注:本文为 “ SCALE” 相关合辑。
英文引文,机翻未校。
中文引文,略作重排。
图片清晰度受引文原图所限。
如有内容异常,请看原文。
AMD上直接跑CUDA程序,英伟达护城河没了?
张玄 EDN 电子技术设计 2024 年 07 月 18 日 15:47 中国香港
最近有个叫 SCALE 的工具出现了,据说有了它 CUDA 程序就能跑在 AMD GPU 上,而且比以前那些兼容工具都高效,英伟达危?
上周末,英国初创企业 Spectral Compute 宣布推出一个名为 SCALE 的 GPGPU 工具链:主要作用是能够让 CUDA 程序直接跑在 AMD GPU 上,不需要进行代码修改 —— 此事最早应该是国外媒体 Phoronix 报道的。
SCALE 在此扮演的主要角色是,针对 AMD 处理器自动编译 CUDA 代码。换句话说,也就是原本给英伟达 GPU 写的软件,借助 SCALE 可以很方便地切换到其他非英伟达平台,不需要进行代码移植,而且据说是完全遵守 EULA 最终用户许可协议的。
SCALE 工具怎么工作的?
从外媒的报道来看,SCALE 面向非英伟达 GPU—— 现在应该确切为 AMD GPU,编译 CUDA 代码,生成 binary; 实现了 CUDA 兼容,包括对于 Inline PTX Assembly 以及 nvcc C++ 的支持;生成的代码实现了 AMD ROCm 6 的可用。
Phoronix 的评价是,SCALE 的能力令其成为了英伟达 nvcc 编译器的 “即插即用替代品”,“并且还有个‘扮演’NVIDIA CUDA 工具集的 runtime”。
虽然我们之前也见过不少所谓 “CUDA 兼容” 的工具,但那些软件和方案一般都是把 CUDA 代码转义为其他语言。这次发布的 SCALE 则是直接编译 CUDA 源码,特别针对 AMD GPU。官网总结 SCALE 的工作方式大致上是这样的:

介绍中提到,SCALE 解决方案用到了一些开源 LLVM 组件。据说这套方案不仅高效,而且使用起来也很友好,相比 ZLUDA 提供更加无缝和高集成度的解决方案。ZLUDA 应该算得上是行业内相对知名的、让 CUDA 库最终能够为 AMD ROCm 服务的开源移植项目。
Spectral Compute 表示 SCALE 开发了长达 7 年时间。据说 SCALE 已经成功通过了包含 Blender, Llama-cpp, XGboost, FAISS, GOMC, STDGPU, Hashcat, 乃至 NVIDIA Thrust 在内的软件测试;Spectral Compute 自己也做了针对 AMD 的 RDNA2/RDNA3 架构 GPU 测试,以及 RDNA1 的基础测试,Vega 架构的支持则还在进行中。
SCALE 有什么价值?
这里援引 Spectral Compute 公司首席执行官 Michael Sondergaard 的说法:“我们相信,写一次代码就让它跑在任何硬件平台,应该成为可能。对于 CPU 代码而言,这原本就是个存在多年的事实,为什么 GPU 就不行呢?我们尝试通过桥接流行的 CUDA 编程语言与其他硬件供应商的兼容性,以直接解决这个问题。”
所以口号是 “one codebase, multiple vendors”—— 也就是写一次基础代码,就面向多供应商。这应该也是绝大部分 HPC 与 AI 应用开发者一直以来期望做到的。毕竟用户总是希望有更多选择,而不是绑定在一个供应商身上的。
比如单就 AI 来看,Intel 过去半年宣传自家的 AI 生态,就在反复强调应该给用户 “选择”,要打造 “开放” 和 “开源” 的生态 —— 所以 Intel 的 oneAPI 甚至支持英伟达 GPU,OpenVINO 推理引擎通过插件可支持 Arm。我们当时评论说,这实际是在英伟达形成排他且强大生态以后,其他芯片企业及供应商要发展的不二之选 ——AI 这么大的蛋糕,大家总是希望能一起分食的。
外媒的评价普遍集中在 “打破英伟达软件栈的统治地位”,以及 GPU 应当构建起开源环境,实现互连接、互操作性等话题。SCALE 则作为这种媒介,可能某种程度打破了英伟达的限制,让 CUDA 从 “排他” 走向相对更广泛的可用范围。
需要注意的是 SCALE 本身并不是开源的,只不过用户仍然可以通过免费软件授权的方式来使用。微软 Copilot 认为,SCALE 没有违反任何相关协议却实现了 CUDA 兼容性,可能与其使用诸多开源组件有关 —— 比如 LLVM; 另外借助自家的 runtime 确保兼容性也遵循了授权协议。
