一. 引言
理论上讲,limit下推到越底层,上游吐出的数据就越少,计算效率就越高。因为,带有limit的计划执行树,在Presto中的RBO优化中,都尽可能将其推到底下执行。本文主要讲几个Presto RBO优化规则中与Limit下推相关的优化。
二. PushLimitThroughOffset
-
实现效果:
PushLimitThroughOffset用于将limit下推到Offset算子的底下执行,如下图所示:

2. 实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
// child是Limit下的OffsetNode,parent是limit Node
OffsetNode child = captures.get(CHILD);
// count就limit的数量
long count;
try {
count = addExact(parent.getCount(), child.getCount());
}
catch (ArithmeticException e) {
return Result.empty();
}
// child时候offsetNode,重新构建一个LimitNode替换OffsetNode的子节点实现替换
return Result.ofPlanNode(
child.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
new LimitNode(
parent.getId(),
child.getSource(),
count,
parent.getTiesResolvingScheme(),
parent.isPartial()))));
}
三. PushLimitThroughProject
-
实现效果
PushLimitThroughProject的规则是将limit算子下推到Project算子的下边,如下图:

2.实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
ProjectNode projectNode = captures.get(CHILD);
// 如果没有带with ties条件的话,直接从Limit -> Project 转成 Project -> Limit 即可
// transpose方法就是做P->C->X to C->P->X的转换
// with ties是配合fetch方法的一个算子,比如sql:select * from num1 order by id fetch first row with ties,具体的含义可以参考
// https://www.cnblogs.com/shuangnet/archive/2013/03/22/2975462.html
if (!parent.isWithTies()) {
return Result.ofPlanNode(transpose(parent, projectNode));
}
// 地下的的操作在于将orderby的字段找出来
// for a LimitNode with ties, the tiesResolvingScheme must be rewritten in terms of symbols before projection
SymbolMapper.Builder symbolMapper = SymbolMapper.builder();
for (Symbol symbol : parent.getTiesResolvingScheme().get().getOrderBy()) {
Expression expression = projectNode.getAssignments().get(symbol);
// if a symbol results from some computation, the translation fails
if (!(expression instanceof SymbolReference)) {
return Result.empty();
}
symbolMapper.put(symbol, Symbol.from(expression));
}
// limit下推后需要做project与source的翻转
// 比如
// limit x
// |-- x = order by(y)
// limit 下推后应该是:
// order(x)
// |-- x = limit (y)
// 因此需要将project的source和outout翻转过来
LimitNode mappedLimitNode = symbolMapper.build().map(parent, projectNode.getSource());
// 将 limit 节点设置为Project节点的子节点
return Result.ofPlanNode(projectNode.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(mappedLimitNode)));
}
四. MergeLimits
-
实现效果
MergeLimits用于将多个Limit进行合并,其实现的效果分成如下3种情况:



2. 实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
LimitNode child = captures.get(CHILD);
// 对应上述情况一,没有with Ties的情况下,只保留Math.min(parent.getCount(), child.getCount())
// parent and child are without ties
if (!child.isWithTies()) {
return Result.ofPlanNode(
new LimitNode(
parent.getId(),
child.getSource(),
Math.min(parent.getCount(), child.getCount()),
parent.getTiesResolvingScheme(),
parent.isPartial()));
}
// 对应上述情况3
// parent is without ties and child is with ties
if (parent.getCount() > child.getCount()) {
return Result.ofPlanNode(
// 将parent设置为子的child,parent的child设置为原来child的child实现parent与child的翻转
child.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
parent.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
child.getSource())))));
}
// 对应上述情况2,直接删除child的limit即可
return Result.ofPlanNode(
parent.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
child.getSource())));
}
无. MergeLimitOverProjectWithSort
-
实现效果
MergeLimitOverProjectWithSort用户将Limit算子和sort算子合并成一个TOPN算子,其实现的效果如下图所示:

2. 实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
ProjectNode project = captures.get(PROJECT);
SortNode sort = captures.get(SORT);
// project地下新建一个TOPN的节点,替换原来的source节点
// parent.getCount()对应着原来的limit x,sort.getSource()对应原来的order by xxx
return Result.ofPlanNode(
project.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
new TopNNode(
parent.getId(),
sort.getSource(),
parent.getCount(),
sort.getOrderingScheme(),
parent.isPartial() ? PARTIAL : SINGLE))));
}
六. MergeLimitWithTopN
-
实现效果
MergeLimitWithTopN用于将TOPN与Limit合并,其实现的效果如下所示:

