EMA(Exponential Moving Average,指数移动平均)本身是一种轻量级的低通滤波器,常用于平滑时间序列数据。虽然它不是传统意义上的“自适应滤波器”(如 LMS、RLS 等),但可以通过让 EMA 的平滑系数(通常记为 α )动态调整,使其具备自适应性,从而实现一种简单的自适应滤波。

“根据信号变化率自适应调整 EMA 平滑系数 α,使用 Sigmoid 型函数” 的实现方法,并附上清晰的公式推导、参数解释和 Python 代码示例



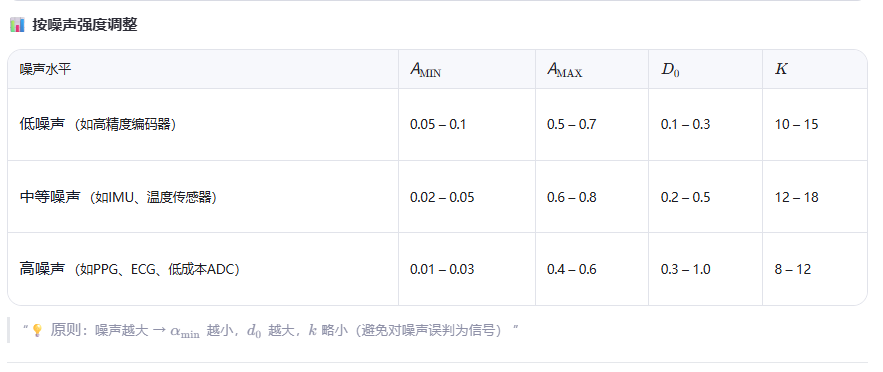 调参技巧
调参技巧
1.先固定 αmin,αmax ,调 d0 和 k

离线估计噪声标准差:
def estimate_d0_offline(signal, N0=100, c=2.0):
"""
从信号前 N0 个点估计噪声标准差,计算 d0
"""
sigma = np.std(signal[:N0])
return c * sigma
在线估计:


下面给出Python 示例代码仅供参考,可根据需要自行调整参数
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 中文显示标题
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei']
class EMAFilter:
"""指数移动平均滤波器"""
def __init__(self, alpha=0.3):
"""
初始化滤波器
:param alpha: 平滑系数(0 < alpha < 1),值越大响应越快,平滑性越差
"""
self.alpha = alpha
self.last_output = None # 保存上一时刻的滤波结果
def filter(self, x):
"""
对单个数据点进行滤波
:param x: 当前输入数据
:return: 滤波后的数据
"""
if self.last_output is None:
# 首次输入时,直接将输入作为初始输出
self.last_output = x
else:
# EMA核心公式:当前输出 = alpha*当前输入 + (1-alpha)*上一时刻输出
self.last_output = self.alpha * x + (1 - self.alpha) * self.last_output
return self.last_output
def reset(self):
"""重置滤波器状态"""
self.last_output = None
class OnlineD0Estimator:
def __init__(self, alpha_slow=0.01, k_d=1.5):
self.alpha_slow = alpha_slow
self.k_d = k_d
self.y_slow = None # 慢速基线
self.mae = None # 噪声尺度估计(MAE)
def update(self, x):
if self.y_slow is None:
self.y_slow = x
self.mae = 0.0
return self.k_d * self.mae # 初始 d0 = 0
# 更新慢速基线
self.y_slow = self.alpha_slow * x + (1 - self.alpha_slow) * self.y_slow
# 计算残差绝对值
err = abs(x - self.y_slow)
# 更新 MAE(噪声尺度)
self.mae = self.alpha_slow * err + (1 - self.alpha_slow) * self.mae
# 返回 d0
return self.k_d * self.mae
class FullyAdaptiveEMA:
def __init__(self, alpha_min=0.02, alpha_max=0.6, k_sigmoid=12.0):
self.alpha_min = alpha_min
self.alpha_max = alpha_max
self.k_sigmoid = k_sigmoid
self.y = None
# 在线 d0 估计器
self.d0_estimator = OnlineD0Estimator(alpha_slow=0.01, k_d=1.5)
def update(self, x):
# 实时估计 d0
d0 = self.d0_estimator.update(x)
if self.y is None:
self.y = x
return self.y
# 计算残差
d = abs(x - self.y)
# Sigmoid 映射
s = 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-self.k_sigmoid * (d - d0 + 1e-8))) # +eps 防 d0=0
alpha = self.alpha_min + (self.alpha_max - self.alpha_min) * s
# 更新输出
self.y = alpha * x + (1 - alpha) * self.y
return self.y
# 生成测试数据(含噪声的正弦波)
def generate_test_data():
# 生成时间序列(0到10秒,共1000个点)
t = np.linspace(0, 10, 1000)
# 原始信号(正弦波)
signal = np.sin(t)
# 添加高斯噪声(均值0,标准差0.5)
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.5, size=len(t))
noisy_signal = signal + noise
return t, signal, noisy_signal
# 主函数:测试不同alpha的滤波效果
def main():
# 生成测试数据
t, original_signal, noisy_signal = generate_test_data()
# 初始化滤波器
ema_fixed_low = EMAFilter(alpha=0.05) # 强平滑
ema_fixed_high = EMAFilter(alpha=0.3) # 快响应
ema_adaptive = FullyAdaptiveEMA(alpha_min=0.02, alpha_max=0.6, k_sigmoid=12.0)
# 存储滤波结果
filtered_low = []
filtered_high = []
filtered_adaptive = []
# 逐点滤波
for x in noisy_signal:
filtered_low.append(ema_fixed_low.filter(x))
filtered_high.append(ema_fixed_high.filter(x))
filtered_adaptive.append(ema_adaptive.update(x))
# 转换为numpy数组
filtered_low = np.array(filtered_low)
filtered_high = np.array(filtered_high)
filtered_adaptive = np.array(filtered_adaptive)
# 计算RMSE(均方根误差)作为客观评价指标
rmse_low = np.sqrt(np.mean((filtered_low - original_signal) ** 2))
rmse_high = np.sqrt(np.mean((filtered_high - original_signal) ** 2))
rmse_adaptive = np.sqrt(np.mean((filtered_adaptive - original_signal) ** 2))
# 绘图
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 8))
plt.plot(t, noisy_signal, 'lightgray', alpha=0.7, linewidth=1, label='含噪声信号')
plt.plot(t, original_signal, 'k--', linewidth=2, label='原始信号')
plt.plot(t, filtered_low, 'b-', linewidth=2, label=f'固定α=0.05 (RMSE={rmse_low:.3f})')
plt.plot(t, filtered_high, 'g-', linewidth=2, label=f'固定α=0.3 (RMSE={rmse_high:.3f})')
plt.plot(t, filtered_adaptive, 'r-', linewidth=2.5, label=f'自适应α (RMSE={rmse_adaptive:.3f})')
plt.xlabel('时间')
plt.ylabel('幅值')
plt.title('固定α vs 自适应α EMA滤波效果对比')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True, alpha=0.3)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 打印客观指标
print(f"RMSE 比较:")
print(f" 固定α=0.05: {rmse_low:.4f}")
print(f" 固定α=0.3: {rmse_high:.4f}")
print(f" 自适应α: {rmse_adaptive:.4f}")
return t, original_signal, noisy_signal, filtered_low, filtered_high, filtered_adaptive
# 运行主函数
if __name__ == "__main__":
results = main()






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








