注:本文为 “科学研究” 相关合辑。
英文引文,机翻未校。
图片清晰度受引文原图所限。
未整理去重,如有内容异常,请看原文。
What Are The Types Of Scientific Research?
科学研究有哪些类型?
Last updated: October 7, 2025
Massimiliano Grassi
Scientific research is a structured inquiry process aimed at collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data to address specific questions or problems while adhering to scientific principles for reliability, accuracy, and validity. It involves a systematic planning stage, including randomization, and is classified into various types: diagnostic and generalizing, chronological and systematic, heuristic and justificatory, universalist and specialist, theoretical and practical, along with explanatory and descriptive methodologies. Research extends beyond simple observation, requiring a disciplined approach to discover and expand knowledge within specific fields.
科学研究是一种结构化的探究过程,旨在收集、分析和解释数据,以解决特定问题或疑问,同时遵循科学原则以确保结果的可靠性、准确性和有效性。该过程包含系统性规划阶段(包括随机化设计),并可分为多种类型:诊断性研究与概括性研究、时序性研究与系统性研究、探索性研究与验证性研究、普适性研究与专项研究、理论性研究与实践性研究,以及解释性研究与描述性研究等方法体系。研究并非单纯的观察活动,而是需要通过严谨的方法在特定领域中发现并拓展知识边界。
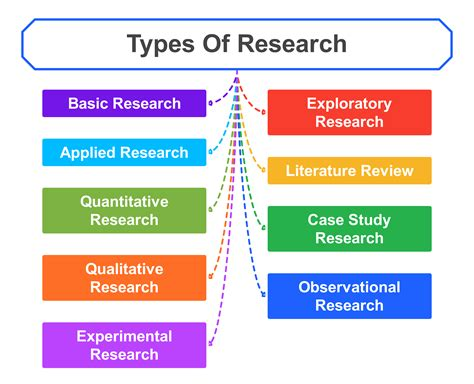
Types of scientific research are categorized based on purpose and methodology, with common classifications including experimental, quantitative, qualitative, applied, basic, mixed, and classification studies. Scientific research aims to answer, interpret, and analyze problems in various scientific domains, producing new knowledge and understanding causal relationships between phenomena.
科学研究的类型可根据研究目的和方法进行划分,常见分类包括实验研究、定量研究、定性研究、应用研究、基础研究、混合方法研究和分类研究等。科学研究致力于解答、阐释和分析各个科学领域中的问题,产出新知识并揭示现象间的因果关系。
The two broad classes of research are fundamental (or basic) and applied research, each focusing on different objectives and methodologies. The field has evolved significantly, influenced by researchers’ worldviews, leading to a diversity of approaches in accessing knowledge. Proper classification of scientific studies helps in achieving specific goals, ensuring the inquiry remains systematic and rigorous.
研究的两大主要类别为基础研究(fundamental research 或 basic research)和应用研究,两者各自侧重不同的研究目标和方法体系。受研究者世界观的影响,该领域已发生显著发展,形成了多样化的知识获取路径。对科学研究进行合理分类有助于实现特定研究目标,确保探究过程的系统性和严谨性。
Significantly, research must be planned meticulously prior to implementation, where each type serves distinct purposes and requires tailored methodologies. Historical development has shaped how researchers operate and understand scientific inquiry’s nature, ensuring adherence to structured processes that yield credible outcomes.
值得注意的是,研究在实施前必须进行细致规划,每种研究类型均具有独特用途,且需要适配的方法体系。历史发展进程塑造了研究者的工作方式及对科学探究本质的理解,确保研究遵循结构化流程以产出可信结果。
Scientific research embodies systematic, evidence-based investigation oriented toward driving innovation and enhancing comprehension of the complexities of the world, making it imperative for practitioners to be well-versed in its various methodologies and classifications.
科学研究是一种系统性、基于证据的探究活动,旨在推动创新并加深对世界复杂性的理解,因此从业者必须熟练掌握其各类方法体系和分类标准。
| Article | Description | Site |
|---|---|---|
| Types of Scientific Research 科学研究的类型 | The research is broadly classified into two main classes: 1. Fundamental or basic research and 2. Applied research. 研究大致分为两大类:1. 基础研究(Fundamental or basic research)和 2. 应用研究(Applied research)。 | innspub.net |
| What is Scientific Research and How Can it be Done? – PMC 什么是科学研究?如何开展科学研究?——PMC | by CÖ Çaparlar · 2016 · Cited by 155 — Research conducted for the purpose of contributing towards science by the systematic collection, interpretation and evaluation of data. 作者:CÖ Çaparlar · 2016年 · 被引次数:155 — 指通过系统性收集、解释和评估数据,旨在为科学发展做出贡献的研究活动。 | pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov |
| Scientific Research Definition, Classifications & Purpose 科学研究的定义、分类与目的 | Scientific research is a process used by scientists to study various phenomenon. It involves evaluating hypotheses using systematic methods of collecting, … 科学研究是科学家用于研究各类现象的过程,包括运用系统性收集方法对假设进行验证…… | study.com |
What is research?
什么是研究?
What comes to mind when you think about research? Probably a laboratory with test tubes, microscopes, and scientists wearing …
当你想到研究时,脑海中浮现的是什么?或许是一个摆放着试管、显微镜,且科学家身着……的实验室。

What Are The Types Of Descriptive Research?
描述性研究有哪些类型?
Descriptive research is a methodology aimed at systematically describing, explaining, and interpreting phenomena, populations, or situations without manipulating variables. It focuses on providing detailed understanding through various approaches, including case studies, surveys, and observational studies. This type of research is crucial for establishing baseline data, capturing trends, and informing decision-making.
描述性研究是一种旨在系统描述、阐释和解读现象、群体或情境的研究方法,不涉及变量操控。该方法通过案例研究、调查研究和观察研究等多种途径,致力于提供详细的认知,对于建立基线数据、捕捉趋势及为决策提供依据具有重要意义。
Different types of descriptive research include:
描述性研究的不同类型包括:
-
Case Reports: Commonly utilized to document detailed instances of specific cases.
病例报告(Case Reports):常用于记录特定病例的详细情况。 -
Surveys: Widely used to collect data from participants via questionnaires or interviews, providing qualitative and quantitative insights.
调查研究(Surveys):通过问卷或访谈的方式广泛收集参与者数据,可提供定性和定量层面的研究洞见。 -
Observational Studies: Focus on watching subjects in their natural environment to gather information without intervention.
观察研究(Observational Studies):侧重于在自然环境中观察研究对象,在不进行干预的情况下收集信息。
These methods help researchers identify characteristics, trends, and behaviors relevant to their field of study. Descriptive research designs are essential for understanding the distribution of diseases or other phenomena over time and location in society.
这些方法有助于研究者识别与研究领域相关的特征、趋势和行为。描述性研究设计对于理解疾病或其他现象在社会中随时间和空间的分布情况至关重要。
By not establishing cause-and-effect relationships, descriptive research descriptions primarily summarize data and patterns. While often considered quantitative, qualitative approaches can also be part of descriptive methodologies. Understanding the various types of descriptive research is vital for conducting high-quality studies and ensuring informative, actionable results.
由于不建立因果关系,描述性研究主要对数据和模式进行总结。尽管该类研究常被归为定量研究范畴,但定性方法也可成为描述性研究方法体系的一部分。理解描述性研究的各类类型,对于开展高质量研究及确保研究结果具有信息价值和可操作性至关重要。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
Why Is The Typology Of Scientific Research Important?
科学研究的类型学为何重要?
The typology of scientific research is vital for developing methodology in science. Besides the UNESCO typology, a new one is proposed, encompassing various research types, including diagnostic research. A typology refers to a set of types describing data, whether from a single sample or multiple, and may derive from theoretical models that require empirical validation. The methodology involves seven steps, starting with understanding the dataset and proceeding through reconstruction and ideal type construction.