最后还是值得提一句,虽然很多媒体普遍认为 CUDA 在英伟达统治的 AI 市场上也扮演极其重要的角色,CUDA 也作为英伟达推出诸多加速库、微服务和上层应用的基础,但在我们过去半年接触的 AI 芯片企业中,很多参与者都认为 CUDA 的影响力或扮演的角色在 AI 时代正在弱化。
这里援引一段今年 Intel Vision 媒体预沟通会上,Intel 发言人说的话:“而在 PyTorch 之下,的确有很多开发者选择来自单一供应商、专用的 CUDA”,“但行业正在朝着寻找替代方案、更多选择的路子上走,典型的比如 Triton (由 OpenAI 开发,也用于 GPU 编程); 要确保能够以开放的方式、像是用 MLIR,让所有的 kernel 跑起来。”
另外 “如果我们去看软件栈的下一个层级,像是 OpenVINO 这样的 inference runtime,大概 95% 的开发者和数据科学家都工作在这个层级或更高层级。”“只有很少一部分人是工作在 CUDA 或者 oneAPI 层级的。”
“这个层级固然在优化和支持上非常重要,但毕竟会需要用到它的开发者少。”“而且我们认为,未来这部分群体还会变得更少。”“尤其现在随着抽象层接入,Triton 语言、MLIR 能力、各种编译基础,实现跨架构更广泛的支持,编程模型更低层级的角色不会那么重要。”
当然,CUDA 也不单是用在 AI 生态上,以及要考虑这是英伟达竞争对手的发言,在此仅供参考。而且还需要注意的是,当前英伟达于 HPC 和 AI 市场的护城河优势并不单纯在 CUDA 上,包括 NVLink, NVSwitch 等在内的硬件及系统生态亦足够为竞争对手感到汗颜。
虽然到目前为止,我们也还没有看到英伟达对于 SCALE 的态度,但此前英伟达对于任何 CUDA 兼容跑在其他硬件上的方案,显然都是没什么好感的。如说今年 3 月外媒报道英伟达在 CUDA 的 EULA 协议中出现新的警示,针对的应该就是 SCALE 这样的工具。
How AMD May Get Across the CUDA Moat
AMD 如何跨越 CUDA 护城河
When discussing GenAI, the term “GPU” almost always enters the conversation and the topic often moves toward performance and access. Interestingly, the word “GPU” is assumed to mean “Nvidia” products. (As an aside, the popular Nvidia hardware used in GenAI are not technically Graphical Processing Units. I prefer SIMD units.)
在讨论 GenAI 时,“GPU” 一词几乎总是进入对话,话题经常转向性能和访问。有趣的是,“GPU” 一词被认为是 “Nvidia” 产品的意思。(顺便说一句,GenAI 中使用的流行 Nvidia 硬件在技术上不是图形处理单元。我更喜欢 SIMD 单元。
The association of GenAI and GPUs with Nvidia is no accident. Nvidia has always recognized the need for tools and applications to help grow its market. They have created a very low barrier to getting software tools (e.g., CUDA) and optimized libraries (e.g., cuDNN) for Nvidia hardware. Indeed, Nvidia is known as a hardware company, but as Bryan Catanzaro, VP of Applied Deep Learning Research, Nvidia has stated ” Many people don’t know this, but Nvidia has more software engineers than hardware engineers.”
