注:英文引文,机翻未校。
如有内容异常,请看原文。
Why is the Square Root of 2 Irrational?
为什么 2 的平方根是无理数?
Added on: July 16, 2025
A familiar yet fascinating number:
2
\sqrt {2}
2. We all know it. But did you know that, once upon a time, mathematicians lost sleep trying to prove why the square root of 2 is irrational?
一个熟悉而又迷人的数字:
2
\sqrt {2}
2。我们都知道它。但你是否知道,曾经有数学家为了证明 2 的平方根是无理数而夜不能寐?
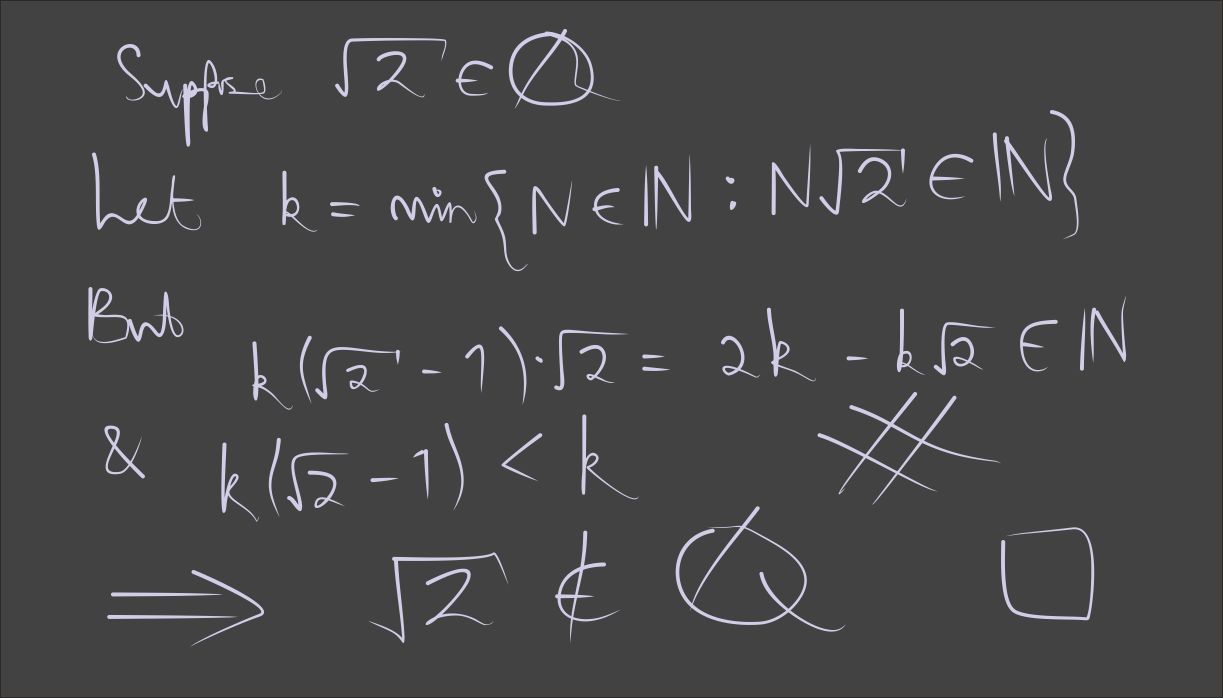
A new proof recently surfaced. Well, “new” might be a stretch—but its approach is definitely different. The classic proof says: suppose
2
=
p
q
\sqrt {2} = \frac {p}{q}
2=qp in lowest terms. Turns out, both
p
p
p and
q
q
q must be even. That’s a contradiction. Elegant and direct.
最近出现了一种新的证明方法。当然,“新” 这个词可能有些夸张 —— 但它的方法确实与众不同。经典的证明方法是这样的:假设
2
=
p
q
\sqrt {2} = \frac {p}{q}
2=qp,其中
p
q
\frac {p}{q}
qp 是最简分数形式。结果发现,
p
p
p 和
q
q
q 都必须是偶数。这就产生了矛盾。 这种方法简洁而直接。
This new proof? It starts the same way: assume
2
\sqrt {2}
2 is rational, so we can write it as
p
q
\frac {p}{q}
qp. Then we define a set of positive integers that, when multiplied by
2
\sqrt {2}
2, give natural numbers. Let’s call the smallest such number
k
k
k.
这种新的证明方法呢?它的起点是相同的:假设
2
\sqrt {2}
2 是有理数,因此我们可以将其表示为
p
q
\frac {p}{q}
qp。然后,我们定义一个正整数集合,当这些正整数乘以
2
\sqrt {2}
2 时,会得到自然数。我们称这个集合中最小的数为
k
k
k。
Now here’s where it gets fun. Take the expression
k
⋅
(
2
−
1
)
k \cdot (\sqrt {2} - 1)
k⋅(2−1). Crunch the numbers, do the math, and you end up with another natural number. But this new number is smaller than
k
k
k. Wait… wasn’t
k
k
k supposed to be the smallest? Boom. Contradiction. That means our assumption—that
2
\sqrt {2}
2 is rational—goes out the window.
现在,有趣的部分来了。取表达式
k
⋅
(
2
−
1
)
k \cdot (\sqrt {2} - 1)
k⋅(2−1), 进行计算,你会发现结果是另一个自然数。但 这个新数比
k
k
k 更小。等一下……
k
k
k 不是应该最小的吗?砰!矛盾了。 这就意味着我们的假设 ——
2
\sqrt {2}
2 是有理数 —— 不成立了。
What makes this proof charming? It leans on real numbers, sets, and concepts like infimum. It doesn’t play the “even or odd” game. Instead, it calls the idea of “the smallest element” to the stage and lets the contradiction unravel from there.
这种证明方法的魅力何在?它依赖于实数、集合以及诸如下确界这样的概念。它不玩 “偶数或奇数” 的游戏。相反,它把 “最小元素” 的概念搬上舞台,让矛盾从那里展开。
Now let’s be honest: this isn’t a proof you show high school students on a sleepy Tuesday morning.You have to accept the existence of real numbers. You have to understand sets. It’s a bit more mature, mathematically speaking.
现在,我们得实话实说:这不是一种适合在周二早上让高中生打起精神来看的证明方法。你必须接受实数的存在。你必须理解集合。 从数学的角度来说,这有点 “成熟”。
Still, it’s beautiful. Why? Because reaching the same result through a different path is always worth celebrating in math. Seeing multiple routes stretches how we think. And if you can formalize that route in a system like Isabelle/HOL, then math becomes part art, part engineering.
即便如此,它还是很美。为什么?因为在数学中,通过不同的路径得出相同的结果总是值得庆祝的。看到多种途径会拓展我们的思维方式。如果你能在像 Isabelle/HOL 这样的系统中形式化这种途径,那么数学就变成了艺术与工程学的一部分。
Bottom line:
2
\sqrt {2}
2 is irrational. This time we proved it a different way. Same destination, new perspective. And sometimes, that’s all it takes to keep things exciting.
最终结论:
2
\sqrt {2}
2 是无理数。这次我们用不同的方法证明了它。同样的目的地,新的视角。有时候,这就足以让事情保持令人兴奋的状态。
via:
- Why is the Square Root of 2 Irrational? - Abakcus
https://abakcus.com/article/why-is-the-square-root-of-2-irrational/





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