科学研究的类型学对于科学方法体系的发展至关重要。除联合国教科文组织(UNESCO)提出的类型学外,已有学者提出一种新的类型学框架,涵盖诊断性研究等多种研究类型。类型学指一组用于描述数据(无论来自单个样本还是多个样本)的类型集合,其可能源于需要实证验证的理论模型。该方法体系包含七个步骤,从理解数据集开始,逐步推进至数据重构和理想类型构建。
This new typology aims to provide a comprehensive view of research activities and enhance decision-making. An analysis of existing typologies in religion and science reveals that they can be classified as conclusion- or concept-oriented and are expected to guide initial investigations. The impetus for refining the typology, a decade later, includes advancements in research methods and technologies. Applying this typology to scientific endeavors can foster responsible decision-making that aligns with public interests.
这种新的类型学旨在全面呈现研究活动的全貌,并提升决策质量。对宗教和科学领域现有类型学的分析表明,这些类型学可分为结论导向型和概念导向型,且有望为初步研究提供指导。十年后,研究方法和技术的进步成为完善该类型学的推动力。将此类型学应用于科学研究,有助于促进符合公共利益的负责任决策。
The paper discusses how scientific breakthroughs vary across disciplines and require distinct considerations. Classification of research activities can typically be divided into fundamental (basic) and applied research, ensuring the reliability of findings. Ultimately, this typology helps researchers formulate pertinent questions and make informed choices regarding their methodologies.
该论文探讨了不同学科间科学突破的差异及其所需的独特考量。研究活动的分类通常可分为基础研究和应用研究,以确保研究结果的可靠性。最终,这种类型学有助于研究者提出相关问题,并在方法选择上做出明智决策。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Is An Example Of Scientific Research?
科学研究的实例有哪些?
Scientific research encompasses primary methods such as lab, field, and natural experiments, alongside secondary methods like meta-analyses and systematic reviews. Laboratory experiments are the epitome of ‘scientific’ research due to their controlled conditions. Medicine delivery is a crucial area where scientists employ the scientific method to optimize the targeting of therapies in the body through experimental data collection. The scientific method itself is a systematic process where scientists observe, formulate hypotheses, and test them to explain natural phenomena.
科学研究包含实验室实验、现场实验和自然实验等初级方法,以及元分析和系统评价等次级方法。由于具备可控条件,实验室实验是“科学性”研究的典型代表。药物递送是一个关键领域,科学家通过收集实验数据,运用科学方法优化疗法在体内的靶向性。科学方法本身是一个系统性过程,科学家通过观察、提出假设并进行验证,以解释自然现象。
Read also: Reverse Engineering Marketing Quizlet: What Is It?
延伸阅读: 逆向工程营销 Quizlet:是什么?
Clinical research, a significant facet of scientific inquiry, begins with hypothesis formation, leading to more detailed investigation. Experimental research employs a scientific approach to analyze research variables, with numerous historical studies exemplifying this method. Accuracy in scientific research is upheld through meticulously calibrated instruments and controlled settings, ensuring reliable results.
临床研究是科学探究的重要组成部分,始于假设提出,进而开展更详细的调查。实验研究采用科学方法分析研究变量,众多历史研究均是该方法的实例。科学研究通过精密校准的仪器和可控环境保障准确性,以确保结果的可靠性。
While many scientific inquiries may seem detached from practical applications, their contributions to knowledge are invaluable. For instance, studying the life cycle of stars or the digestive processes of dinosaurs enriches our understanding of the universe, even when no direct applications arise. Diverse scientific domains include physical sciences such as physics and chemistry, and life sciences like biology, offering a rich landscape for exploration and discovery. Topics like gut microbiota and gene therapy represent emerging areas ripe for investigation.
尽管许多科学探究看似与实际应用脱节,但其对知识体系的贡献具有不可估量的价值。例如,对恒星生命周期或恐龙消化过程的研究,即便没有直接应用场景,也能丰富我们对宇宙的认知。多样的科学领域包括物理学、化学等物理科学,以及生物学等生命科学,为探索和发现提供了广阔空间。肠道微生物群和基因治疗等主题是亟待研究的新兴领域。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Is Scientific Research?
什么是科学研究?
Scientific research is the systematic and planned inquiry aimed at contributing to knowledge through the collection, interpretation, and evaluation of data. It is essential for advancing understanding across various fields and employs a structured approach known as the scientific method. The process begins with observation and the formulation of research questions or hypotheses, followed by the design of methodologies for experimentation. Various types of scientific research exist, categorized by their purpose, methodology, and nature of study, including both basic and applied research.
科学研究是一种系统性、有计划的探究活动,旨在通过收集、解释和评估数据为知识体系做出贡献。它对于推动各个领域的认知进步至关重要,并采用一种被称为科学方法的结构化路径。该过程始于观察和研究问题/假设的提出,随后设计实验方法。科学研究存在多种类型,可根据研究目的、方法和研究性质进行分类,包括基础研究和应用研究。
Research involves meticulous planning and a disciplined inquiry to unveil new insights about specific phenomena. The significance of scientific research lies in its credibility and its ability to produce reliable results through systematic processes, emphasizing the importance of randomization in study planning to mitigate bias. The scientific method is iterative, comprising steps of observation, experimentation, and analysis, ultimately aimed at expanding knowledge that may not have been documented previously.
研究需要细致的规划和严谨的探究,以揭示特定现象的新见解。科学研究的意义在于其可信度,以及通过系统性过程产出可靠结果的能力,这一过程强调在研究规划中采用随机化设计以减少偏倚。科学方法是一个迭代过程,包括观察、实验和分析等步骤,最终旨在拓展此前未被记录的知识领域。
In different scientific disciplines, the peer review process is crucial to validate findings and ensure objectivity. Researchers must navigate the complexities of the inquiry process, as scientific research can often lead to unexpected results or require shifts in focus. The role of a researcher is pivotal, as they are the agents conducting the studies to push the boundaries of what is known. Overall, scientific research remains a cornerstone of understanding the natural world, facilitating discoveries that inform further investigation and application across various scientific realms.
在不同的科学学科中,同行评审过程对于验证研究结果和确保客观性至关重要。研究者必须应对探究过程中的复杂性,因为科学研究往往会产生意外结果或需要调整研究重点。研究者的角色至关重要,他们是开展研究的主体,致力于突破现有知识的边界。总体而言,科学研究仍是理解自然世界的基石,其推动的发现为各个科学领域的进一步探究和应用提供了依据。

(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Is Meant By Scientific Research?
科学研究的含义是什么?
Scientific research is a systematic process where scientists study natural phenomena through methods of data collection, analysis, and interpretation. It is a creative endeavor aimed at testing ideas, leading to new insights and knowledge. This research is characterized by its planned nature, allowing researchers to systematically gather, evaluate, and interpret data. The investigation can involve various methodologies, such as empirical studies, experiments, surveys, and theoretical analyses, across diverse academic, scientific, and professional fields.
科学研究是科学家通过数据收集、分析和解释等方法研究自然现象的系统性过程。它是一项创造性活动,旨在验证观点,进而产生新的见解和知识。该类研究具有计划性特征,使研究者能够系统地收集、评估和解释数据。探究过程可采用多种方法,如实证研究、实验、调查和理论分析等,应用于不同的学术、科学和专业领域。
Through observation and experimentation, scientific research helps generate new knowledge or validate existing theories, often distinguishing between inductive research, beneficial in areas with limited theories, and deductive research, advantageous when multiple theories exist. In science, the definition of research is more rigorous than in everyday conversation, emphasizing the scientific method to formulate hypotheses and yield analyzable outcomes.
