TextView绘制流程
TextView是android提供的一个文本展示ui控件,同时也是android开发者最先熟悉的Weight组件,可以配合Html和Spannable进行展示文字、展示html、进行高亮处理,还能通过autolink进行email、tel等功能的识别跳转,本篇文章将带你从系统源码的角度彻底搞定TextView的绘制流程。
在上一篇TextView绘制流程中
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/wanggang514260663/article/details/113996117
简要分析了TextView的onMeasure、onLayout、onDraw。在TextView中,有一个贯穿了整个流程的类-Layout,本节主要对Layout进行分析。
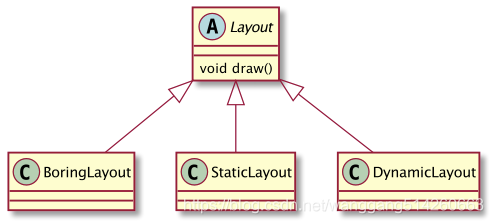
Layout主要有三个实现类
- StaticLayout
StaticLayout在文字被排列布局之后不允许修改。
- BoringLayout
BoringLayout是Layout的最简单的实现,主要用于适配单行文字展示,并且只支持从左到右的展示方向。不建议在自己的开发过程中直接使用,如果需要使用的话,首先使用isBoring判断文字是否符合要求。
- DynamicLayout
DynamicLayout支持在排列布局之后修改文字,修改之后会更新text内容。
BoringLayout

上面是BoringLayout的类依赖图。
BoringLayout#isBoring
如果想要使用BoringLayout方法的话,首先需要调用BoringLayout.isBoring方法,判断是否支持BoringLayout。
/**
* 如果text支持BoringLayout的话,返回Metrics对象,否则返回null
*/
public static Metrics isBoring(CharSequence text, TextPaint paint) {
return isBoring(text, paint, TextDirectionHeuristics.FIRSTSTRONG_LTR, null);
}
public static Metrics isBoring(CharSequence text, TextPaint paint,
TextDirectionHeuristic textDir, Metrics metrics) {
//返回文字长度
final int textLength = text.length();
// hasAnyInterestingChars 方法用来判断文字如果是\t、\n或者是bidi unicode字符或者代理对unicode字符的话,直接返回true
if (hasAnyInterestingChars(text, textLength)) {
return null; // There are some interesting characters. Not boring.
}
//判断文字方向是否是从右向左排列
if (textDir != null && textDir.isRtl(text, 0, textLength)) {
return null; // The heuristic considers the whole text RTL. Not boring.
}
// 是否是Spanned对象
// text中进行样式操作,比如高亮、可点击等操作,都是spanned支持实现
if (text instanceof Spanned) {
Spanned sp = (Spanned) text;
Object[] styles = sp.getSpans(0, textLength, ParagraphStyle.class);
if (styles.length > 0) {
return null; // There are some ParagraphStyle spans. Not boring.
}
}
Metrics fm = metrics;
if (fm == null) {
fm = new Metrics();
} else {
fm.reset();
}
//下面会专门介绍TextLine
TextLine line = TextLine.obtain();
line.set(paint, text, 0, textLength, Layout.DIR_LEFT_TO_RIGHT,
Layout.DIRS_ALL_LEFT_TO_RIGHT, false, null,
0 /* ellipsisStart, 0 since text has not been ellipsized at this point */,
0 /* ellipsisEnd, 0 since text has not been ellipsized at this point */);
fm.width = (int) Math.ceil(line.metrics(fm));
TextLine.recycle(line);
return fm;
}
- BoringLayout#hasAnyInterestingChars
private static boolean hasAnyInterestingChars(CharSequence text, int textLength) {
final int MAX_BUF_LEN = 500;
final char[] buffer = TextUtils.obtain(MAX_BUF_LEN);
try {
for (int start = 0; start < textLength; start += MAX_BUF_LEN) {
final int end = Math.min(start + MAX_BUF_LEN, textLength);
// No need to worry about getting half codepoints, since we consider surrogate code
// units "interesting" as soon we see one.
