随着项目的运行,数据量的累加,系统就会变得越来越慢,优化成为必然。主流的优化方式有开源、节流,开源为调整服务器配置,节流为提升系统的运行效率。其中mysql的查询占有较高的时间复杂度,以下会介绍mysql的优化方法。
优化原则:
1、面向相应时间
指在一定的工作负载下尽可能的降低相应时间
2、定位时间用在什么地方并进行优化
优化思路:

优化方式:
一、数据类型优化
#to be continue
二、索引的行程过程
|
C1
|
c2
|
c3
|
|
5
|
3
|
Y
|
|
4
|
4
|
A
|
|
3
|
9
|
D
|
|
8
|
7
|
A
|
|
20
|
2
|
E
|
|
10
|
4
|
O
|
|
1
|
4
|
U
|
create index idx_t on t(c1);
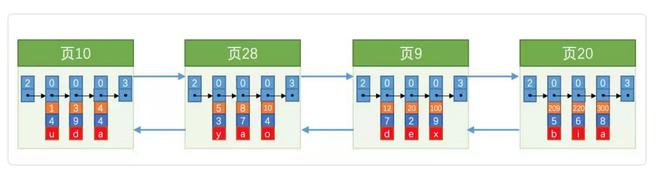
1、创建叶子节点
1)提取数据(索引列+行记录地址或主键)
2)将提取的数据进行排序,然后存入列中
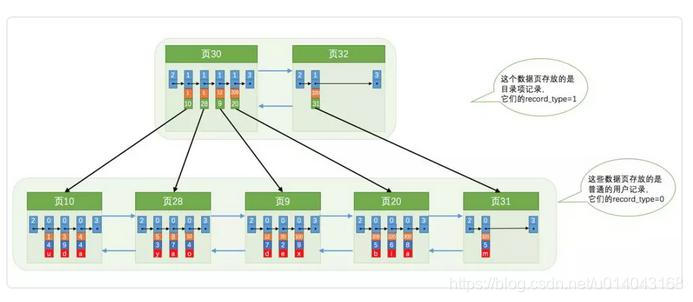
2、创建页目录
1)提取数据(每个页中的最小记录+页号)
2)排序(页内、页间)
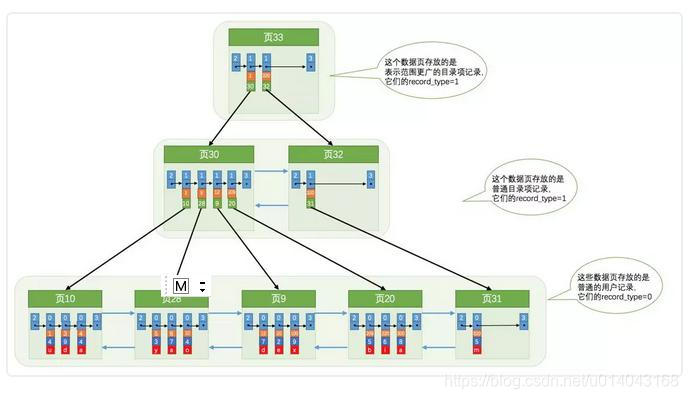
3、创建根节点
查询的逻辑过程如下图,如果索引数中包含全部select的字段,则查询完索引树后即可返回结果,称之为索引覆盖;如果索引树中不完全包含select的字段,则查询完索引树之后需要回表查询。
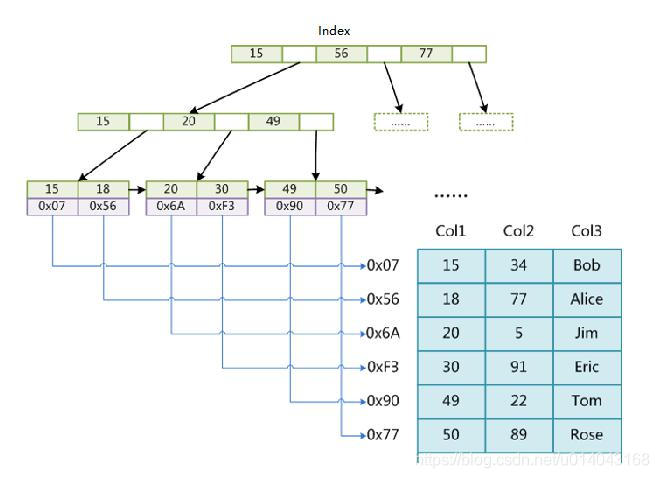
索引树的检索过程
1)确定where条件中是否含有索引的前导列(第一列),有则进行2,否则停止索引检索
2)在索引树中进行检索。检索规则按照所建立的索引顺序,也where中的顺序无关,比如建立索引create index idx_t on t(c1,c3,c2); 然后 select * from table where c3=‘A’ and c2=3 and c1=1; 检查顺序为c1>c3>c2
组合索引命中情况:
建立索引(c1,c2,c3)
全匹配(完美命中) where c1=2 and c2=2 and c3=3;
前导列匹配(只能够命中前导列) where c1=2 and c3=3;
不包含前导列(不能命中) where c2=2 and c3=3;
三、索引优化
· 1)通过索引的选择性确定该索引是否合理(计算值>70%)
SELECT * FROM employees WHERE first_name='Martial' AND last_name='DuCasse';
1.单列的选择性:distinct first_name)/count(*) from employees; --0.45%
select count(distinct last_name)/count(*) from employees; --0.58%
2.组合列的选择性:
select count(distinct(concat(first_name,last_name)))/count(*) from employees --99.32% --30
2)创建组合索引时,根据最左原则,选择性高的列为前导列。因此1)的案例创建语句为:create index idx_name01 on employees(last_name,first_name);
3)每个索引的叶子节点都是又索引列+主键组成。
4)当索引列长度过长,且列前缀的选择性接近全列索引,可以用前缀索引代替,因为索引变短能减少索引的叶子节点,从而降低内存的负载。建立语句:create index idx_name02 on employees(last_name,first_name(4));
5)innodb默认聚蔟索引,根据主键查询条目时不用回表,叶子节点就是行记录。