GenAI 和 GPU 与 Nvidia 的关联并非偶然。英伟达一直认识到需要工具和应用程序来帮助发展其市场。他们为获得 Nvidia 硬件的软件工具(例如 CUDA)和优化库(例如 cuDNN)创造了非常低的门槛。事实上,英伟达被称为一家硬件公司,但正如应用深度学习研究副总裁布莱恩・卡坦扎罗(Bryan Catanzaro)所说,英伟达曾表示:“很多人不知道这一点,但英伟达的软件工程师比硬件工程师还多。
As a result, Nvidia has built a powerful software “moat” around their hardware. While CUDA is not open source, it is freely available and under the firm control of Nvidia. While this situation has benefited Nvidia (As it should. They invested time and money into CUDA), it has created difficulties for those companies and users that want to grab some of the HPC and GenAI market with alternate hardware.
因此,英伟达围绕其硬件建立了强大的软件 “护城河”。虽然 CUDA 不是开源的,但它是免费提供的,并且在 Nvidia 的严格控制下。虽然这种情况使英伟达受益(它应该。他们在 CUDA 上投入了时间和金钱),这给那些希望通过替代硬件抢占一些 HPC 和 GenAI 市场的公司和用户带来了困难。
Building on the Castle Foundation
The number of foundational models developed for GenAI continues to grow. Many of these are “open source” because they can be used and shared freely. (For example, the Llama foundational model from Meta) In addition, they require a large number of resources (both people and machines) to create and are limited mainly to the hyperscalers (AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud, Meta Platforms, and Apple) that have huge amounts of GPUs available, In addition to the hyperscalers, other companies have invested in hardware (i.e. purchased a massive amount of GPUs) to create their own foundational models.
为 GenAI 开发的基础模型数量持续增长。其中许多是 “开源” 的,因为它们可以自由使用和共享。(例如,Meta 的 Llama 基础模型)此外,它们需要大量资源(包括人和机器)来创建,并且主要局限于拥有大量可用 GPU 的超大规模提供商(AWS、Microsoft Azure、Google Cloud、Meta Platforms 和 Apple),除了超大规模提供商之外,其他公司还投资了硬件(即购买了大量 GPU)来创建自己的基础模型。
From a research perspective, the models are interesting and can be used for a variety of tasks; however, the expected use and need for even more GenAI computing resources is two fold;
从研究的角度来看,这些模型很有趣,可以用于各种任务;然而,对更多 GenAI 计算资源的预期使用和需求是双重的;
- Fine-tuning — Adding domain-specific data to foundational models to make it work for your use case.
微调 — 将特定于域的数据添加到基础模型中,使其适用于您的用例。 - Inference – Once the model is fine-tuned, it will require resources when used (i.e., asked questions).
推理 – 一旦模型被微调,它在使用时将需要资源(即提出的问题)。
These tasks are not restricted to hyperscalers and will need accelerated computing, that is, GPUs. The obvious solution is to buy more “unavailable” Nvidia GPUs, and AMD is ready and waiting now that the demand has far outstripped the supply. To be fair, Intel and some other companies are also ready and waiting to sell into this market. The point is that GenAI will continue to squeeze GPU availability as fine-tuning and inference become more pervasive, and any GPU (or accelerator) is better than no GPU.
这些任务不仅限于超大规模提供商,还需要加速计算,即 GPU。显而易见的解决方案是购买更多 “不可用” 的 Nvidia GPU,而 AMD 已经准备好并等待,因为需求已经远远超过供应。公平地说,英特尔和其他一些公司也准备好并等待向这个市场出售。关键是,随着微调和推理变得越来越普遍,GenAI 将继续挤压 GPU 的可用性,任何 GPU(或加速器)都比没有 GPU 好。
Moving away from Nvidia hardware suggests that other vendor GPUs and accelerators must support CUDA to run many of the models and tools. AMD has made this possible with HIP CUDA conversion tool; however, the best results often seem to use the native tools surrounding the Nvidia castle.
远离 Nvidia 硬件表明,其他供应商的 GPU 和加速器必须支持 CUDA 才能运行许多模型和工具。AMD 通过 HIP CUDA 转换工具使这成为可能;然而,最好的结果似乎通常使用 Nvidia 城堡周围的原生工具。
The PyTorch Drawbridge
In the HPC sector, CUDA-enabled applications rule the GPU-accelerated world. Porting codes can often realize a speed-up of 5-6x when using a GPU and CUDA. (Note: Not all codes can achieve this speed up, and some may not be able to use the GPU hardware.) However, in GenAI, the story is quite different.