//根据text的类型判断使用对应的类调用getChars实现将字符串复制到目标数组buffer中
TextUtils.getChars(text, start, end, buffer, 0);
final int len = end - start;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
final char c = buffer[i];
//TextUtils.couldAffectRtl(c) 判断如果是bidi算法unicode、代理对unicode字符的话,直接返回true
if (c == '\n' || c == '\t' || TextUtils.couldAffectRtl(c)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
} finally {
TextUtils.recycle(buffer);
}
}
BoringLayout#make
public static BoringLayout make(CharSequence source, TextPaint paint, int outerWidth,
Alignment align, float spacingmult, float spacingadd, BoringLayout.Metrics metrics,
boolean includePad, TextUtils.TruncateAt ellipsize, int ellipsizedWidth) {
return new BoringLayout(source, paint, outerWidth, align, spacingmult, spacingadd, metrics,
includePad, ellipsize, ellipsizedWidth);
}
- BoringLayout#BoringLayout
public BoringLayout(CharSequence source, TextPaint paint, int outerWidth, Alignment align,
float spacingMult, float spacingAdd, BoringLayout.Metrics metrics, boolean includePad,
TextUtils.TruncateAt ellipsize, int ellipsizedWidth) {
/*
* It is silly to have to call super() and then replaceWith(),
* but we can't use "this" for the callback until the call to
* super() finishes.
*/
// 注意outerWidth不能<0,在Layout中有判断,<0抛出IllegalArgumentException
super(source, paint, outerWidth, align, spacingMult, spacingAdd);
boolean trust;
//如果ellipsize == null 或者 ellipsize类型是MARQUEE,则返回文字包括的宽度
if (ellipsize == null || ellipsize == TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE) {
mEllipsizedWidth = outerWidth;
mEllipsizedStart = 0;
mEllipsizedCount = 0;
trust = true;
} else {
// replaceWith方法在Layout类中,只是对构造方法中的参数进行了重新赋值
// TextUtils.ellipsize 用于计算并裁剪,如果文字在限定的宽度内,则直接返回原始文本,如果文本内容超过限制,则根据文字方向和TruncateAt类型判断是否展示省略号。
replaceWith(TextUtils.ellipsize(source, paint, ellipsizedWidth, ellipsize, true, this),
paint, outerWidth, align, spacingMult, spacingAdd);
mEllipsizedWidth = ellipsizedWidth;
trust = false;
}
init(getText(), paint, align, metrics, includePad, trust);
}
void init(CharSequence source, TextPaint paint, Alignment align,
BoringLayout.Metrics metrics, boolean includePad, boolean trustWidth) {
int spacing;
//如果mDirect == null,则使用Layout#draw进行绘制,否则使用canvas.drawText绘制
if (source instanceof String && align == Layout.Alignment.ALIGN_NORMAL) {
mDirect = source.toString();
} else {
mDirect = null;
}
mPaint = paint;
//includePad对应于TextView_includeFontPadding属性
//当设置为false的时候,告诉计算会去除top和ascent之间的间距,以及bottom和descent之间的间距,所以字体的整体占用空间会比设置为true的时候较小
//TextView_includeFontPadding属性默认值为true
if (includePad) {
//需要注意的话baseline上方的值为负数,baseline下方的值为正数,所以mertics.bottom - mertics.top实际上就是bottom和top之间的距离,下面的descent和ascent是一样的道理
spacing = metrics.bottom - metrics.top;
mDesc = metrics.bottom;
} else {
spacing = metrics.descent - metrics.ascent;
mDesc = metrics.descent;
}
mBottom = spacing;
//baseline = mBottom - mDesc,mBottom计算出来的值实际上就是文字的高度,减去mdesc的高度,刚好就是baseline高度
//这里计算并返回一个最大的行宽度
if (trustWidth) {
mMax = metrics.width;
} else {
/*
* If we have ellipsized, we have to actually calculate the
* width because the width that was passed in was for the
* full text, not the ellipsized form.
