之前已经介绍了人工智能高性能计算集群建设,但是还遗留了软件包管理仓库的建设内容。这里将补充这部分内容,并沿用之前的章节序号。
目录
6. 软件包管理仓库
Modules 是一个环境模块系统,主要用于在高性能计算集群中管理软件包的环境配置。它允许用户通过简单的命令行指令来改变其 shell 环境中的路径和其他环境变量,从而可以轻松地切换不同的软件版本和配置。
Modules 的主要功能
- 环境管理:Modules 允许用户动态地添加或删除环境变量,如 PATH、MANPATH 和 LD_LIBRARY_PATH 等,使得不同应用程序可以共存并且互不干扰。
- 版本控制:可以为同一软件的不同版本提供独立的环境配置。
- 依赖管理:通过定义模块间的依赖关系,确保软件包按照正确的顺序加载。
- 用户友好:简化了用户操作,只需要几条简单的命令即可完成复杂的环境配置更改。
使用 Modules 的基本命令
一些常见的 Modules 命令包括:
module load <module_name>:加载指定的模块。module unload <module_name>或module rm <module_name>:卸载指定的模块。module switch <old_module> <new_module>:卸载旧模块并加载新模块。module list:显示当前加载的所有模块。module help <module_name>:获取指定模块的帮助信息。module spider:搜索可用模块及其位置。Modules 的应用场景
Modules 经常用于以下场景:
- 在学术研究机构和企业数据中心的 HPC 集群中,为研究人员提供一致且可重复的软件环境。
- 在多用户共享的计算资源中,保证每个用户可以根据个人需求加载所需的软件配置而不影响他人。
- 在测试和生产环境中切换不同的软件版本。
这部分内容可以参考:
0. modules模块概述 — 孪烽超算平台用户手册 0.1.0 文档![]() https://lfpara.com/docs/hpc/tools/modules/modules.html
https://lfpara.com/docs/hpc/tools/modules/modules.html
6.1. Modules安装
6.1.1 安装
- 使用yum直接安装
yum install epel-release -y
yum install environment-modules -y安装完成之后,退出当前终端,重新打开终端。查看版本
module --version
- 使用源码安装
# 获取tarball源码包
curl -LJO https://github.com/cea-hpc/modules/releases/download/v5.0.1/modules-5.0.1.tar.gz
# 解压缩源码包
tar xfz modules-5.0.1.tar.gz
# 简单编译安装,有特别需求可以手动设置配置参数
./configure
make
make install
# 常用的配置参数
--prefix=PREFIX #执行文件安装路径
--modulefilesdir=DIR #modulefile文件目录6.1.2 modulespath配置
在使用yum直接安装时候,默认MODULEPATH 为 /usr/share/Modules/modulefiles:/etc/modulefiles:/usr/share/modulefiles
Modulefiles 的位置通常可以在系统的模块文件系统中找到。 在大多数情况下,这些模块文件存储在特定的目录下,例如 /etc/modulefiles ,/usr/share/modulefiles, /usr/share/Modules/modulefiles。用户可以通过命令行工具查看当前加载的模块文件信息。具体来说,可以使用 module 命令来查看当前加载的模块文件。例如,使用 module list 命令可以列出当前所有已加载的模块文件
在 /usr/share/Modules/init/ 目录下面的脚本,用来初始化Module模块。

- 创建或编辑配置文件
vim .modulespath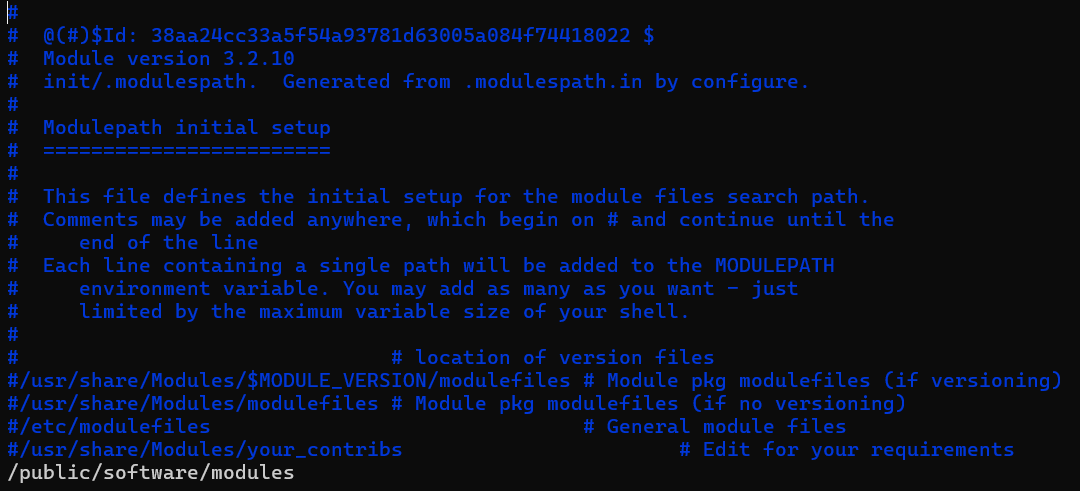
将我们自定义的路径/public/software/modules 添加到软件模块默认位置。(注释掉系统默认的位置 /usr/share/Modules/modulefiles 和 /etc/modulefiles)
在init目录下有一个sh文件,内容(默认)如下
module() { eval `/usr/bin/modulecmd sh $*`; }
MODULESHOME=/usr/share/Modules
export MODULESHOME
if [ "${LOADEDMODULES:-}" = "" ]; then
LOADEDMODULES=
export LOADEDMODULES
fi
if [ "${MODULEPATH:-}" = "" ]; then