在 HPC 领域,支持 CUDA 的应用程序统治着 GPU 加速的世界。当使用 GPU 和 CUDA 时,移植代码通常可以实现 5-6 倍的加速。(注意:并非所有代码都能实现这种加速,有些代码可能无法使用 GPU 硬件。然而,在 GenAI 中,情况却大不相同。
Initially, TensorFlow was the tool of choice for creating AI applications using GPUs. It works both with CPUs and was accelerated with CUDA for GPUs. This situation is changing rapidly.
最初,TensorFlow 是使用 GPU 创建 AI 应用程序的首选工具。它既适用于 CPU,也适用于 GPU 的 CUDA 进行加速。这种情况正在迅速变化。
An alternative to TensorFlow is PyTorch, an open-source machine learning library for developing and training neural network-based deep learning models. Facebook’s AI research group primarily develops it.
TensorFlow 的替代品是 PyTorch,这是一个开源机器学习库,用于开发和训练基于神经网络的深度学习模型。Facebook 的人工智能研究小组主要开发它。
In a recent blog post by Ryan O’Connor, a Developer Educator at AssemblyAI notes that the popular site HuggingFace, (that allows users to download and incorporate trained and tuned state of the art models into application pipelines with just a few lines of code), 92% of models available are PyTorch exclusive.
在 AssemblyAI 的开发人员教育家 Ryan O’Connor 最近的一篇博客文章中指出,流行的网站 HuggingFace(允许用户只需几行代码即可下载经过训练和调整的最先进的模型并将其合并到应用程序管道中),92% 的可用模型是 PyTorch 独有的。
In addition, as shown in Figure One, a comparison of Machine Learning papers shows a significant trend toward PyTorch and away from TensorFlow.
此外,如图 1 所示,机器学习论文的比较显示了 PyTorch 和 TensorFlow 的显着趋势。
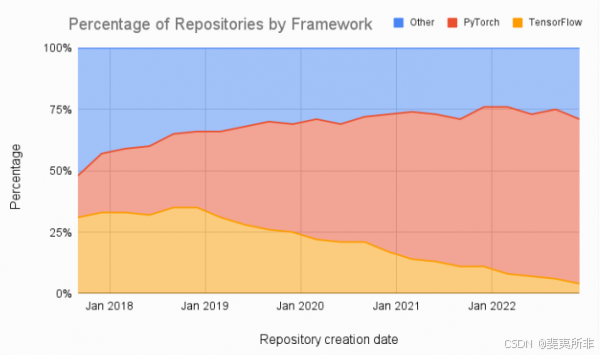
Figure One: Percentage of papers that utilize PyTorch, TensorFlow, or another framework over time, with data aggregated quarterly, from late 2017, Source: assemblyai.com.
Of course, underneath PyTorch are calls to CUDA, but that is not required because PyTorch insulates the user from the underlying GPU architecture. There is also a version of PyTorch that uses AMD ROCm, an open-source software stack for AMD GPU programming. Crossing the CUDA moat for AMD GPUs may be as easy as using PyTorch.
当然,在 PyTorch 下面是对 CUDA 的调用,但这不是必需的,因为 PyTorch 将用户与底层 GPU 架构隔离开来。还有一个使用 AMD ROCm 的 PyTorch 版本,这是一个用于 AMD GPU 编程的开源软件堆栈。跨越 AMD GPU 的 CUDA 护城河可能就像使用 PyTorch 一样简单。
Instinct for Inference
In both HPC and GenAI, the Nvidia 72-core ARM-based Grace-Hopper superchip with a shared memory H100 GPU (and also the 144-core Grace-Grace version) is highly anticipated. All Nvidia released benchmarks thus far indicate much better performance than the traditional server where the GPU is attached and accessed over the PCIe bus. Grace-Hopper represents an optimized hardware for both HPC and GenAI. It also is expected to find wide use in both fine-tuning and inference. Demand is expected to be high.
