 /zzz/123 /zzz12 /zzz/1
/zzz 为静态路径, 它只可以匹配 /zzz
静态路径全部放在 一棵树里。路径匹配时,优先匹配。
每个http方法(get put delete post)都是树里的分支,
比如注册了下面3个 中间件
r.get('zzz', callback1);
r.post('zzz', callback2);
r.post('yyy', callback3);
那么静态树的 post 分支 下包含 {‘zzz’:callback2, 'yyy':callback3} 子节点
get 分支下 包含 {‘zzz’:callback1} 子节点
这样 curl localhost:3000/zzz 时, 只要先找到静态路径树的get分支。然后看看有没有 zzz 就可以匹配完毕
curl -X POST -d’一些数据‘ localhost:3000/zzz/other 时, 就会先找 静态路径树的post 分支,然后看看有没 zzz/other 子节点\
动态路径树 也是根据 http方法 建立第一层分支的。
每一个http方法,对应一颗子树。
每颗子树都是路径多叉树。
r.get('/zzz/{a:number}' , cb1) //动态路径树 get 分支 有 zzz 子树, zzz子树下含 {a:number}叶子节点
r.get('/zzz' , cb2) // 静态路径树 get分支 有 zzz 子节点
curl localhost:3000/zzz/123 时 先匹配 静态树的 get 分支, 找找看 有没 zzz/123 子节点, 显然找不到, 因为只有 zzz子节点
于是去动态树找, 先找到 get 分支, 然后找到 zzz 子树, 再往下找 123, 123 可由 {a:number} 匹配到





















 1701
1701

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