6)一个索引包含了所有需要查询的字段,则成为索引覆盖,即只需扫描索引而无需回表。使用了索引覆盖在explain的extra列为using index。
四、EXPLAIN的使用
使用方式:explain select * from t1;
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-------+
id:
Id如果相同,可以认为是一组,从上往下顺序执行;
在所有组中,id值越大,优先级越高,越先执行;
Select_type:
主要有SIMPLE、PRIMARY、SUBQUERY、DERIVED、UNION、UNION RESULT。分别用来表示查询的类型,主要用户区别普通查询、联合查询、子查询的复杂查询
SIMPLE : 简单的select查询,查询中不包含子查询或者UNION
PRIMARY : 查询中若包含任何复杂的字部分,最外层查询则被标记为PRIMARY
SUBQUERY : 在select或where列表中包含的子查询
DERIVED : 在from列表中包含的子查询被标记为derived(衍生),mysql会递归执行这些子查询,把结果放在临时表中
UNION : 若第二个select出现在union之后,则被标记问union;若union包含在from子句的子查询中,外层select将被标记为:derived
UNION RESULT : 从union表获取结果的select
type:
Type所显示的是查询使用了哪种类型,包括all、index、range、ref、eq_ref、const,system、null
从好到坏排行:system > const > eq_ref > ref > range > index > all
system : 系统表专用,可以忽略
const : 用于比较primary key或unique index,只通过索引一次就能找到
ed_ref : 唯一性索引扫描,对于每个索引键,表中只有一条记录与之匹配,常见于主键或唯一索引扫描
ref : 非唯一碎银扫描
range : 只检索给定范围的行,使用一个索引来选择行,key列显示使用了哪个索引,一般就是使用between、<、>、in等where查询。
index : full index scan,index与all区别为index类型只遍历索引树,这通常比all快,因为索引文件通常比数据文件下。
all : full table scan 遍历权标以找到匹配的行
extra:
额外信息
using filesort : 说明mysql会对数据使用一个外部的索引排序,而不是按照表内的索引顺序进行读取,mysql中无法利用索引完成的排序操作成为文件排序。效率评分为差
using temporary : 使用了用临时表保存中间结果,mysql在对查询结果排序使用临时表。常见于排序ordr by和分组查询group by。效率评分为很差
using index : 标识相应的select操作中使用了覆盖索引,避免访问了表的数据行,效率不错。如果同时出现using where,表明索引被用来执行索引键值的查找;如果没有出现using where,表明索引用来读取数据而非执行查找动作。
using where : 表明使用where过滤
using join buffer : 表明使用了链接缓存,比如说在查询的时候,多表join的次数非常多,name将配置文件找那个的缓冲区的join buffer调大一些。
五、sql语句的新特性(我也看不懂,纯复制)
1、ICP(Index Condition Pushdown Optimization)
描述:在存储引擎层通过索引列提前过滤掉数据,从而减少服务器层访问的数据量,同时也减少存储引擎访问基表的次数
使ICP的用条件
1. optimizer_switch=
'index_condition_push down=on';
2.