在 HPC 和 GenAI 中,基于 Nvidia 72 核 ARM 的 Grace-Hopper 超级芯片与共享内存 H100 GPU(以及 144 核 Grace-Grace 版本)备受期待。到目前为止,所有 Nvidia 发布的基准测试都表明,GPU 通过 PCIe 总线连接和访问的传统服务器的性能要好得多。Grace-Hopper 代表了针对 HPC 和 GenAI 的优化硬件。它还有望在微调和推理中得到广泛应用。预计需求将很高。
AMD has had shared memory CPU-GPU designs since 2006 (AMD acquired graphics card company ATI in 2006). Beginning as the “Fusion” brand many AMD x86_64 processors are now implemented as a combined CPU/GPU called an Accelerated Processing Unit (APU).
自 2006 年以来,AMD 一直采用共享内存 CPU-GPU 设计(AMD 于 2006 年收购了显卡公司 ATI)。从 “Fusion” 品牌开始,许多 AMD x86_64 处理器现在都作为称为加速处理单元 (APU) 的组合 CPU/GPU 实现。
The upcoming Instinct MI300A processor (APU) from AMD will offer competition for Grace-Hopper superchip. It will also power the forthcoming El Capitan at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory. The Integrated MI300A will provide up to 24 Zen4 cores in combination with a CDNA 3 GPU Architecture and up to 192 GB of HBM3 memory, providing uniform access memory for all the CPU and GPU cores. The chip-wide cache-coherent memory reduces data movement between the CPU and GPU, eliminating the PCIe bus bottleneck and improving performance and power efficiency.
AMD 即将推出的 Instinct MI300A 处理器(APU)将与 Grace-Hopper 超级芯片竞争。它还将为即将到来的劳伦斯利弗莫尔国家实验室的 El Capitan 提供动力。集成的 MI300A 将提供多达 24 个 Zen4 内核,结合 CDNA 3 GPU 架构和高达 192 GB 的 HBM3 内存,为所有 CPU 和 GPU 内核提供统一的访问内存。芯片级缓存一致性内存可减少 CPU 和 GPU 之间的数据移动,消除 PCIe 总线瓶颈,提高性能和能效。
AMD is readying the Instinct MI300A for the upcoming inference market. As stated by AMD CEO Lisa Su in a recent article on Yahoo!Finance. “We actually think we will be the industry leader for inference solutions because of some of the choices that we’ve made in our architecture.”
AMD 正在为即将到来的推理市场准备 Instinct MI300A。正如 AMD 首席执行官苏姿丰(Lisa Su)最近在雅虎财经(Yahoo!Finance)上发表的一篇文章中所说。“我们实际上认为,由于我们在架构中做出的一些选择,我们将成为推理解决方案的行业领导者。”
For AMD and many other hardware vendors, PyTorch has dropped the drawbridge on the CUDA moat around the foundational models. AMD has the Instinct MI3000A battle wagon ready to go. The hardware battles for the GenAI market will be won by performance, portability, and availability. The AI day is young.
对于 AMD 和许多其他硬件供应商来说,PyTorch 已经放弃了围绕基础模型的 CUDA 护城河上的吊桥。AMD 已经准备好了 Instinct MI3000A 战车。GenAI 市场的硬件争夺战将通过性能、便携性和可用性来赢得。人工智能时代还很年轻。
SCALEing the CUDA Castle
围攻 CUDA 城堡

In a previous article, HPCwire has reported on a way in which AMD can get across the CUDA moat that protects the Nvidia CUDA castle (at least for PyTorch AI projects.). Other tools have joined the CUDA castle siege. AMD has created open-source HIP, a C++ runtime API and kernel language that allows developers to create portable applications for AMD and NVIDIA GPUs from single source code. HIP is not CUDA and is natively based on AMD ROCm, the AMD equivalent of Nvidia CUDA. AMD also provides the open-source HIPIFY translation tool. HIPIFY can take CUDA source code and convert it to AMD HIP, which can then be run on AMD GPU hardware.