通过观察和实验,科学研究有助于产生新知识或验证现有理论,其常区分归纳研究和演绎研究:归纳研究在理论基础薄弱的领域具有优势,而演绎研究在存在多种理论的情况下更为适用。在科学领域,研究的定义比日常语境中的定义更为严谨,强调运用科学方法提出假设并产出可分析的结果。
Each study built on predictive reasoning, grounded in scientific evidence and logical steps, aims to uncover future knowledge. Scientific research thus represents a structured search for valuable information, contributing significantly to the scientific body through ethical study designs. Ultimately, it is a fundamental approach to understanding and expanding knowledge across various disciplines.
每项研究均基于预测性推理,以科学证据和逻辑步骤为基础,旨在揭示未来的知识。因此,科学研究是一种结构化的有价值信息探索过程,通过符合伦理的研究设计为科学体系做出重要贡献。最终,它是跨学科理解和拓展知识的基本途径。

(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Is The Main Characteristic Of Scientific Research?
科学研究的主要特征是什么?
The main characteristic of scientific research is empirical research, which relies on observable and measurable evidence, directly engaging with the material world rather than theoretical aspects. Effective scientific research requires prior planning and the establishment of clear goals. It is a voyage of discovery, generating new knowledge and insights that can lead to innovative materials, devices, products, and processes. Key qualities of good scientific research include objectivity, verifiability, ethical neutrality, and a systematic approach.
科学研究的主要特征是实证性,其依赖可观察、可测量的证据,直接与物质世界互动而非局限于理论层面。有效的科学研究需要预先规划并确立明确目标,它是一场探索之旅,能够产生新的知识和见解,进而催生创新材料、设备、产品及工艺。优质科学研究的关键特质包括客观性、可验证性、伦理中立性和系统性方法。
Research must adhere to a structured process to collect, analyze, and interpret data, answering specific questions or solving problems. Logical processes underlie research, relying on clear evidence rather than hearsay, with findings needing to be reliable, consistent, and accurate. Empirical observation is central, emphasizing objective evaluations of the natural world. Research practices follow an orderly and sequential procedure aimed at producing valid results.
研究必须遵循结构化流程来收集、分析和解释数据,以解答特定问题或解决实际难题。研究以逻辑过程为基础,依赖明确证据而非传闻,其结果需具备可靠性、一致性和准确性。实证观察是核心环节,强调对自然世界的客观评估。研究实践遵循有序且连贯的步骤,旨在产出有效结果。
The foundation of good research includes four key qualities: systematic, logical, empirical, and replicable. Ethical neutrality is also a significant component of credible scientific findings. A comprehensive list of references is crucial in scientific publications to substantiate results and clarify sources. Overall, scientific research’s primary characteristic is its empirical nature, ensuring that conclusions and insights are grounded in direct observation and objective analysis of evidence.
优质研究的基础包含四项关键特质:系统性、逻辑性、实证性和可重复性。伦理中立性也是可信科学发现的重要组成部分。科学出版物中,详尽的参考文献列表至关重要,可用于佐证结果并明确信息来源。总体而言,科学研究的核心特征在于其实证性,确保结论和见解均基于对证据的直接观察和客观分析。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Are The Basic Principles Of Scientific Research?
科学研究的基本原则有哪些?
Among the basic principles guiding scientists are respect for knowledge integrity, collegiality, honesty, objectivity, and openness. These principles underpin the scientific method, which involves formulating hypotheses, designing experiments, and collecting data. Scientific research has liberated humanity from ignorance, superstition, and illness through the accumulation of knowledge. The paper posits that scientific research is organized by two key principles that influence all types of inquiry.
指导科学家的基本原则包括尊重知识完整性、学术协作、诚信、客观性和开放性。这些原则是科学方法的基石,该方法涵盖提出假设、设计实验和收集数据等环节。通过知识积累,科学研究将人类从无知、迷信和疾病中解放出来。该论文提出,科学研究由两项关键原则主导,这些原则影响着各类探究活动。
Although the discussion is centered on clinical research, many principles are relevant to basic biomedical research and other fields. Core principles include research objectives, systematic processes, and a commitment to innovation. Scientific research aims to improve humanity by addressing problems methodically, requiring inquisitiveness, clear goal articulation, and data analysis. These principles manifest in two dimensions: the creativity and expertise of researchers and generalized guiding principles for inquiry.
尽管讨论聚焦于临床研究,但许多原则同样适用于基础生物医学研究及其他领域。核心原则包括研究目标、系统性流程和创新承诺。科学研究旨在通过有条理地解决问题来改善人类生活,这需要好奇心、明确的目标表述和数据分析能力。这些原则体现在两个维度:研究者的创造力与专业知识,以及探究活动的通用指导原则。
-
Six principles of scientific inquiry are outlined:
文中概述了六项科学探究原则:(1) Pose significant, empirically investigated questions;
提出具有重要意义且可实证研究的问题;(2) Link research to theory;
将研究与理论相结合;(3) Utilize various methods.
运用多种方法。
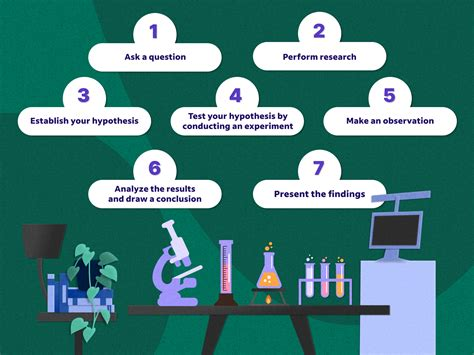
Foundational principles include integrity, diligence, and transparency. Effective research is built on a stated purpose, following key steps: asking questions, conducting background research, formulating and testing hypotheses, and analyzing data. Rigorous methodology is essential to achieve reliable and valid results in scientific research.
基础原则包括诚信、勤勉和透明度。有效的研究建立在明确的目的之上,遵循以下关键步骤:提出问题、开展背景研究、提出并验证假设、分析数据。严谨的方法体系对于科学研究获得可靠且有效的结果至关重要。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Are The Different Types Of Scientific Research?
科学研究有哪些不同类型?
The author presents a new typology of scientific research alongside UNESCO’s classification, identifying types such as diagnostic and generalizing, chronological and systematic, heuristic and justificatory, universalist and specialist, theoretical and practical, explanatory and descriptive. Scientific research is categorized by purpose, methodology, and nature, primarily divided into fundamental (basic) and applied research. Basic research aims to understand underlying principles, while applied research addresses practical applications.
作者在联合国教科文组织(UNESCO)分类体系的基础上,提出了一种新的科学研究类型学,明确了诊断性研究与概括性研究、时序性研究与系统性研究、探索性研究与验证性研究、普适性研究与专项研究、理论性研究与实践性研究、解释性研究与描述性研究等类型。科学研究可根据研究目的、方法和性质进行分类,主要分为基础研究和应用研究:基础研究旨在理解底层原理,而应用研究聚焦实际应用问题。
Research can also be classified into different types, including quantitative, qualitative, mixed, and explanatory research, each with distinct strengths and applications. Specific study types include randomized controlled trials (RCTs), cohort studies, case-control studies, and qualitative studies. The classification often hinges on the methodology used and research objectives, leading to broader categorizations such as exploratory, descriptive, and explanatory types.
研究还可分为定量研究、定性研究、混合方法研究和解释性研究等不同类型,每种类型均具有独特优势和应用场景。具体研究类型包括随机对照试验(RCTs)、队列研究、病例对照研究和定性研究等。分类通常取决于所采用的方法和研究目标,进而形成探索性研究、描述性研究和解释性研究等更广泛的分类。
Other classifications include primary vs. secondary research and types of data used (quantitative vs. qualitative). Thus, scientific research encompasses a vast array of topics across disciplines like science, business, psychology, and politics, with various outlined methodologies and approaches tailored to achieve specific research goals. Each research type and method contributes to the development of knowledge and solutions within its field, underpinning a structured process for exploring and analyzing diverse subjects.
