1.三角形面积
描述
求两邻边长为3.5和4.72米,两边夹角为37°的三角形的面积。pi=3.1416,结果保留四位小数。
输入
无
输出
该三角形的面积
提示
三角形面积:S=(absinx)/2; (x为a,b两边的夹角的弧度)
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
#define PI 3.1416
int main() {
double a=3.5,b=4.72;
double angle_degree=37.0;
double angle_radian=angle_degree*(PI/180.0);
double area=0.5*a*b*sin(angle_radian);
printf("%.4f\n",area);
return 0;
}
2.n的阶乘
描述
编写函数实现,计算n的阶乘
函数接口:
int fact(int num){函数体};
输入
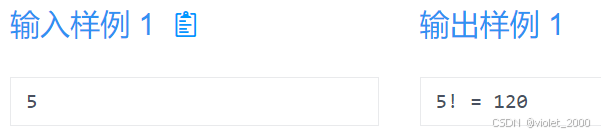
一个正整数n (0<n<15)
输出
n! = n的阶乘
提示
递归
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
int fact(int number)
{
int i,result=1;
for(i=1;i<=number;i++)
{
result*=i;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int factorial=fact(n);
printf("%d\n",factorial);
return 0;
}
cpp代码:
1.递归:当num不为0或1时,就一直调用本函数。
缺点:递归函数效率低,在多次调用时性能会下降
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>//min
#include <bitset>//去除前缀0
using namespace std;
//递归算法求函数阶乘
long long fact(int num){
if(num==0||num==1){
return 1;
}
return num*fact(num-1);
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<n<<"! = "<<fact(n)<<endl;
return 0;
}
2.迭代:通过循环更新每次函数的值
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>//min
#include <bitset>//去除前缀0
using namespace std;
//迭代算法求函数阶乘
long long fact(int num){
long long result=1;
for(int i=1;i<=num;i++){
result*=i;
}
return result;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<n<<"! = "<<fact(n)<<endl;
return 0;
}
3.一元二次方程的根
描述
编写函数,实现:传入三个参数,分别为一元二次方程 ax^2+bx+c=0 的三个系数a,b,c,求解此二次方程的根,且打印输出。
函数接口:
void root(int a,int b,int c)
{
函数体
}
输入
三个系数a、b、c。a,b,c为整数
输出
如果有两个实根,则输出:Two real roots:x1,x2(保留4位小数,且x1>x2)
如果有一个实根,则输出:One real root:x1(保留4位小数)
如果无实根,则输出:No real root

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
void root(int a,int b,int c)
{
if(b*b-4*a*c<0)
{
printf("No real root");
}else if(b*b-4*a*c==0)
{
double result=0.5*(-b)/a;
printf("One real root:%.4f",result);
}else
{
double result1=0.5*(-b+sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/a;
double result2=0.5*(-b-sqrt(b*b-4*a*c))/a;
printf("Two real roots:%.4f,%.4f",result1,result2);
}
}
int main() {
int a,b,c;
scanf("%d%d%d",&a,&b,&c);
root(a,b,c);
return 0;
}
4.乘法表
描述
编写函数实现:传入整数n,输出n*n的乘法表
函数接口:
void Print(int n)
{函数体}
输入
一个整数 n (1<=n<=100)
输出
n*n 的乘法表

提示
每个等式后面有一个空格
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
void Print(int n)
{
int i,j;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
for(j=1;j<=i;j++)
{
printf("%d*%d=%d",j,i,i*j);
if(j<i)printf(" ");
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
Print(n);
return 0;
}
5.平均值
描述
编写函数实现:传入一个整数数组a,和该数组的长度,返回该数组的平均值。
函数接口:
int Average(int a[],int n)
{函数体}
在主函数中,输入整数数组,打印输出该数组的平均值。
输入
第一行是一个整数n,代表数组的长度,(1<=n<=100)
第二行是n个整数,代表该数组中每个数的值x (x<1e5)
输出
该数组的平均值,结果保留整数

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include<math.h>
int Average(int array[],int n)
{
int i,sum=0;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
sum+=array[i];
}
int aver=(int)sum/n;
return aver;
}
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
int array[n];
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&array[i]);
}
printf("%d",Average(array,n));
return 0;
}
6.统计数字
描述
编写函数实现,统计某一整数中某个位数出现的次数
函数接口:
int Count_Digit ( int num, int d ){函数体}
输入
第一行是需要统计的一个整数n(n不超过int范围)
第二行是[0,9]中的某一个数字d
输出
输出n中数字d出现的次数