只能用于二级索引。
3. explain显示的执行计划中type值为range、 ref、 eq_ref或者ref_or_null,且不是通过索 引覆盖获得查询结果。
4. ICP可以用于MyISAM和InnnoDB存储引擎, 包括分区表(5.7)
2、Nested-Loop Join
1)SNLJ(Simple Nested Loop Join)
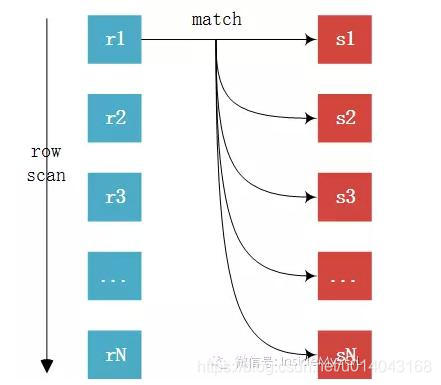
2)INLJ(Index Nested Loop Join)
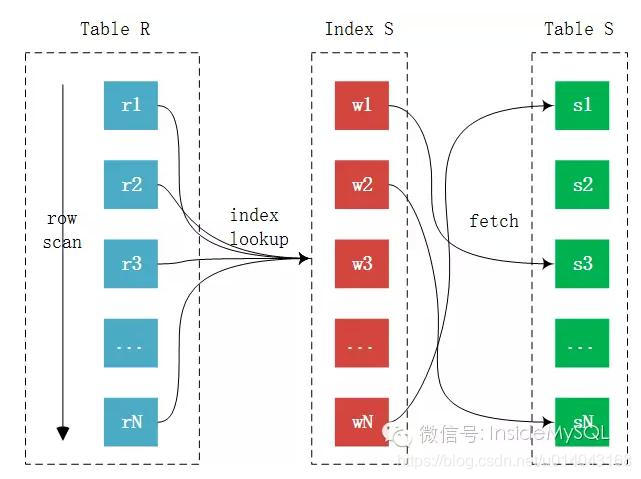
3)BNL(Block Nested Loop)
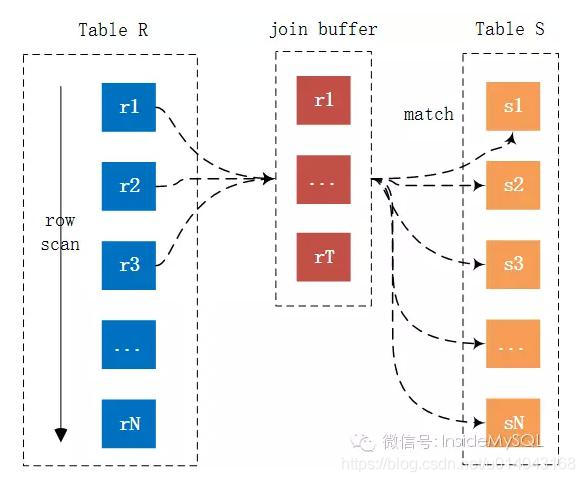
MySQL使用Join
Buffer有以下要点:
1.
set optimizer_switch=
'block_nested_loop=on';
2. join_buffer_size变量决定buffer大小。
3. 只有在type类型为all, index, range的时候才可以 使用BNL。
4. 在join之前就会分配join buffer, 在query执行完 毕即释放。
3、MRR(multi-Range Read)
描述:MTT(多范围读),他的作用针对二级索引的查询,将随机IP转化为顺序IO,提高查询效率。
使用MRR条件
1. optimizer_switch=
'mrr=on,mrr_cost_bas ed=off' 表示总是开启MRR优化。
2. optimizer_switch=
'mrr=on,mrr_cost_bas ed=on' 表示基于成本控制是否使用MRR优化。
3. explain显示的执行计划中type值为range、 ref或eq_ref。
4. read_rnd_buffer_size 用来控制键值缓冲区 的大小。
MRR未开启时
MySQL(Innodb)
针对基于二级索引的查询策略 是这样的:
1.
先根据where条件中的二级索引获取索引列与 主键的集合。
2. 通过第一步获取的主键来获取对应的行记录。
MRR开启时
MySQL(Innodb)
针对基于二级索引的查询策略 是这样的:
1.