其他分类方式包括初级研究与次级研究,以及所用数据类型(定量数据与定性数据)。因此,科学研究涵盖科学、商业、心理学和政治学等多个学科的广泛主题,拥有多种明确的方法和路径,这些方法和路径均为实现特定研究目标而量身定制。每种研究类型和方法都为其所在领域的知识发展和问题解决做出贡献,为探索和分析各类主题提供了结构化流程。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
How Do You Identify Scientific Research?
如何识别科学研究?
Research studies are typically found in peer-reviewed journals, characterized by sections like Literature Review, Method, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Articles solely reviewing other studies without presenting new findings are not classified as research studies. To differentiate a research study from other articles, one must assess whether it is published in a credible journal. The research process involves five key steps: formulating a focused question, planning the search, executing the search, tracking and storing results, and staying updated with new publications.
研究论文通常发表在同行评审期刊上,其特征是包含文献综述、研究方法、研究结果、讨论和结论等章节。仅对其他研究进行综述而未呈现新发现的文章不属于研究论文。要区分研究论文与其他文章,需评估其是否发表在可信期刊上。研究过程包含五个关键步骤:提出聚焦问题、规划检索方案、执行检索、跟踪和存储结果、及时关注新发表文献。
Recognizing the sections of a primary research study, which may use different terminology across disciplines, is essential. Online databases, including Google Scholar, facilitate the search for scholarly sources, particularly when searching by title or author. Although non-research articles can also employ similar search techniques, the focus here is on traditional research literature. Narrowing down the research problem and reviewing existing literature helps clarify the research approach.
识别原始研究论文的各个章节至关重要(不同学科可能使用不同术语)。包括 Google Scholar 在内的在线数据库为学术资源检索提供了便利,尤其适用于按标题或作者检索的场景。尽管非研究类文章也可能采用类似的检索技巧,但此处重点关注传统研究文献。缩小研究问题范围并综述现有文献,有助于明确研究路径。
Each research study should detail its methodology, indicating whether it is qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods. Scholarly, peer-reviewed articles should adhere to numerous characteristics, ensuring reliability and credibility by exploring the qualifications of the authors and the potential for conflicts of interest. Key steps in the scientific method include asking a question, conducting background research, formulating a hypothesis, and testing this through experiments. Ultimately, scientific inquiry relies on creating testable hypotheses, statistical analysis, and meticulous documentation of findings.
每项研究都应详细说明其方法体系,明确其属于定性研究、定量研究还是混合方法研究。学术性、经同行评审的文章需符合多项特征,通过考察作者资质和潜在利益冲突来确保可靠性和可信度。科学方法的关键步骤包括提出问题、开展背景研究、提出假设、通过实验验证假设。最终,科学探究依赖于构建可检验的假设、进行统计分析以及对研究结果进行细致记录。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Is The Primary Goal Of Scientific Research?
科学研究的主要目标是什么?
The primary aim of scientific research is to uncover laws and develop theories that explain natural or social phenomena, thereby constructing scientific knowledge. The goals of scientific social research, specifically, are to answer questions and acquire new knowledge, categorized into four objectives: description, prediction, explanation, and application. Researchers generally agree that these elements are crucial for advancing understanding within any field of inquiry.
科学研究的主要目标是揭示规律并构建解释自然或社会现象的理论,进而形成科学知识体系。具体而言,社会科学研究的目标是解答问题并获取新知识,可分为四个维度:描述、预测、解释和应用。研究者普遍认为,这些要素对于推动任何探究领域的认知进步都至关重要。
The ultimate objective of research is to enhance the existing body of knowledge and inform decision-making processes across academic, scientific, and professional realms. Scientific research is vital as it generates theories that elucidate observable events through hypothesis testing. The process should be systematically planned, focusing on classification and description at the planning stage. The foundational goal of science, through careful observation, is to describe phenomena accurately, aligning them with objective reality.
研究的最终目标是拓展现有知识体系,并为学术、科学和专业领域的决策过程提供依据。科学研究的重要性在于,它通过假设检验生成能够阐释可观察事件的理论。研究过程应进行系统性规划,在规划阶段重点关注分类和描述工作。通过细致观察准确描述现象,使其与客观现实保持一致,是科学研究的基础性目标。
Scientific inquiry strives for true knowledge, leading to a collective understanding of verifiable facts. This pursuit not only contributes to societal advancement but also allows individuals to improve their social status and livelihood, similar to other human activities. Moreover, it fosters a growing corpus of knowledge about behaviors and their underlying reasons. The scientific method, employed since the 17th century, serves as an empirical approach to acquiring knowledge, illustrating the necessity of describing and predicting behaviors within scientific research. Overall, scientific research is a structured method for expanding knowledge and comprehensively understanding various phenomena.
科学探究致力于追求真实知识,形成对可验证事实的集体认知。这种追求不仅推动社会进步,还能像其他人类活动一样,帮助个人提升社会地位和生活水平。此外,它还促进了关于行为及其深层原因的知识体系不断发展。自 17 世纪以来,科学方法一直作为获取知识的实证路径被广泛应用,这也体现了科学研究中描述和预测行为的必要性。总体而言,科学研究是一种拓展知识、全面理解各类现象的结构化方法。
(图片来源:Pixabay.com)
What Are The 5 Main Types Of Scientific Study?
科学研究的五大主要类型是什么?
There are various types of scientific research, primarily categorized into quantitative, qualitative, applied, and fundamental research. The five main types of studies include case studies, correlational studies, longitudinal studies, experimental studies, and clinical trial studies. Scientific research aims to address, explain, and evaluate issues across numerous scientific domains. It can be challenging to classify individual studies, given that the three main areas of research encompass basic medical research, clinical research, and epidemiological research.
科学研究存在多种类型,主要分为定量研究、定性研究、应用研究和基础研究。五大主要研究类型包括案例研究、相关研究、纵向研究、实验研究和临床试验研究。科学研究旨在解决、解释和评估众多科学领域中的问题。由于研究的三大主要领域包括基础医学研究、临床研究和流行病学研究,对单个研究进行分类可能具有一定挑战性。
The article outlines major study types, which include randomized controlled trials (RCTs), cohort studies, case-control studies, and qualitative studies, along with meta-analysis and systematic reviews. Research types can further be divided into levels, including pure/basic research, applied research, action research, evaluation research, and interdisciplinary research. Key categories of research methods consist of experimental, observational, descriptive, correlational, qualitative, and quantitative research. This overview provides a foundational understanding of various study types and highlights their respective advantages and disadvantages.
该文章概述了主要研究类型,包括随机对照试验(RCTs)、队列研究、病例对照研究、定性研究,以及元分析和系统评价。研究类型还可进一步分为不同层级,包括纯基础研究、应用研究、行动研究、评估研究和跨学科研究。研究方法的主要类别包括实验研究、观察研究、描述性研究、相关研究、定性研究和定量研究。本概述提供了对各类研究类型的基础性认知,并强调了它们各自的优势和劣势。
Six Key Classifications Of Scientific Research: A Comprehensive Guide
科学研究的六大核心分类:综合指南
Written by MedLexis Team
Medically Reviewed by Dr. Hayder Mazin
医学审核:海德尔·马津(Hayder Mazin)博士
MBChB(医学学士学位)
Last Update: 18/10/2025
Accurate medical content relies on a precise understanding of the classifications used in scientific research. For freelance medical writers, researchers, and health publishers, transforming complex scientific data into accessible, authoritative communication requires more than summarizing findings—it demands evaluating the quality of the source.