*/
//TextLine比较复杂,后续专门介绍
TextLine line = TextLine.obtain();
line.set(paint, source, 0, source.length(), Layout.DIR_LEFT_TO_RIGHT,
Layout.DIRS_ALL_LEFT_TO_RIGHT, false, null,
mEllipsizedStart, mEllipsizedStart + mEllipsizedCount);
mMax = (int) Math.ceil(line.metrics(null));
TextLine.recycle(line);
}
if (includePad) {
mTopPadding = metrics.top - metrics.ascent;
mBottomPadding = metrics.bottom - metrics.descent;
}
}
BoringLayout#replaceOrMake
BoringLayout#replaceOrMake方法和make方法在大体实现上差不多,区别就是make是构建出来一个新的BoringLayout,而replaceOrMake是进行复用
public BoringLayout replaceOrMake(CharSequence source, TextPaint paint, int outerWidth,
Alignment align, float spacingMult, float spacingAdd, BoringLayout.Metrics metrics,
boolean includePad, TextUtils.TruncateAt ellipsize, int ellipsizedWidth) {
boolean trust;
if (ellipsize == null || ellipsize == TextUtils.TruncateAt.MARQUEE) {
replaceWith(source, paint, outerWidth, align, spacingMult, spacingAdd);
mEllipsizedWidth = outerWidth;
mEllipsizedStart = 0;
mEllipsizedCount = 0;
trust = true;
} else {
//该方法是在Layout中实现,主要是对使用的变量进行一个重新赋值。
//TextUtils.ellipsize 用于计算并裁剪,如果文字在限定的宽度内,则直接返回原始文本,如果文本内容超过限制,则根据文字方向和TruncateAt类型判断是否展示省略号。
replaceWith(TextUtils.ellipsize(source, paint, ellipsizedWidth, ellipsize, true, this),
paint, outerWidth, align, spacingMult, spacingAdd);
mEllipsizedWidth = ellipsizedWidth;
trust = false;
}
init(getText(), paint, align, metrics, includePad, trust);
return this;
}
- layout#replaceWith
void replaceWith(CharSequence text, TextPaint paint,
int width, Alignment align,
float spacingmult, float spacingadd) {
if (width< 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Layout: " + width + " < 0");
}
mText = text;
mPaint = paint;
mWidth = width;
mAlignment = align;
mSpacingMult = spacingmult;
mSpacingAdd = spacingadd;
mSpannedText = text instanceof Spanned;
}
BoringLayout#draw
在上一篇文章-TextView绘制流程中有说过,TextView的onDraw中如果是非可编辑文字的话,使用layout#draw方法。那么看一下BoringLayout的draw方法实现。
public void draw(Canvas c, Path highlight, Paint highlightpaint,
int cursorOffset) {
//在init中,有一个判断用来控制mDirect的值
//source instanceof String && align == Layout.Alignment.ALIGN_NORMAL
if (mDirect != null && highlight == null) {
//mbottom-mdesc用来计算绘制线的baselineY位置
c.drawText(mDirect, 0, mBottom - mDesc, mPaint);
} else {
//调用Layout#draw方法绘制
super.draw(c, highlight, highlightpaint, cursorOffset);
}
}
mBottom - mDesc计算baselineY,这块牵扯到Metrics相关的知识,对于Metrics的相关知识,可以参考canvas.drawText理解和FontMetrics文字测量。
TextLine
之前在介绍BoringLayout的时候有提到TextLine这个类,接下来将介绍它。
/**
* Represents a line of styled text, for measuring in visual order and
* for rendering.
*
* <p>Get a new instance using obtain(), and when finished with it, return it
* to the pool using recycle().
*
* <p>Call set to prepare the instance for use, then either draw, measure,
* metrics, or caretToLeftRightOf.
*
* @hide
*/
public class TextLine{
...
}
简单回顾下,BoringLayout中使用的地方。
...