MODULEPATH=`sed -n 's/[ #].*$//; /./H; $ { x; s/^\n//; s/\n/:/g; p; }' ${MODULESHOME}/init/.modulespath`
export MODULEPATH
fi该sh文件或csh文件(最后四行代码)会自动将 隐藏文件 .modulespath 中的配置自动加载设置到 MODULEPATH中。类似于:
export MODULEPATH=${MODULEPATH}:/public/software/modules退出终端,重新进入,查看环境变量 MODULEPATH
echo $MODULEPATH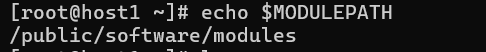
6.2. modules模块使用说明
modules模块的指令格式如下(可以使用 module --help 进行查看):
6.2.1. module 3.2.10版本
Usage: module [ switches ] [ subcommand ] [subcommand-args ]
Switches:
-H|--help this usage info
-V|--version modules version & configuration options
-f|--force force active dependency resolution
-t|--terse terse format avail and list format
-l|--long long format avail and list format
-h|--human readable format avail and list format
-v|--verbose enable verbose messages
-s|--silent disable verbose messages
-c|--create create caches for avail and apropos
-i|--icase case insensitive
-u|--userlvl <lvl> set user level to (nov[ice],exp[ert],adv[anced])
Available SubCommands and Args:
+ add|load modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ rm|unload modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ switch|swap [modulefile1] modulefile2
+ display|show modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ avail [modulefile [modulefile ...]]
+ use [-a|--append] dir [dir ...]
+ unuse dir [dir ...]
+ update
+ refresh
+ purge
+ list
+ clear
+ help [modulefile [modulefile ...]]
+ whatis [modulefile [modulefile ...]]
+ apropos|keyword string
+ initadd modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ initprepend modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ initrm modulefile [modulefile ...]
+ initswitch modulefile1 modulefile2
+ initlist
+ initclear6.2.2. module 4.5.2 版本
Usage: module [options] [command] [args ...]
Loading / Unloading commands:
add | load modulefile [...] Load modulefile(s)
rm | unload modulefile [...] Remove modulefile(s)
purge Unload all loaded modulefiles
reload | refresh Unload then load all loaded modulefiles
switch | swap [mod1] mod2 Unload mod1 and load mod2
Listing / Searching commands:
list [-t|-l|-j] List loaded modules
avail [-d|-L] [-t|-l|-j] [-S|-C] [--indepth|--no-indepth] [mod ...]