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <limits.h>
//function declaration
int Count_Digit(int num,int d);
int main() {
int n,d;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&d);
int count=0;
count=Count_Digit(n,d);
//最大输入一个9位数,再大就超过int范围了
printf("%d",count);
return 0;
}
//function definition
int Count_Digit(int num,int d)
{
int count=0;
//convert to absolute value first
num=abs(num);
//check the numbers bit by bit and count them
while(num>0)
{
int last_digit=num%10;
if(last_digit==d)count++;
num/=10;
}
return count;
}
7.十进制转换
描述
编写函数实现,将一个十进制数转换为二进制数并输出
函数接口:
void Change(int num){函数体};
输入
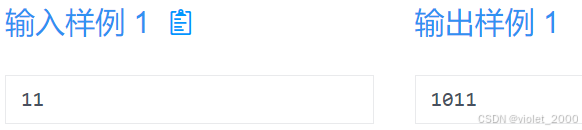
一个正整数n(1<=n<=1e6)
输出
n的二进制表示
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
void Change(int num);
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
Change(n);
return 0;
}
void Change(int num)
{
//special situation
if(num==0)
{
printf("0");
return;
}
char binary[33];//存放了33个元素,保证能放下int能表示的二进制位数
binary[32]='\0';//保证数组以'\0'结尾
int index=0,i;
while(num>0)
{
binary[index]=(num%2)?1:0;
//num%2成真,即num为单数,赋值1,否则赋值0
index++;//最后index多+1,要减去
//binary[index++]=(num%2)?1:0; 是后缀,赋值完index才会+1
num/=2;
}
//逆序输出
for(i=index-1;i>=0;i--)
{
printf("%d",binary[i]);
}
}
cpp代码:
代码1:引入bitset类型(需要去除前缀0),将int转化为二进制字符串
头文件:#include <bitset>
bitset<32> b(num);//建立一个bitset类型并用num初始化,此时b就是num的二进制形式了 to_string();//将其转化为字符串
substr(b.to_string().find(‘1’));//
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>//min
#include <bitset>//去除前缀0
using namespace std;
//十进制转二进制
void Change(int num){
bitset<32> b(num);
cout<<b.to_string().substr(b.to_string().find('1'))<<endl;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
Change(n);
return 0;
}
代码2:与C语言的方法一致
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <string>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>//min
#include <bitset>//去除前缀0
using namespace std;
//十进制转二进制
void Change(int num){
//speicial situation
if(num==0){
cout<<"0"<<endl;//不要直接输出num,num是int类型,不是二进制字符串
return;
}
char digits[33];//最多32位,最后一位是'\0'
int index=0;//位数
while(num>0){
digits[index]=(num%2)?'1':'0';//奇数-字符1 偶数-字符0
index++;//位数+1
num/=2;//num减半
}
//逆序输出
for(int i=index-1;i>=0;i--){
cout<<digits[i];
}
cout<<endl;
}
int main() {
int n;
cin>>n;
Change(n);
return 0;
}
8.表格输出
描述
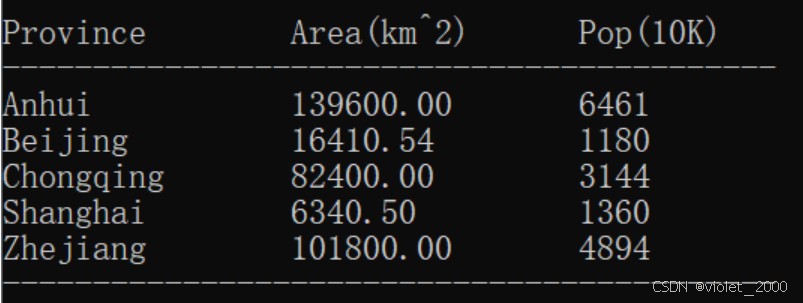
如表格所示,建立Province的结构体,
struct Province{
char name[20];
double area;
int pop;
};
将5个省的信息存入结构体,然后打印输出。
输入
无输入
输出
每一行代表一个省的数据,数据之间用空格隔开,最后一个数据后面没有空格。