TextLine line = TextLine.obtain();
line.set(paint, text, 0, textLength, Layout.DIR_LEFT_TO_RIGHT,
Layout.DIRS_ALL_LEFT_TO_RIGHT, false, null,
0 /* ellipsisStart, 0 since text has not been ellipsized at this point */,
0 /* ellipsisEnd, 0 since text has not been ellipsized at this point */);
fm.width = (int) Math.ceil(line.metrics(fm));
TextLine.recycle(line);
...
其实TextLine本身使用到的方法也就这几个,下面挨个做个介绍。
TextLine#obtain
从TextLine的介绍中可以知道,这个方法是用来获取一个TextLine对象。
//创建一个大小为3个TextLine共享数据集合
private static final TextLine[] sCached = new TextLine[3];
...略若干代码
public static TextLine obtain() {
TextLine tl;
synchronized (sCached) {
for (int i = sCached.length; --i >= 0;) {
//如果集合中有可用的TextLine,则取出使用,使用后并从集合中移除。
if (sCached[i] != null) {
tl = sCached[i];
//相当于从集合中移除
sCached[i] = null;
return tl;
}
}
}
//如果sCached中没有可用的TextLine,则创建一个新的。
tl = new TextLine();
return tl;
}
TextLine#recycle
recycle是与TextLine#obtain方法结对出现的方法
/**
* Puts a TextLine back into the shared pool. Do not use this TextLine once
* it has been returned.
* @param tl the textLine
* @return null, as a convenience from clearing references to the provided
* TextLine
* 将TextLine对象设置回sCached共享池中
*/
public static TextLine recycle(TextLine tl) {
tl.mText = null;
tl.mPaint = null;
tl.mDirections = null;
tl.mSpanned = null;
tl.mTabs = null;
tl.mChars = null;
tl.mComputed = null;
//这三个都是SpanSet的实现,而SpanSet的作用是将指定范型类型的span对象从Spanned类型数据中拆分出来保存在数组中。可通过getNextTransition方法进行访问。
//private final SpanSet<MetricAffectingSpan> mMetricAffectingSpanSpanSet =
// new SpanSet<MetricAffectingSpan>(MetricAffectingSpan.class);
//MetricAffectingSpan是牵扯到文字的宽、高变化的
tl.mMetricAffectingSpanSpanSet.recycle();
//private final SpanSet<CharacterStyle> mCharacterStyleSpanSet =
// new SpanSet<CharacterStyle>(CharacterStyle.class);
//CharacterStyle从名称就可以看出来是和样式相关的
tl.mCharacterStyleSpanSet.recycle();
//private final SpanSet<ReplacementSpan> mReplacementSpanSpanSet =
// new SpanSet<ReplacementSpan>(ReplacementSpan.class);
//ReplacementSpan从名称可以看出来是支持内容替换的
tl.mReplacementSpanSpanSet.recycle();
synchronized(sCached) {
for (int i = 0; i < sCached.length; ++i) {
//因为之前obtain中,使用的时候会做移除,所以这边,没有共享池还有空位,则丢到共享池中。
if (sCached[i] == null) {
sCached[i] = tl;
break;
}
}
}
return null;
}
TextLine#set
/**
* Initializes a TextLine and prepares it for use.
* 主要是用来TextLine的初始化操作
*
* @param paint the base paint for the line
* @param text the text, can be Styled
* @param start the start of the line relative to the text
* @param limit the limit of the line relative to the text
* @param dir the paragraph direction of this line
* @param directions the directions information of this line
* @param hasTabs true if the line might contain tabs
* @param tabStops the tabStops. Can be null
* @param ellipsisStart the start of the ellipsis relative to the line
* @param ellipsisEnd the end of the ellipsis relative to the line. When there
* is no ellipsis, this should be equal to ellipsisStart.