2.实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
TopNNode child = captures.get(CHILD);
if (parent.isWithTies()) {
if (parent.getCount() < child.getCount()) {
return Result.empty();
}
else {
// 上边的情况1
return Result.ofPlanNode(child);
}
}
// 上边的情况2
return Result.ofPlanNode(
new TopNNode(
parent.getId(),
child.getSource(),
Math.min(parent.getCount(), child.getCount()),
child.getOrderingScheme(),
parent.isPartial() ? TopNNode.Step.PARTIAL : TopNNode.Step.SINGLE));
}
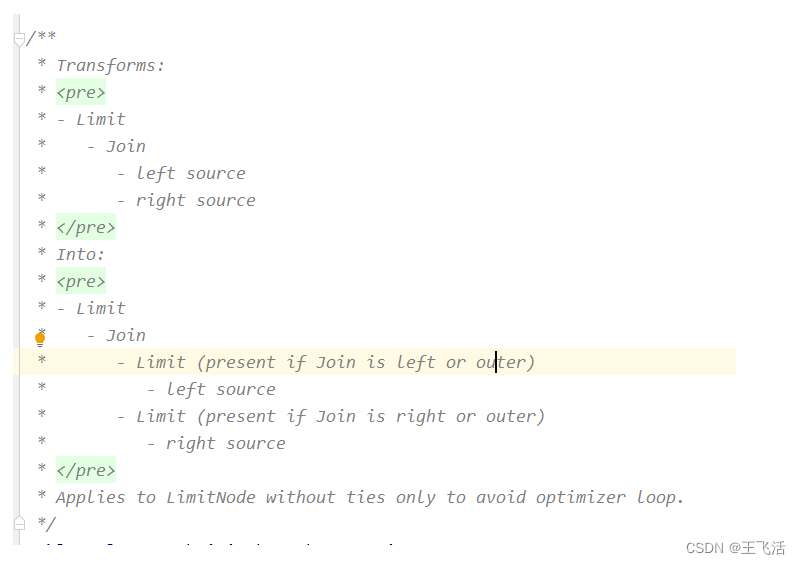
七. PushLimitThroughOuterJoin
-
实现效果
PushLimitThroughOuterJoin用于将limit算在下推到Join算子之下。如下图:
2. 实现原理
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
JoinNode joinNode = captures.get(CHILD);
PlanNode left = joinNode.getLeft();
PlanNode right = joinNode.getRight();
// isAtMost的意思是只有limit输出的范围比source的输出的范围小,才会将limit下推到join之下
if (joinNode.getType() == LEFT && !isAtMost(left, context.getLookup(), parent.getCount())) {
return Result.ofPlanNode(
// 将Join 左边的Node替换成LimitNode,LimitNode的输出为原来的leftNode,数量为limit的数量
parent.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
joinNode.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
new LimitNode(context.getIdAllocator().getNextId(), left, parent.getCount(), true),
right)))));
}
// 同left
if (joinNode.getType() == RIGHT && !isAtMost(right, context.getLookup(), parent.getCount())) {
return Result.ofPlanNode(
parent.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
joinNode.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
left,
new LimitNode(context.getIdAllocator().getNextId(), right, parent.getCount(), true))))));
}
return Result.empty();
}
八. PushLimitThroughMarkDistinct,PushLimitThroughSemiJoin
-
实现效果
这两个优化规则和PushLimitThroughProject一样,通过transpose实现将Limit算子下推。
九. PushLimitThroughUnion
-
实现效果
PushLimitThroughOuterJoin用于将limit算在下推到Union算子之下。如下图所示:

2. 实现原理:
public Result apply(LimitNode parent, Captures captures, Context context)
{
UnionNode unionNode = captures.get(CHILD);
ImmutableList.Builder<PlanNode> builder = ImmutableList.builder();
boolean shouldApply = false;
// 对于Union的每一个Source,看下limit的结果是否比与原来的结果小,如果小的话,新建一个LimitNode替换原来的sourceNode, 新建的LimitNode输入时原来的source,条数是parent的limit count
for (PlanNode source : unionNode.getSources()) {
// This check is to ensure that we don't fire the optimizer if it was previously applied.
if (isAtMost(source, context.getLookup(), parent.getCount())) {
builder.add(source);
}
else {
shouldApply = true;
builder.add(new LimitNode(context.getIdAllocator().getNextId(), source, parent.getCount(), true));
}
}
if (!shouldApply) {
return Result.empty();
}
return Result.ofPlanNode(
parent.replaceChildren(ImmutableList.of(
unionNode.replaceChildren(builder.build()))));
}





 本文详细探讨了Presto数据库的RBO优化中与limit下推相关的规则,包括PushLimitThroughOffset、PushLimitThroughProject、MergeLimits等,展示了如何提高计算效率和优化查询执行计划。
本文详细探讨了Presto数据库的RBO优化中与limit下推相关的规则,包括PushLimitThroughOffset、PushLimitThroughProject、MergeLimits等,展示了如何提高计算效率和优化查询执行计划。
















 928
928

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