先根据where条件中的二级索引获取索引列与主键 的集合。
2. 将集合放在buffer里面,然后对集合按照 pk_column排序,得到新的集合。
3. 利用已经排序过的集合回表取数,此时是顺序IO。
4、BKA(Batched Key Access)
描述: 多表关联(索引)
时,将外层循环的结果集存入join buffer,内存循环的数据通过索引与整个buffer中 的记录做比较。
BKA的算法
1. 多表关联时,将外层循环的结果集存入join buffer。
2. BAK根据buffer中的数据与内表的关联条件去 内表获取相关索引,并将索引发送到MRR接口。
3. MRR把收到的索引,根据主键进行重新排序, 然后再回表读取行记录。
4. 返回结果集给客户端。
BKA优点
使用join buffer,减少了对内表的遍历次数
使用MRR,对内表的随机IO转换为了顺序IO
六、SQL语句优化
1)sql语句优化的方向已命中索引为主。总所周知,建立了索引也不一定能命中,没有命中的索引就毫无意义了,而且会占用内存,可用explain工具查看索引使用情况。
2)其次,在实现功能的情况下尽量减少数据的遍历次数,基本体现在explain 的 rows返回。
3)大数据分页查询
limit offset,N的时候,随着offset增加,语句耗时也在增加,因为mysql取offset+N行记录,然后放弃前offset行,只返回N行记录。当offset特别大的时候,效率非常低下。
解决方案有几种:
1、利用索引覆盖,查询信息少的时候可用,当查询的列信息过多也不甚理想。
2、建立where索引,先走索引覆盖查询出分页的主键,然后根据主键走聚蔟索引查询出所需信息,语句:select * from employees m inner join(select emp_no from employees limit 100000,10) s on s.emp_no=m.emp_no;
案例对比:
#普通分页
select * from employees limit 100000,10; --0.17s
select * from employees limit 600000,10; --0.46s
select * from employees limit 1200000,10; —1.31s
#通过关联获取数据
select * from employees m inner join(select emp_no from employees limit 100000,10) s on s.emp_no=m.emp_no; --0.08
select * from employees m inner join(select emp_no from employees limit 600000,10) s on s.emp_no=m.emp_no; --0.21
select * from employees m inner join(select emp_no from employees limit 1200000,10) s on s.emp_no=m.emp_no; --0.46
Mysql 查询案例:
在网上看到了不少mysql查询优化的题目,我从中摘抄了几题有意思的。
创建数据表
create table student(sid varchar(6), sname varchar(10), sage datetime, ssex varchar(10));
insert into student values('01' , '赵雷' , '1990-01-01' , '男');
insert into student values('02' , '钱电' , '1990-12-21' , '男');
insert into student values('03' , '孙风' , '1990-05-20' , '男');
insert into student values('04' , '李云' , '1990-08-06' , '男');
insert into student values('05' , '周梅' , '1991-12-01' , '女');
insert into student values('06' , '吴兰' , '1992-03-01' , '女');
insert into student values('07' , '郑竹' , '1989-07-01' , '女');
insert into student values('08' , '王菊' , '1990-01-20' , '女');
create table sc(sid varchar(10), cid varchar(10), score decimal(18,1));
insert into sc values('01' , '01' , 80);
insert into sc values('01' , '02' , 90);
insert into sc values('01' , '03' , 99);
insert into sc values('02' , '01' , 70);
insert into sc values('02' , '02' , 60);
insert into sc values('02' , '03' , 80);
insert into sc values('03' , '01' , 80);
insert into sc values('03' , '02' , 80);
insert into sc values('03' , '03' , 80);
insert into sc values('04' , '01' , 50);
insert into sc values('04' , '02' , 30);
insert into sc values('04' , '03' , 20);
insert into sc values('05' , '01' , 76);
insert into sc values('05' , '02' , 87);
insert into sc values('06' , '01' , 31);
insert into sc values('06' , '03' , 34);
insert into sc values('07' , '02' , 89);
insert into sc values('07' , '03' , 98);
create table course(cid varchar(10),cname varchar(10),tid varchar(10));
insert into course values('01' , '语文' , '02');
insert into course values('02' , '数学' , '01');
insert into course values('03' , '英语' , '03');
create table teacher(tid varchar(10),tname varchar(10));
insert into teacher values('01' , '张三');
insert into teacher values('02' , '李四');
insert into teacher values('03' , '王五');
查询平均成绩大于等于
60 分的同学的学生编号和学生姓名和平均成绩
select s.sid, sname, avg(score) as avg_score
from student as s, sc
where s.sid = sc.sid
group by s.sid
having avg_score > 60;
