You are given an array points representing integer coordinates of some points on a 2D-plane, where points[i] = [xi, yi].
The cost of connecting two points [xi, yi] and [xj, yj] is the manhattan distance between them: |xi - xj| + |yi - yj|, where |val| denotes the absolute value of val.
Return the minimum cost to make all points connected. All points are connected if there is exactly one simple path between any two points.
Example 1:
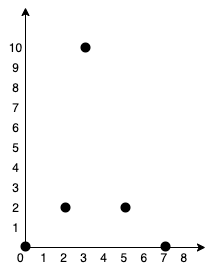
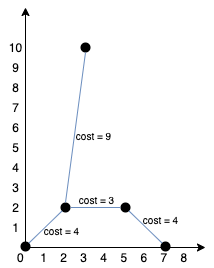
Input: points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]]
Output: 20
Explanation:
We can connect the points as shown above to get the minimum cost of 20.
Notice that there is a unique path between every pair of points.
Example 2:
Input: points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]]
Output: 18
Constraints:
- 1 <= points.length <= 1000
- -106 <= xi, yi <= 106
- All pairs (xi, yi) are distinct.
这题涉及到一个 MST(Minimum Spanning Tree)的概念
A minimum spanning tree (MST) or minimum weight spanning tree is a subset of the edges of a connected, edge-weighted undirected graph that connects all the vertices together, without any cycles and with the minimum possible total edge weight.
以上是 MST 的定义, 理解起来不难, 创建 MST 的方式有很多种, 教程里面描述了两种, 一种叫 Kruskal’s Algorithm, 另一种叫 Prim’s algorithm, 我都看了一下, 发觉对我来说 Prim’s algorithm 更简单一些, 于是就选择用这种方式来解, 主要步骤如下:
- 先根据
points来创建每一个点到其他任意一点的变并计算出距离 - 任意取出一点作为树的根节点, 从这一点开始每次找到离该点最近的点加入到树中, 并且将所加入的点的关联的边都加入到待检查的边当中。如果所要加入的点已经存在于树中了, 则略过去寻找下一个最近的点
- 当树有了 n-1 个边的时候(n 为
points的数量), 退出循环
use std::cmp::Reverse;
use std::collections::BinaryHeap;
impl Solution {
pub fn min_cost_connect_points(points: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> i32 {
let mut edges = vec![BinaryHeap::new(); points.len()];
for i in 0..points.len() {
for j in i + 1..points.len() {
let pi = points[i].clone();
let pj = points[j].clone();
let dist = (pi[0] - pj[0]).abs() + (pi[1] - pj[1]).abs();
edges[i].push(Reverse((dist, j)));
edges[j].push(Reverse((dist, i)));
}
}
let mut visited = vec![false; points.len()];
let mut count = 0;
let mut ans = 0;
let mut stack = edges[0].clone();
visited[0] = true;
'outer: while count < points.len() - 1 {
while let Some(Reverse((dist, i))) = stack.pop() {
if visited[i] {
continue 'outer;
}
visited[i] = true;
count += 1;
ans += dist;
stack.append(&mut edges[i].clone());
continue 'outer;
}
}
ans
}
}







 本文介绍如何使用Prim算法解决给定二维坐标点集的最小连接问题,通过曼哈顿距离计算连接成本,实现所有点间的唯一路径连接。涉及MST概念及Prim算法的应用实例。
本文介绍如何使用Prim算法解决给定二维坐标点集的最小连接问题,通过曼哈顿距离计算连接成本,实现所有点间的唯一路径连接。涉及MST概念及Prim算法的应用实例。
















 7万+
7万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