准确的医学内容依赖于对科学研究中所用分类的精准理解。对于自由医学撰稿人、研究者和健康领域出版商而言,将复杂的科学数据转化为易懂且权威的内容,不仅需要总结研究结果,还需对信息来源的质量进行评估。
Misinterpreting a study’s design, scope, or rigor can lead to flawed conclusions and compromise your professional credibility. To achieve precision in writing, you must first master the taxonomy of scientific evidence.
误解研究的设计、范围或严谨性可能导致有缺陷的结论,并损害专业可信度。要实现写作的精准性,首先必须掌握科学证据的分类体系。
This definitive MedLexis guide uses six complementary classification axes to explain how research studies are categorized—not to imply six mutually exclusive types. Understanding these axes empowers you to:
本份 MedLexis 权威指南通过六个互补的分类维度解释研究的分类方式——并非指六种相互排斥的类型。理解这些维度将使你能够:
-
Evaluate Credibility: Determine a study’s intrinsic strength and limitations.
评估可信度:判断一项研究的内在优势和局限性。 -
Contextualize Findings: Position individual results accurately within the broader scientific context.
情境化呈现结果:将单个研究结果准确置于更广泛的科学背景中。 -
Enhance Content Authority: Ground your articles and educational materials in appropriate evidence.
提升内容权威性:使文章和教育材料以恰当的证据为支撑。
How to Use This Guide
**本指南的使用方法### How to Use This Guide
本指南的使用方法
Writers should prioritize the Level of Evidence (Axis 6) and Methodology (Axis 2) sections, as these most directly affect the strength of claims you can make in your content.
撰稿人应优先关注证据级别(第6维度) 和研究方法(第2维度) 部分,因为这两个维度最直接影响你在内容中所能提出主张的可信度。
Quick Taxonomy Overview / 分类体系快速概览
| Axis | Focus | Key Question Answered |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Purpose 研究目的 | The study’s aim or goal 研究的宗旨或目标 | Why is the research being conducted? 开展这项研究的原因是什么? |
| 2. Methodology 研究方法 | The nature of the data 数据的性质 | How is data collected and analyzed (numeric vs. narrative)? 数据如何(以数值型或叙述型)收集和分析? |
| 3. Application 应用场景 | The setting of the research 研究的实施环境 | Where is the research applied (lab, clinic, or population)? 研究应用于何处(实验室、临床场景或人群层面)? |
| 4. Temporal Design 时间设计 | The timing of data collection 数据收集的时间节点 | When is the data gathered relative to the outcome? 数据相对于研究结果的收集时机是什么? |
| 5. Data Source 数据来源 | The data’s origin 数据的产生主体 | Who generated the data (original collection or synthesis)? 数据由谁生成(原始收集或二次整合)? |
| 6. Level of Evidence 证据级别 | The rigor of the design 研究设计的严谨程度 | How strong is the evidence for clinical decision-making? 该证据对临床决策的支持力度如何? |
1. Classifications Of Scientific Research By Purpose
按研究目的划分的科学研究类型
Every study begins with a question that determines its method and scope. The purpose classification follows a natural continuum from initial knowledge generation to making actionable predictions.
每项研究均始于一个决定其方法和范围的问题。研究目的分类遵循从初始知识生成到形成可执行预测的自然演进逻辑。
Exploratory, Descriptive, and Explanatory Research
探索性研究、描述性研究与解释性研究
These three types form the essential sequence for building comprehensive scientific knowledge.
这三种类型构成了构建完整科学知识体系的核心序列。
-
Exploratory Research: Investigates poorly understood or undefined problems. It aims to establish context or identify key variables. Content Implication: Findings are suggestive, not conclusive, and are used to frame future research.
探索性研究(Exploratory Research):针对理解不充分或未明确界定的问题展开探究,旨在建立研究背景或识别关键变量。内容应用启示:研究结果具有提示性而非结论性,常用于构建未来研究的框架。 -
Descriptive Research: Accurately portrays the characteristics of a population or phenomenon (e.g., prevalence rates). Content Implication: Provides precise figures for background information or disease burden.
描述性研究(Descriptive Research):精准描绘群体或现象的特征(如患病率)。内容应用启示:为背景信息或疾病负担分析提供精确数据支撑。 -
Explanatory (Analytical) Research: Seeks to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables. Content Implication: This type of study provides definitive proof of association, often forming the basis for clinical recommendations.
解释性研究(Explanatory Research,又称分析性研究):旨在揭示变量间的因果关系。内容应用启示:此类研究为变量关联提供确定性证据,常作为临床建议的核心依据。
Predictive and Evaluative Research
预测性研究与评估性研究
-
Predictive Research: Develops models to forecast the likelihood of a future event (e.g., recurrence risk). Content Implication: Provides quantifiable data on probability, informing content on prognosis and shared decision-making.
预测性研究(Predictive Research):构建模型以预测未来事件发生的概率(如复发风险)。内容应用启示:提供可量化的概率数据,为预后相关内容创作和共同决策提供参考。 -
Evaluative Research: Systematically assesses the effectiveness, merit, or cost-efficiency of specific interventions, programs, or policies. Content Implication: Crucial for writing about quality improvement, healthcare policy, and real-world system effectiveness.
评估性研究(Evaluative Research):系统评估特定干预措施、项目或政策的有效性、价值或成本效益。内容应用启示:对医疗质量改进、医疗政策及真实世界系统有效性相关内容的创作至关重要。
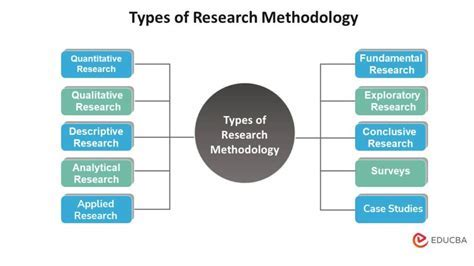
2. Classifications Of Scientific Research By Methodology: Quantitative Vs. Qualitative
按研究方法划分的科学研究类型:定量研究与定性研究
This fundamental axis focuses on how data is collected and the nature of that data—whether it is numerical and measurable or descriptive and experiential.
这一核心维度聚焦于数据的收集方式及其本质属性——数据是数值化且可测量的,还是描述性且基于经验的。
Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Methods Research
定量研究、定性研究与混合方法研究
Quantitative Research
定量研究(Quantitative Research)
Involves the systematic empirical investigation of phenomena using statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It seeks to measure variables and generalize results.
采用统计、数学或计算技术对现象进行系统性实证探究,旨在测量变量并推广研究结果。
-
Data Type: Numbers, measurements, and statistics (e.g., incidence rates, ( p )-values).
数据类型:数值、测量结果及统计量(如发病率、( p ) 值)。 -
Content Implication: The bedrock for establishing statistical significance and supporting claims of efficacy.
内容应用启示:是确立统计显著性和支持有效性主张的核心基础。
Qualitative Research
定性研究(Qualitative Research)
A method for exploring and understanding the meaning, experiences, and perceptions individuals or groups ascribe to a problem. It seeks depth over breadth.
一种探索和理解个人或群体对某一问题赋予的意义、体验及认知的研究方法,追求研究深度而非广度。
-
Data Type: Text, narrative accounts, interview transcripts, and observations.
数据类型:文本、叙述性记录、访谈转录稿及观察笔记。 -
Content Implication: Essential for developing empathetic, patient-centered content, understanding health literacy, and explaining the “why” behind health behaviors.
内容应用启示:对创作富有同理心、以患者为中心的内容,理解健康素养,以及解释健康行为背后的“原因”具有关键作用。
Mixed Methods Research
混合方法研究(Mixed Methods Research)
Combines numeric measures with qualitative insights to answer both “what” (quantitative) and “why” (qualitative) in a single study.