在上文中,HPCwire 报道了 AMD 可以跨越保护 Nvidia CUDA 城堡的 CUDA 护城河的方法(至少对于 PyTorch AI 项目而言)。其他工具也加入了 CUDA 城堡围攻。AMD 创建了开源 HIP,这是一种 C++ 运行时 API 和内核语言,允许开发人员从单个源代码为 AMD 和 NVIDIA GPU 创建便携式应用程序。HIP 不是 CUDA,而是原生基于 AMD ROCm,相当于 Nvidia CUDA。AMD 还提供开源 HIPIFY 翻译工具。HIPIFY 可以获取 CUDA 源代码并将其转换为 AMD HIP,然后可以在 AMD GPU 硬件上运行。
The HIPIFY is a source-to-source compiler that works by providing HIP equivalent API calls that can be substituted for CUDA API calls. If there is no equivalent call, then the HIPIFY process will not work. It should be noted that either AMD or Nvidia hardware can be targeted once translated to (or written in) the HIP API.
HIPIFY 是一个源到源编译器,它通过提供可以替代 CUDA API 调用的 HIP 等效 API 调用来工作。如果没有等效调用,则 HIPIFY 进程将不起作用。应该注意的是,一旦将 AMD 或 Nvidia 硬件转换为 HIP API(或写入其中),就可以成为目标。
Another path to cross the moat is the open-source ZLUDA project. ZLUDA runs unmodified binary CUDA applications with near-native performance on AMD GPUs. Considered alpha quality, ZLUDA has been confirmed to work with various native CUDA applications (e.g., LAMMPS, NAMD, OpenFOAM, and others). Until recently, AMD quietly funded ZLUDA, but that sponsorship has ended. The project continues as there have been recent commits to the codebase.
另一条跨越护城河的途径是开源的 ZLUDA 项目。ZLUDA 在 AMD GPU 上运行未经修改的二进制 CUDA 应用程序,具有近乎原生的性能。ZLUDA 被认为是 alpha 质量,已被确认可与各种原生 CUDA 应用程序(例如 LAMMPS、NAMD、OpenFOAM 等)配合使用。直到最近,AMD 还悄悄地资助了 ZLUDA,但这种赞助已经结束。该项目仍在继续,因为最近已经提交了代码库。
Scaling the CUDA Castle Walls
While AMD HIP and HIPIFY are workable and open solutions, developers often prefer direct source code compilation. From a pragmatic standpoint, using one CUDA or HIP codebase is preferable to managing both. While HIP offers AMD and Nvidia hardware targets, a vast amount of Nvidia GPU code has been and continues to be written in CUDA.
虽然 AMD HIP 和 HIPIFY 是可行的开放解决方案,但开发人员通常更喜欢直接编译源代码。从务实的角度来看,使用一个 CUDA 或 HIP 代码库比同时管理两者更可取。虽然 HIP 提供了 AMD 和 Nvidia 硬件目标,但大量的 Nvidia GPU 代码已经并将继续用 CUDA 编写。
As recently reported by Phoronix, a new CUDA to AMD GPU compiler is now available. This development is a direct assault on the Nvidia CUDA castle.
正如 Phoronix 最近报道的那样,现在可以使用新的 CUDA 到 AMD GPU 编译器。这一发展是对英伟达 CUDA 城堡的直接攻击。

The SCALE CUDA compiler directly targets AMD hardware. (Source: Spectral Compute)
Developed by UK firm Spectral Compute, the SCALE GPGPU (general purpose GPU) compiler that allows CUDA applications to be natively compiled for AMD GPUs. SCALE does not require the CUDA software for operation and works within existing CUDA development pathways. Support for more GPU vendors and CUDA APIs is in development.