+------+-------+-----------+
| sid | sname | avg_score |
+------+-------+-----------+
| 01 | ?? | 89.66667 |
| 02 | ?? | 70.00000 |
| 03 | ?? | 80.00000 |
| 05 | ?? | 81.50000 |
| 07 | ?? | 93.50000 |
+------+-------+-----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询平均成绩大于等于
60 分的同学的学生编号和学生姓名和平均成绩
select s.*, rank_01, rank_02, rank_03, rank_total
from student s
left join (select sid, dense_rank() over(partition by cid order by score desc) as rank_01 from sc where cid=01) A on s.sid=A.sid
left join (select sid, dense_rank() over(partition by cid order by score desc) as rank_02 from sc where cid=02) B on s.sid=B.sid
left join (select sid, dense_rank() over(partition by cid order by score desc) as rank_03 from sc where cid=03) C on s.sid=C.sid
left join (select sid, dense_rank() over(order by avg(score) desc) as rank_total from sc group by sid) D on s.sid=D.sid
order by rank_total asc;
+------+-------+---------------------+------+---------+---------+---------+------------+
| sid | sname | sage | ssex | rank_01 | rank_02 | rank_03 | rank_total |
+------+-------+---------------------+------+---------+---------+---------+------------+
| 08 | ?? | 1990-01-20 00:00:00 | ? | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL |
| 07 | ?? | 1989-07-01 00:00:00 | ? | NULL | 2 | 2 | 1 |
| 01 | ?? | 1990-01-01 00:00:00 | ? | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 05 | ?? | 1991-12-01 00:00:00 | ? | 2 | 3 | NULL | 3 |
| 03 | ?? | 1990-05-20 00:00:00 | ? | 1 | 4 | 3 | 4 |
| 02 | ?? | 1990-12-21 00:00:00 | ? | 3 | 5 | 3 | 5 |
| 04 | ?? | 1990-08-06 00:00:00 | ? | 4 | 6 | 5 | 6 |
| 06 | ?? | 1992-03-01 00:00:00 | ? | 5 | NULL | 4 | 7 |
+------+-------+---------------------+------+---------+---------+---------+------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
统计各科成绩各分数段人数:课程编号,课程名称,[100-85]
,[85-70]
,[70-60]
,[60-0]
及所占百分比
select c.cid as '课程编号', c.cname as '课程名称', A.*
from course as c,
(select cid,
sum(case when score >= 85 then 1 else 0 end)/count(*) as 100_85,
sum(case when score >= 70 and score < 85 then 1 else 0 end)/count(*) as 85_70,
sum(case when score >= 60 and score < 70 then 1 else 0 end)/count(*) as 70_60,
sum(case when score < 60 then 1 else 0 end)/count(*) as 60_0
from sc group by cid) as A
where c.cid = A.cid;
+------+------+------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| | | cid | 100_85 | 85_70 | 70_60 | 60_0 |
+------+------+------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
| 01 | ?? | 01 | 0.0000 | 0.6667 | 0.0000 | 0.3333 |
| 02 | ?? | 02 | 0.5000 | 0.1667 | 0.1667 | 0.1667 |
| 03 | ?? | 03 | 0.3333 | 0.3333 | 0.0000 | 0.3333 |
+------+------+------+--------+--------+--------+--------+
3 rows in set (0.00 sec)
查询各科成绩前三名的记录
select * from (select *, rank() over(partition by cid order by score desc) as graderank from sc) A
where A.graderank <= 3;
+------+------+-------+-----------+
| sid | cid | score | graderank |
+------+------+-------+-----------+
| 01 | 01 | 80.0 | 1 |
| 03 | 01 | 80.0 | 1 |
| 05 | 01 | 76.0 | 3 |
| 01 | 02 | 90.0 | 1 |
| 07 | 02 | 89.0 | 2 |
| 05 | 02 | 87.0 | 3 |
| 01 | 03 | 99.0 | 1 |
| 07 | 03 | 98.0 | 2 |
| 02 | 03 | 80.0 | 3 |
| 03 | 03 | 80.0 | 3 |
+------+------+-------+-----------+
10 rows in set (0.00 sec)


























 1679
1679

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