在一项研究中整合数值测量与定性洞见,同时解答“是什么”(定量层面)和“为什么”(定性层面)的问题。
- Value in Content: Provides a balanced, holistic perspective by integrating statistical generalizability with the depth of human experience.
内容应用价值:通过融合统计推广性与人类体验的深度,提供均衡且全面的研究视角。
Addressing Bias and Confounding
偏倚与混杂因素的处理
All methodological designs must address bias (systematic error) and confounding (a variable that influences both the exposure and the outcome). High-quality studies mitigate this through:
所有研究方法设计均需处理偏倚(系统性误差)和混杂因素(同时影响暴露因素与结局的变量)。高质量研究通过以下方式降低其影响:
-
Randomization: Used in RCTs to distribute unknown confounders evenly.
随机化(Randomization):在随机对照试验(RCTs)中应用,以均衡分配未知混杂因素。 -
Adjustment/Stratification: Statistical techniques used in observational studies to account for known confounders (e.g., adjusting for age or smoking history).
调整/分层(Adjustment/Stratification):观察性研究中采用的统计技术,用于控制已知混杂因素(如按年龄或吸烟史进行调整)。
3. Classifications Of Scientific Research By Application And Domain
按应用场景与领域划分的科学研究类型
This axis categorizes research based on where the study takes place and how its findings are intended to be utilized, moving from theory to implementation.
该维度根据研究的实施场所及研究结果的应用方式进行分类,呈现从理论到实践的转化路径。
Fundamental, Applied, and Translational Research
基础研究、应用研究与转化研究
-
Fundamental (Basic): Aims to discover new knowledge (e.g., cellular pathways) without a specific, immediate application. It forms the scientific foundation cited when discussing biological mechanisms.
基础研究(Fundamental Research,又称 Basic Research):旨在探索新知识(如细胞通路),无特定即时应用目标,是讨论生物学机制时引用的科学基础。 -
Applied Research: Designed to solve a specific, practical problem (e.g., optimizing drug delivery). Provides data supporting the practical utility and efficacy of commercial products.
应用研究(Applied Research):旨在解决特定实际问题(如优化药物递送系统),为商业产品的实际实用性和有效性提供数据支持。 -
Translational Research: The “bench-to-bedside” bridge that moves basic science into clinical applications and then into public health practice. Essential for content covering medical innovation and implementation.
转化研究(Translational Research):作为“从实验室到病床”的桥梁,将基础科学成果转化为临床应用,进而推广至公共卫生实践,对医疗创新与实施相关内容创作至关重要。
Clinical, Epidemiological, and Health Systems Research
临床研究、流行病学研究与卫生系统研究
-
Clinical Research: Studies conducted on human participants to understand, diagnose, treat, or prevent disease (e.g., drug trials). The most frequently cited source for claims about treatment safety and efficacy.
临床研究(Clinical Research):在人类受试者中开展的研究,旨在理解、诊断、治疗或预防疾病(如药物试验),是治疗安全性和有效性主张最常引用的证据来源。 -
Epidemiological Research: The study of the distribution and determinants of health-related states in specified populations. Provides essential data for public health campaigns, risk assessment, and understanding disease prevalence.
流行病学研究(Epidemiological Research):研究特定人群中与健康相关状态的分布及决定因素,为公共卫生宣传、风险评估及疾病患病率理解提供核心数据。 -
Health Systems Research: Focuses on the organization, financing, and delivery of healthcare services. Critical for topics related to healthcare policy, quality improvement, and client-centric delivery of care.
卫生系统研究(Health Systems Research):聚焦医疗服务的组织、融资与提供,对医疗政策、质量改进及以服务对象为中心的医疗服务提供等相关主题至关重要。
4. Classifications Of Scientific Research By Temporal Design
按时间设计划分的科学研究类型
The temporal design defines when data is gathered relative to the exposure or outcome, which is critical for inferring causality.
时间设计明确了数据相对于暴露因素或结局的收集时机,这对推断因果关系具有关键意义。
Cross-Sectional vs. Longitudinal Studies
横断面研究与纵向研究
-
Cross-Sectional Studies: Observes a population at a single point in time (“snapshot”). Measures cause and effect simultaneously, thus suggesting association but not definitive causation.
横断面研究(Cross-Sectional Studies):在单一时间点对群体进行观察(“快照式”研究),同时测量暴露因素与结局,仅能提示关联而非确定性因果关系。 -
Longitudinal Studies: Collect data repeatedly from the same individuals over an extended period. Crucial for tracking disease progression and establishing sequence.
纵向研究(Longitudinal Studies):在较长时期内对同一批个体重复收集数据,对追踪疾病进展和确立事件发生顺序至关重要。
Prospective vs. Retrospective Studies
前瞻性研究与回顾性研究
-
Prospective Studies: The researcher begins in the present and follows the cohort forward in time to observe the outcome. This design minimizes temporal ambiguity, as exposure precedes outcome, making it ideal for establishing cause-and-effect.
前瞻性研究(Prospective Studies):研究者从当前时点开始,对队列进行长期随访以观察结局,由于暴露因素先于结局发生,该设计降低了时间模糊性,是确立因果关系的理想选择。 -
Retrospective Studies: The researcher looks backward in time, starting with an outcome (cases) and investigating past exposures (e.g., reviewing medical records). This design is more vulnerable to recall bias (inaccurate memory) and selection bias.
回顾性研究(Retrospective Studies):研究者回顾过去,从已发生的结局(病例)出发,追溯既往暴露因素(如查阅病历),该设计更易受回忆偏倚(记忆不准确)和选择偏倚影响。
5. Classification By Data Source
按数据来源划分的科学研究类型
This axis distinguishes between research that generates new data and research that synthesizes existing findings.
该维度区分生成原始数据的研究与整合现有研究结果的研究。
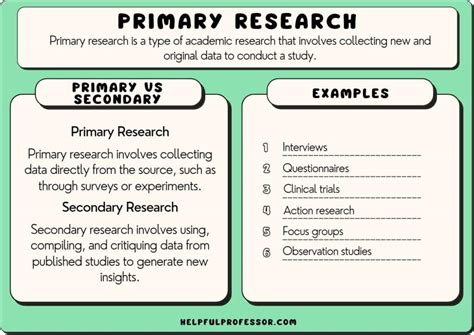
Primary Research:
初级研究(Primary Research):
The collection of original data directly from the source (e.g., a new clinical trial, laboratory experiment, or patient survey). Citing primary research means referencing the original discovery or testing of a hypothesis.
直接从来源处收集原始数据的研究(如一项新的临床试验、实验室实验或患者调查),引用初级研究即参考对假设的原始发现或验证过程。
Secondary Research (Evidence Synthesis):
次级研究(Secondary Research,又称证据整合研究):
Gathering, summarizing, synthesizing, and interpreting data collected by others. While not generating new raw data, high-quality secondary research (Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses) often provides the highest level of evidence for clinical decision-making.
收集、总结、整合并解读他人已收集的数据,尽管不生成新的原始数据,但高质量的次级研究(系统评价和元分析)通常为临床决策提供最高级别的证据支持。
6. Classification By Level Of Evidence (The EBM Pyramid)
按证据级别划分的科学研究类型(循证医学金字塔)
Based on Evidence-Based Medicine (EBM) principles, studies are ranked by their ability to minimize bias and establish a causal link. This is the most crucial axis for determining the strength of your claims.