由英国公司 Spectral Compute 开发的 SCALE GPGPU(通用 GPU)编译器允许为 AMD GPU 原生编译 CUDA 应用程序。SCALE 不需要 CUDA 软件即可运行,并且可以在现有的 CUDA 开发路径中工作。 对更多 GPU 供应商和 CUDA API 的支持正在开发中。
According to Phoronix, SCALE began seven years ago and is a “clean room” implementation of CUDA leveraging some open-source LLVM components that natively compile CUDA sources for AMD GPUs without modification. The SCALE compiler takes unmodified CUDA code and directly produces binary files that can run on AMD GPUs using the AMD ROCm libraries. It can even handle CUDA programs that rely on the NVPTX assembly language. Essentially, the SCALE compiler is also a drop-in replacement to Nvidias’s nvcc compiler and has a runtime that “impersonates” (plug-and-play?) the Nvidia CUDA toolchain, so existing build tools and scripts like cmake just work.
根据 Phoronix 的说法,SCALE 始于七年前,是 CUDA 的 “洁净室” 实现,利用一些开源 LLVM 组件,这些组件无需修改即可为 AMD GPU 本地编译 CUDA 源代码。SCALE 编译器采用未经修改的 CUDA 代码,并直接生成可使用 AMD ROCm 库在 AMD GPU 上运行的二进制文件。它甚至可以处理依赖于 NVPTX 汇编语言的 CUDA 程序。从本质上讲,SCALE 编译器也是 Nvidias 的 nvcc 编译器的直接替代品,并且具有 “模拟”(即插即用?)Nvidia CUDA 工具链的运行时,因此现有的构建工具和脚本(如 cmake)可以正常工作。
According to Spectral Compute, SCALE has been validated by compiling open-source CUDA projects and verifying against package test suites. The following projects are currently part of nightly automated tests: Blender, Llama-cpp, XGboost, FAISS, GOMC, STDGPU, Hashcat, and Nvidia Thrust. SCALE is tested across RDNA2 and RDNA3 GPUs, along with basic testing on RDNA1, while Vega support is still a work in progress.
根据 Spectral Compute 的说法,SCALE 已经通过编译开源 CUDA 项目并针对软件包测试套件进行验证。以下项目目前是夜间自动化测试的一部分:Blender、Llama-cpp、XGboost、FAISS、GOMC、STDGPU、Hashcat 和 Nvidia Thrust。SCALE 在 RDNA2 和 RDNA3 GPU 上进行了测试,并在 RDNA1 上进行了基本测试,而对 Vega 的支持仍在进行中。
In terms of specific hardware support, the following GPU targets are supported and tested nightly:
在具体硬件支持方面,支持并每晚测试以下 GPU 目标:
-
AMD gfx1030 (Navi 21, RDNA 2.0)
-
AMD gfx1100 (Navi 31, RDNA 3.0)
The following GPU targets have undergone ad-hoc manual testing and “seem to work”:
以下 GPU 目标已经过临时手动测试,并且 “似乎有效”:
- AMD gfx1010
- AMD gfx1101
Spectral Compute is working on supporting the AMD gfx900 (Vega 10, GCN 5.0) and will presumably target other GPGPUs.
Spectral Compute 正在努力支持 AMD gfx900(Vega 10、GCN 5.0),并可能针对其他 GPGPU。
According to Spectral Compute, the primary benefits of SCALE over other cross-compiling or emulation methods are
根据 Spectral Compute 的说法,与其他交叉编译或仿真方法相比,SCALE 的主要优势是
- Instead of providing a new way to write GPGPU software, SCALE allows programs written using the widely popular CUDA language to be directly compiled for AMD GPUs.
SCALE 没有提供编写 GPGPU 软件的新方法,而是允许使用广泛流行的 CUDA 语言编写的程序直接为 AMD GPU 编译。 - SCALE aims to be fully compatible with Nvidia CUDA. Spectral Compute believes that users should not have to maintain multiple codebases or compromise on performance to support multiple GPU vendors.
SCALE 旨在与 Nvidia CUDA 完全兼容。Spectral Compute 认为,用户不必为了支持多个 GPU 供应商而维护多个代码库或牺牲性能。 - SCALE’s language is a superset of Nvidia CUDA, offering some opt-in language extensions to make writing GPU code easier and more efficient for users who wish to move away from nvcc.
SCALE 的语言是 Nvidia CUDA 的超集,提供一些选择加入的语言扩展,使希望摆脱 nvcc 的用户更容易、更高效地编写 GPU 代码。 - SCALE is a work in progress, and it plans to address any missing APIs that prevent SCALE from working.