*/
@VisibleForTesting(visibility = VisibleForTesting.Visibility.PACKAGE)
public void set(TextPaint paint, CharSequence text, int start, int limit, int dir,Directions directions, boolean hasTabs, TabStops tabStops,
int ellipsisStart, int ellipsisEnd) {
mPaint = paint;
mText = text;
mStart = start;
mLen = limit - start;
mDir = dir;
mDirections = directions;
if (mDirections == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Directions cannot be null");
}
mHasTabs = hasTabs;
mSpanned = null;
boolean hasReplacement = false;
//判断类型是否支持Spanned
if (text instanceof Spanned) {
//强转为Spanned
mSpanned = (Spanned) text;
//replementSpan是一般使用的span的类型,前面有介绍过spanset是将spanned数据中的所有
//支持的类型的span对象拆出来,将拆出来的span对象、span开始位置、span结束位
//置、spanFlags分别保存在数组中。spanset提供了getNextTransition方法用于访问
//spanset中保存的数据。
mReplacementSpanSpanSet.init(mSpanned, start, limit);
//numberOfSpans方法用于获取总共拆分了多少个span对象。
hasReplacement = mReplacementSpanSpanSet.numberOfSpans > 0;
}
mComputed = null;
//PrecomputedText是在android p中提供的一个新的api,PrecomputedTextCompat能够
//使 app 可以事先甚至在后台线程中执行文本布局最耗费时间的部分工作,以缓存布局结果,
//并返回宝贵的测量数据。
//更多关于PrecomputedText可以参考文章:
//https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/ecjtuhq/article/details/104366104
if (text instanceof PrecomputedText) {
// Here, no need to check line break strategy or hyphenation frequency since there is no
// line break concept here.
mComputed = (PrecomputedText) text;
if (!mComputed.getParams().getTextPaint().equalsForTextMeasurement(paint)) {
mComputed = null;
}
}
mCharsValid = hasReplacement;
//如果text类型是Spanned && spanset的大小>0,则mCharsValid == true
if (mCharsValid) {
if (mChars == null || mChars.length < mLen) {
mChars = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedCharArray(mLen);
}
//将text文本拆分为char数据,并赋值到目标mChars中
TextUtils.getChars(text, start, limit, mChars, 0);
//理论上能进入到这里,应该为true
if (hasReplacement) {
// Handle these all at once so we don't have to do it as we go.
// Replace the first character of each replacement run with the
// object-replacement character and the remainder with zero width
// non-break space aka BOM. Cursor movement code skips these
// zero-width characters.
//用对象替换字符替换每个替换运行的第一个字符,
//并用零宽度不间断空格(又称为BOM)替换其余字符
char[] chars = mChars;
for (int i = start, inext; i < limit; i = inext) {
inext = mReplacementSpanSpanSet.getNextTransition(i, limit);
if (mReplacementSpanSpanSet.hasSpansIntersecting(i, inext)
&& (i - start >= ellipsisEnd || inext - start <= ellipsisStart)) {
// transition into a span
chars[i - start] = '\ufffc';
for (int j = i - start + 1, e = inext - start; j < e; ++j) {
chars[j] = '\ufeff'; // used as ZWNBS, marks positions to skip
}
}
}
}
}
mTabs = tabStops;
mAddedWidthForJustify = 0;
mIsJustifying = false;
//省略号开始和结束位置
mEllipsisStart = ellipsisStart != ellipsisEnd ? ellipsisStart : 0;
mEllipsisEnd = ellipsisStart != ellipsisEnd ? ellipsisEnd : 0;
}
到这里boringLayout讲完了,后续文章会陆续说明StaticLayout和DynamicLayout。







 本文详细剖析了BoringLayout在TextView绘制流程中的角色,包括如何判断是否适用、核心方法isBoring和make的实现,以及TextLine类在其中的作用。BoringLayout主要适用于单行文本,不支持修改和复杂样式。
本文详细剖析了BoringLayout在TextView绘制流程中的角色,包括如何判断是否适用、核心方法isBoring和make的实现,以及TextLine类在其中的作用。BoringLayout主要适用于单行文本,不支持修改和复杂样式。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