基于循证医学(EBM)原则,根据研究降低偏倚和确立因果关系的能力对其进行分级,该维度是判断主张可信度的最核心依据。
Hierarchy of Evidence: From Expert Opinion to Systematic Reviews
证据层级:从专家意见到系统评价
| Level | Research Type | Reporting Guideline (Examples) | Content Authority |
|---|---|---|---|
| Level I I 级 | Systematic Reviews & Meta-Analyses 系统评价与元分析 | PRISMA PRISMA 规范 | Highest Authority. Represents the consensus of the strongest evidence. 权威性最高,代表最强证据的共识性结论。 |
| Level II II 级 | Randomized Controlled Trials (RCTs) 随机对照试验(RCTs) | CONSORT CONSORT 规范 | High Authority. Strongest single-study design for proving efficacy under controlled conditions. 权威性高,在受控条件下证明有效性的最强单个研究设计。 |
| Level III III 级 | Observational Analytic Studies 观察性分析研究 | STROBE STROBE 规范 | Moderate Authority. Suggests correlation, identifies risk factors, but cannot definitively prove causation. 权威性中等,提示变量关联、识别风险因素,但无法明确证明因果关系。 |
| Level IV IV 级 | Descriptive Studies 描述性研究 | CARE (Case Reports) CARE 规范(病例报告) | Lower Authority. Useful for generating hypotheses or defining a problem. 权威性较低,适用于提出假设或界定研究问题。 |
| Level V V 级 | Expert Opinion & Theoretical Research 专家意见与理论研究 | N/A 无 | Lowest Authority. Expert opinion should be cited only when higher-level evidence is unavailable, and always identified as consensus rather than primary data. 权威性最低,仅当缺乏更高级别证据时方可引用专家意见,且需明确标注为共识性内容而非原始数据。 |
Nuance on the Gold Standard: While RCTs are the strongest design for testing drug efficacy, they may not be ethical or feasible for all questions (e.g., studying harm). For these, high-quality observational studies (Level III) or pragmatic real-world evidence trials are essential.
金标准的细微考量:尽管随机对照试验(RCTs)是测试药物有效性的最强设计,但并非所有研究问题都适合采用该设计(如伤害相关研究),因其可能存在伦理争议或可行性限制。对于此类问题,高质量的观察性研究(III 级证据)或务实性真实世界证据试验至关重要。
Ethics, Reporting, And Reproducibility
伦理、报告规范与可重复性
For professional medical writing, methodological rigor extends beyond design to ethics and transparency. Every study you cite should adhere to the following principles:
在专业医学写作中,方法学严谨性不仅体现在研究设计上,还延伸至伦理规范与透明度。你引用的每项研究均应遵循以下原则:
-
Ethical Approval & Informed Consent: All human research must demonstrate institutional ethical oversight and patient consent.
伦理审批与知情同意:所有涉及人类受试者的研究均需提供机构伦理审查证明及受试者知情同意文件。 -
Pre-registration: Clinical trials must be registered (e.g., on ClinicalTrials.gov) to prevent outcome-switching and publication bias.
研究预注册:临床试验必须进行注册(如在 ClinicalTrials.gov 平台),以避免结局指标替换和发表偏倚。 -
Reproducibility: The study design and data must be sufficiently transparent (open data/code) to allow other researchers to verify the findings.
可重复性:研究设计和数据需具备充分透明度(开放数据/代码),确保其他研究者能够验证研究结果。
Practical Checklist For Writers
撰稿人实用核查清单
Use this checklist when evaluating a source for your content:
评估内容信息来源时,可使用以下核查清单:
-
Identify the Purpose: Is it exploratory (suggestive) or explanatory (causal)?
明确研究目的:该研究属于探索性(提示性)研究还是解释性(因果性)研究? -
Determine the Methodology: Is it Quantitative (numbers/statistics) or Qualitative (experience/narrative)?
确定研究方法:该研究属于定量研究(基于数值/统计)还是定性研究(基于体验/叙述)? -
Check the Temporal Design: Is it Prospective (high causal strength) or Retrospective (vulnerable to bias)?
核查时间设计:该研究属于前瞻性研究(因果推断力度强)还是回顾性研究(易受偏倚影响)? -
Confirm the Evidence Level: What is the highest level of evidence available for this claim (Level I/II is best)?
确认证据级别:支持该主张的最高证据级别是什么(I/II 级证据最优)? -
Look for Reporting Guidelines: Does the paper mention adhering to CONSORT (for RCTs) or PRISMA (for reviews)?
查找报告规范说明:论文是否提及遵循相关报告规范(如 RCT 研究的 CONSORT 规范、系统评价的 PRISMA 规范)? -
Assess Limitations: Does the author discuss potential bias (selection, recall, confounding)? Acknowledging limitations increases the paper’s credibility.
评估研究局限性:作者是否讨论了潜在偏倚(选择偏倚、回忆偏倚、混杂偏倚)?主动承认局限性可提升论文可信度。
Precision In Practice: Conclusion
实践精准性:结论
Mastering these six classifications is the hallmark of an elite scientific communicator. This knowledge allows you to ensure your content is not just engaging but rigorously scientifically accurate. The ability to classify research correctly ensures you write with conviction where evidence is strong (Level I/II) and with appropriate caution where evidence is limited.
掌握这六大分类是顶尖科学传播者的标志性能力。这些知识不仅能让你的内容更具吸引力,还能确保其具备严谨的科学准确性。正确分类研究的能力,能让你在证据充分(I/II 级)时坚定地阐述观点,在证据有限时保持恰当的谨慎态度。
Elevate Your Content Accuracy with MedLexis
借助 MedLexis 提升内容准确性
Your commitment to using high-quality evidence is the foundation of your professional success. At MedLexis, we specialize in ensuring that this foundation is unshakable through meticulous scientific editing and rigorous content creation.
对高质量证据的坚守是你职业成功的基石。MedLexis 专注于通过细致的科学编辑和严谨的内容创作,确保这一基石坚不可摧。
Collaborate with MedLexis to ensure your research-based content meets the highest standards of accuracy and evidence reporting.
与 MedLexis 合作,确保你的研究类内容达到准确性和证据报告的最高标准。
Scientific Research – Types, Purpose and Guide
科学研究——类型、目的与指南
March 26, 2024
by Muhammad Hassan
Scientific research is a systematic investigation aimed at acquiring new knowledge, validating existing knowledge, or addressing specific questions through rigorous methodologies. It serves as the backbone of progress across disciplines, enabling advancements in medicine, technology, social sciences, and other fields. This article explores the definition, types, purpose, and essential steps involved in conducting scientific research.
科学研究是一种系统性探究活动,旨在通过严谨的方法体系获取新知识、验证现有知识或解决特定问题。它是跨学科进步的核心支柱,推动医学、技术、社会科学等多个领域的发展。本文将探讨科学研究的定义、类型、目的以及实施过程中的关键步骤。
Scientific Research
科学研究
Scientific research is defined as a structured process of inquiry designed to collect, analyze, and interpret data to answer a specific question or solve a problem. It adheres to established scientific principles and methodologies to ensure reliability, accuracy, and validity of findings. The core characteristic of scientific research is its objective approach, where personal biases are minimized, and evidence-based conclusions are drawn.
科学研究被定义为一种结构化的探究过程,旨在收集、分析和解释数据,以解答特定问题或解决实际难题。它遵循既定的科学原则和方法体系,确保研究结果的可靠性、准确性和有效性。科学研究的核心特征是其客观性方法,即最大限度减少个人偏倚,并基于证据得出结论。
Types of Scientific Research
科学研究的类型
Scientific research can be categorized based on its purpose, methodology, and the nature of the study. Below are the primary types:
科学研究可根据研究目的、方法和研究性质进行分类,主要类型如下:
1. Based on Purpose
按研究目的划分
-
Basic Research: Focuses on understanding fundamental principles without immediate application. For example, studying the structure of DNA.