List all or matching available modules
aliases List all module aliases
whatis [-j] [modulefile ...] Print whatis information of modulefile(s)
apropos | keyword | search [-j] str
Search all name and whatis containing str
is-loaded [modulefile ...] Test if any of the modulefile(s) are loaded
is-avail modulefile [...] Is any of the modulefile(s) available
info-loaded modulefile Get full name of matching loaded module(s)
Collection of modules handling commands:
save [collection|file] Save current module list to collection
restore [collection|file] Restore module list from collection or file
saverm [collection] Remove saved collection
saveshow [collection|file] Display information about collection
savelist [-t|-l|-j] List all saved collections
is-saved [collection ...] Test if any of the collection(s) exists
Shell's initialization files handling commands:
initlist List all modules loaded from init file
initadd modulefile [...] Add modulefile to shell init file
initrm modulefile [...] Remove modulefile from shell init file
initprepend modulefile [...] Add to beginning of list in init file
initswitch mod1 mod2 Switch mod1 with mod2 from init file
initclear Clear all modulefiles from init file
Environment direct handling commands:
prepend-path [-d c] var val [...] Prepend value to environment variable
append-path [-d c] var val [...] Append value to environment variable
remove-path [-d c] var val [...] Remove value from environment variable
Other commands:
help [modulefile ...] Print this or modulefile(s) help info
display | show modulefile [...] Display information about modulefile(s)
test [modulefile ...] Test modulefile(s)
use [-a|-p] dir [...] Add dir(s) to MODULEPATH variable
unuse dir [...] Remove dir(s) from MODULEPATH variable
is-used [dir ...] Is any of the dir(s) enabled in MODULEPATH
path modulefile Print modulefile path
paths modulefile Print path of matching available modules
clear [-f] Reset Modules-specific runtime information
source scriptfile [...] Execute scriptfile(s)
config [--dump-state|name [val]] Display or set Modules configuration
Switches:
-t | --terse Display output in terse format
-l | --long Display output in long format
-j | --json Display output in JSON format
-d | --default Only show default versions available
-L | --latest Only show latest versions available
-S | --starts-with
Search modules whose name begins with query string
-C | --contains Search modules whose name contains query string
-i | --icase Case insensitive match
-a | --append Append directory to MODULEPATH
-p | --prepend Prepend directory to MODULEPATH
--auto Enable automated module handling mode
--no-auto Disable automated module handling mode
-f | --force By-pass dependency consistency or confirmation dialog
Options:
-h | --help This usage info
-V | --version Module version
-D | --debug Enable debug messages
-v | --verbose Enable verbose messages
-s | --silent Turn off error, warning and informational messages
--paginate Pipe mesg output into a pager if stream attached to terminal
--no-pager Do not pipe message output into a pager
--color[=WHEN] Colorize the output; WHEN can be 'always' (default if
omitted), 'auto' or 'never'6.2.3. 常见的使用命令
常见的module命令有: load/unload/switch/avail/list/show。
add|load modulefile [modulefile ...] # 加载模块
rm|unload modulefile [modulefile ...] # 卸载模块
switch|swap [modulefile1] modulefile2 # 切换模块
display|show modulefile [modulefile ...] # 查看模块的相关信息
avail [modulefile [modulefile ...]] # 查看系统中可用的模块
list # 列出已经加载的模块使用方式为:
module avail #系统中可用的模块。
6.3. modulefile实战练习
规划目录:
/public/software/apps 管理员进行软件安装的目录
/public/software/modules/apps 管理软件modulesfiles文件
/public/software/sources 软件源代码,用于编译配置与安装使用
mkdir -p /public/software/apps
mkdir -p /public/software/modules/apps
mkdir -p /public/software/sources6.3.1 编译安装gcc
- 编译安装gcc
Index of /gnu/gcc![]() https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/
https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/
下载gcc,解压,安装所需的依赖,以及编译安装
cd /public/software/sources/
wget https://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/gcc/gcc-14.2.0/gcc-14.2.0.tar.gz
tar -xvf gcc-14.2.0.tar.gz
cd gcc-14.2.0
./contrib/download_prerequisites
./configure --prefix=/public/software/apps/gcc/gcc-14.2.0 --disable-multilib
make && make install
# 查看版本信息
/public/software/apps/gcc/gcc-14.2.0/bin/gcc --version
- 编辑modulefile文件
mkdir -p /public/software/modules/apps/gcc
cd /public/software/modules/apps/gcc
vim 14.2.0#%Module1.0
proc ModulesHelp { } {
puts stderr "\tGCC 14.2.0"
}
set version "14.2.0"
set prefix "/public/software/apps/gcc/gcc-$version"
module-whatis "Sets up the GCC $version environment."