代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Province
{
char name[20];
double area;
int pop;
};
int main() {
struct Province pro[]=
{
{"Anhui",139600.00,6461},
{"Beijing",16410.54,1180},
{"Chongqing",82400.00,3144},
{"Shanghai",6340.50,1360},
{"Zhejiang",101800.00,4894},
};
int num=sizeof(pro)/sizeof(pro[0]);
int i;
for(i=0;i<num;i++)
{
printf("%s %.2f %d",pro[i].name,pro[i].area,pro[i].pop);
if(i!=num-1)printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
9.同一年生日
描述
编写程序,实现在所有人中,输出某一年出生的人的姓名和出生年月日。
出生年月日和人的结构体:
struct Date{ int year,month,day;};
struct Person{ char name[20]; Date birth;};
输入
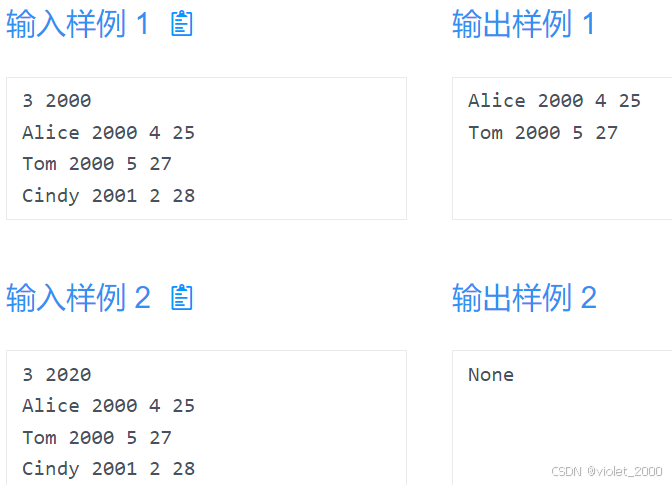
第一行两个整数 ,第一个 n 代表人的个数,第二个 year 代表需要统计的年份。(1<=n<=1000)
后面 n 行,每一行代表一个人的姓名,出生年,月,日
输出
输出 year 年出生的人的姓名,出生年月日,一个人一行。
如果没有,则输出 "None".
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Date
{
int year,month,day;
};
struct Person
{
char name[20];
struct Date birth;//使用了上一个结构体
};
int main() {
int n,year;
int i;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&year);
struct Person people[1000];
bool found=false;//初始化为假
//input
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s %d %d %d",people[i].name,
&people[i].birth.year,&people[i].birth.month,&people[i].birth.day);
}
//judgment
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
if(people[i].birth.year==year)
{
printf("%s %d %d %d\n",people[i].name,
people[i].birth.year,people[i].birth.month,people[i].birth.day);
found=true;
}
}
if(!found)//found为假,非found为真,成真即执行if语句
{
printf("None");
}
return 0;
}
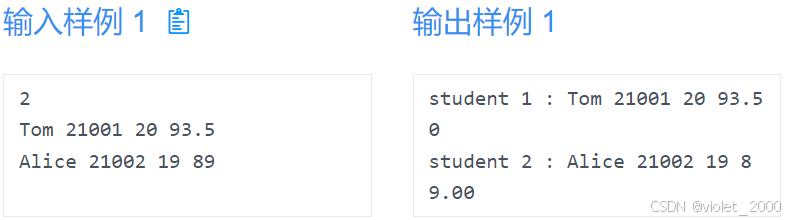
10.多个学生信息打印
描述
编写程序,实现输出多个学生的姓名,学号,年龄,和成绩。
学生结构体:struct Student{ char name[20]; int id; int age; float score;};
输入
第一行一个整数 n ,代表学生的个数(1<=n<=100)
下面 i 行,每一行分别代表一个学生的姓名,学号,年龄,成绩。
输出
按照格式输出每个学生的信息,一个学生一行,成绩保留两位小数。注意空格
代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Student
{
char name[20];
int id;
int age;
float score;
};
int main() {
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
struct Student stu[1000];
int i;
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%s %d %d %f",stu[i].name,&stu[i].id,
&stu[i].age,&stu[i].score);
}
for(i=0;i<n;i++)
{
printf("student %d : %s %d %d %.2f\n",
i+1,stu[i].name,stu[i].id,stu[i].age,stu[i].score);
}
return 0;
}























 5339
5339

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