基础研究:侧重于理解基本原理,无即时应用目标。例如,对 DNA 结构的研究。 -
Applied Research: Aims to solve specific, practical problems. For instance, developing a new drug for a disease.
应用研究:旨在解决特定的实际问题。例如,为某种疾病研发新药。 -
Translational Research: Bridges the gap between basic and applied research by translating findings into practical applications.
转化研究:通过将研究成果转化为实际应用,搭建基础研究与应用研究之间的桥梁。
2. Based on Methodology
按研究方法划分
-
Quantitative Research: Uses numerical data to measure and analyze phenomena. It relies on statistical tools and aims for generalizable results.
定量研究:使用数值数据对现象进行测量和分析,依赖统计工具,旨在获得可推广的结果。 -
Qualitative Research: Focuses on understanding human behavior and experiences through non-numerical data such as interviews or observations.
定性研究:通过访谈、观察等非数值数据,致力于理解人类行为和体验。 -
Mixed-Methods Research: Combines quantitative and qualitative approaches to provide a more comprehensive understanding.
混合方法研究:整合定量和定性方法,以获得更全面的认知。
3. Based on Nature of Study
按研究性质划分
-
Descriptive Research: Observes and describes characteristics of a subject without influencing it.
描述性研究:观察并描述研究对象的特征,不施加干预影响。 -
Exploratory Research: Investigates unknown phenomena to develop hypotheses.
探索性研究:探究未知现象,以提出研究假设。 -
Explanatory Research: Seeks to explain causes or relationships among variables.
解释性研究:旨在解释变量之间的因果关系或关联。 -
Experimental Research: Involves manipulating variables in a controlled environment to test hypotheses.
实验研究:在受控环境中操控变量,以检验研究假设。
Purpose of Scientific Research
科学研究的目的
The purpose of scientific research extends beyond mere knowledge acquisition. It encompasses several objectives:
科学研究的目的不仅限于获取知识,还包括以下多个目标:
1. Advancing Knowledge
推动知识进步
Scientific research uncovers new information, refines existing theories, and broadens our understanding of various phenomena.
科学研究揭示新信息、完善现有理论,并拓宽我们对各类现象的认知。
2. Problem Solving
解决实际问题
Applied research addresses practical challenges, providing evidence-based solutions in fields such as healthcare, engineering, and environmental science.
应用研究应对实际挑战,在医疗保健、工程、环境科学等领域提供基于证据的解决方案。
3. Informing Policy
为政策制定提供依据
Research findings guide policymakers in making informed decisions, ensuring that regulations and programs are grounded in evidence.
研究结果为政策制定者提供决策参考,确保法规和项目以证据为基础。
4. Driving Innovation
驱动创新发展
Scientific inquiry fosters technological advancements and creative solutions, driving societal and economic progress.
科学探究促进技术进步和创新性解决方案的产生,推动社会和经济发展。
Guide to Conducting Scientific Research
科学研究实施指南
Conducting scientific research requires a structured approach. Below are the key steps involved:
开展科学研究需要遵循结构化方法,关键步骤如下:
1. Identify a Research Problem
确定研究问题
Select a specific issue or question that aligns with your interests and the needs of your field.
选择一个与个人兴趣和所在领域需求相符的特定问题或疑问。
2. Conduct a Literature Review
开展文献综述
Review existing studies to understand the current state of knowledge and identify gaps.
回顾现有研究,了解知识现状并识别研究空白。
3. Formulate a Hypothesis
提出研究假设
Develop a testable statement or research question that guides your investigation.
制定可检验的陈述或研究问题,为探究过程提供指导。
4. Choose a Methodology
选择研究方法
Select the appropriate research design, tools, and techniques based on your objectives.
根据研究目标,选择合适的研究设计、工具和技术。
5. Collect Data
收集数据
Gather information systematically using experiments, surveys, interviews, or other methods.
通过实验、调查、访谈或其他方法,系统性地收集信息。
6. Analyze Data
分析数据
Use statistical or qualitative analysis to interpret your findings.
采用统计分析或定性分析方法,对研究结果进行解读。
7. Draw Conclusions
得出结论
Compare results with your hypothesis and discuss their implications.
将结果与研究假设进行对比,并探讨其意义。
8. Disseminate Findings
传播研究成果
Share your research through publications, presentations, or reports to contribute to the broader scientific community.
通过发表论文、学术报告或研究报告等形式分享研究成果,为更广泛的科学界做出贡献。
Ethical Considerations in Scientific Research
科学研究中的伦理考量
Ethics play a crucial role in ensuring the integrity of scientific research. Key considerations include:
伦理在确保科学研究的完整性方面起着至关重要的作用,主要考量因素包括:
-
Informed Consent: Participants must voluntarily agree to take part after understanding the study’s purpose and risks.
知情同意:参与者在了解研究目的和风险后,必须自愿同意参与。 -
Confidentiality: Researchers must protect the privacy of participants.
保密性:研究者必须保护参与者的隐私。 -
Avoiding Bias: Efforts should be made to maintain objectivity and transparency.
避免偏倚:应努力保持客观性和透明度。 -
Plagiarism: Proper attribution of sources is essential to uphold academic honesty.
杜绝剽窃:正确标注信息来源对于维护学术诚信至关重要。
Conclusion
结论
Scientific research is a fundamental tool for expanding human knowledge, solving real-world problems, and driving innovation. By understanding its types, purposes, and methodologies, researchers can approach their investigations with clarity and rigor. The adherence to ethical practices and systematic processes ensures that the outcomes are credible, impactful, and contribute meaningfully to the global body of knowledge.
科学研究是拓展人类知识、解决现实问题和驱动创新的基本工具。通过理解其类型、目的和方法,研究者能够以清晰、严谨的态度开展探究。遵循伦理规范和系统性流程,可确保研究结果具有可信度和影响力,并为全球知识体系做出有意义的贡献。
References
参考文献
-
Babbie, E. (2020). The Practice of Social Research. Cengage Learning.
巴比(E. Babbie).(2020).《社会研究方法实践》. 圣智学习出版公司. -
Creswell, J. W. (2021). Research Design: Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Approaches. Sage Publications.
克雷斯韦尔(J. W. Creswell).(2021).《研究设计:定性、定量与混合方法路径》. 塞奇出版社. -
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners. SAGE Publications.
库马尔(R. Kumar).(2019).《研究方法论:初学者分步指南》. 塞奇出版社. -
National Science Foundation (2023). “What is Basic Research?” Retrieved from https://www.nsf.gov/
美国国家科学基金会(2023).《什么是基础研究?》. 取自 https://www.nsf.gov/ -
World Health Organization (2023). “Translational Research in Health.” Retrieved from https://www.who.int/
世界卫生组织(2023).《健康领域的转化研究》. 取自 https://www.who.int/
via:
- datasciencemilan.org/what-are-the-types-of-scientific-research.html
https://datasciencemilan.org/what-are-the-types-of-scientific-research.html - Scientific Research - Types, Purpose and Guide - Research Method
https://researchmethod.net/scientific-research/ - Discove The Six Key Classifications Of Scientific Research
https://medicallexis.com/six-key-classifications-of-scientific-research-a-comprehensive-guide/ - What Is Scientific Research And Its Typology
https://datasciencemilan.org/what-are-the-types-of-scientific-research.html - Scientific Research Definition, Classifications & Purpose - Lesson | Study.com
https://study.com/academy/lesson/what-is-scientific-research.html - What is Scientific Research and How Can it be Done? - PMC
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5019873/ - Types of Scientific Research
https://innspub.net/types-of-scientific-research/
 科学研究的类型与方法解析
科学研究的类型与方法解析





















 1424
1424

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