prepend-path PATH $prefix/bin
prepend-path LD_LIBRARY_PATH $prefix/lib6.3.2 编译安装Python
- 下载python源码并编译安装
Python Source Releases | Python.org![]() https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
https://www.python.org/downloads/source/
cd /public/software/sources/
wget https://www.python.org/ftp/python/3.13.0/Python-3.13.0rc3.tgz
tar xvf Python-3.13.0rc3.tgz
cd Python-3.13.0rc3
./configure --prefix=/public/software/apps/Python/Python-3.13.0rc3
make && make install
# 测试python
/public/software/apps/Python/Python-3.13.0rc3/bin/python3 --version- 编写Python的Modulefile文件:
mkdir -p /public/software/modules/apps/Python/
cd /public/software/modules/apps/Python/
vim 3.13.0rc3#%Module1.0
proc ModulesHelp { } {
puts stderr "\tPython 3.13.0rc3"
}
set version "3.13.0rc3"
set prefix "/public/software/apps/Python/Python-$version"
module-whatis "Sets up the Python $version environment."
prepend-path PATH $prefix/bin
prepend-path LD_LIBRARY_PATH $prefix/lib
prepend-path PYTHONPATH $prefix/lib/python3.13/site-packages这个Modulefile定义了一个帮助信息,设置了版本号和前缀,并通过prepend-path命令将Python的可执行文件目录添加到用户的PATH环境变量中。当加载这个模块时,用户的PATH将被修改,使得相关Python版本的命令(如python或pip)可以直接调用。
- PATH: 添加 Python 可执行文件的路径到环境变量 PATH 中,以便可以直接运行 python3 或 pip3 等命令。
- LD_LIBRARY_PATH: 添加 Python 库的路径到环境变量 LD_LIBRARY_PATH 中,以确保在运行时能够找到动态链接库。
- PYTHONPATH: 添加 Python 包的路径到环境变量 PYTHONPATH 中,以确保 Python 能够找到安装的模块
6.3.3. 环境测试
使用普通用户进行测试:
# 当前环境python3 版本
python3 --version
# 当前环境列表
module list
# 环境可用模块
module av
# 加载模块 apps/Python/3.13.0rc3
module add apps/Python/3.13.0rc3
# 查看当前环境列表变化
module list
# 查看当前环境python3 版本
python3 --version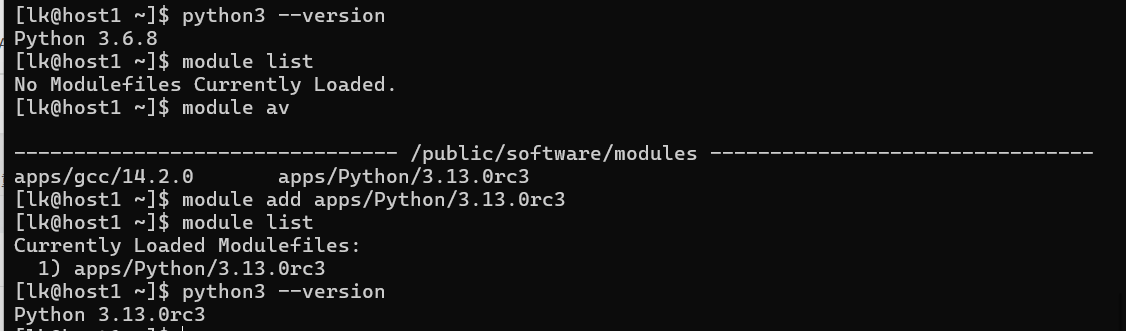
至此 高性能计算集群建设完成。




















 1683
1683

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