SCALE 是一项正在进行的工作,它计划解决任何阻止 SCALE 工作的缺失 API。
For HPC, the prospect of an AMD CUDA compiler is exciting. Gaining portability between Nvidia and AMD hardware will provide more hardware choices among end users. Nvidia still controls the CUDA API (there is no standards committee), and any tools outside of the Nvidia castle will need to track future API changes.
对于 HPC 来说,AMD CUDA 编译器的前景令人兴奋。在 Nvidia 和 AMD 硬件之间获得可移植性将为最终用户提供更多硬件选择。Nvidia 仍然控制着 CUDA API(没有标准委员会),Nvidia 城堡之外的任何工具都需要跟踪未来的 API 更改。
SCALE has indicated that the compiler is not open-source, however, the documentation page indicates a freely available version for Linux-based systems (as either a.deb package or tarball). Since SCALE is new, there have not been any benchmarks for performance comparisons with HIPIFY or ZLUDA. Let’s hope Phoronix can turn its legendary benchmarking expertise on this new tool to help cross the CUDA moat and scale the castle walls.
SCALE 指出编译器不是开源的,但是,文档页面指出了基于 Linux 的系统的免费版本(作为 a.deb 包或 tarball)。由于 SCALE 是新的,因此没有任何与 HIPIFY 或 ZLUDA 进行性能比较的基准。让我们希望 Phoronix 能够将其传奇的基准测试专业知识运用到这个新工具上,以帮助穿越 CUDA 护城河并攀登城墙。
NVIDIA’s AI Supremacy is All About CUDA
NVIDIA 的 AI 霸主地位就是 CUDA
CUDA is a moat for NVIDIA. But the company’s pursuit of an upmarket strategy, focusing on high-priced data centre offerings, might let other companies be able to catch up with their software.

Published on August 8, 2023
by Mohit Pandey

By now, it is clear that no matter who wins the AI race, the biggest profiteer is NVIDIA. It’s common knowledge that the company is a market leader in the hardware category with its GPUs being widely used by all AI-focused companies in the world. That’s not all. NVIDIA, the biggest chip company in the world, is leading the battle from the software side of things as well, with its CUDA (Computing Unified Device Architecture) software.
到目前为止,很明显,无论谁赢得了 AI 竞赛,最大的获利者都是 NVIDIA。众所周知,该公司是硬件类别的市场领导者,其 GPU 被世界上所有专注于 AI 的公司广泛使用。这还不是全部。NVIDIA 是世界上最大的芯片公司,凭借其 CUDA(计算统一设备架构)软件,也在软件方面引领这场战斗。
CUDA, in essence, is like the magic wand that connects software to NVIDIA GPUs. It’s the handshake that enables your AI algorithms to work with the computing power of these graphical beasts. But to NVIDIA’s advantage, CUDA isn’t just any ordinary enchantment, but a closed-source, low-level API that wraps the software around NVIDIA’s GPUs, creating an ecosystem for parallel computing. It’s so potent that even the most formidable competitors such as AMD and Intel struggle to match its finesse.
CUDA 本质上就像是将软件连接到 NVIDIA GPU 的魔杖。正是握手使您的 AI 算法能够与这些图形野兽的计算能力配合使用。但对 NVIDIA 来说,CUDA 不仅仅是普通的魔法,而是一个闭源的低级 API,它将软件包装在 NVIDIA 的 GPU 周围,为并行计算创建一个生态系统。它是如此强大,以至于即使是 AMD 和 Intel 等最强大的竞争对手也难以匹敌它的技巧。
While other contenders such as Intel and AMD attempt to juggle one or the other, NVIDIA has mastered the art of both. Their GPUs are sleek, powerful, and coveted – and it’s no coincidence that they’ve also laid down the foundations of software that make the most of these machines.
当 Intel 和 AMD 等其他竞争者试图兼顾其中之一时,NVIDIA 已经掌握了两者的艺术。他们的 GPU 时尚、强大且令人垂涎——他们也为充分利用这些机器的软件奠定了基础,这并非巧合。
Software companies can’t just waltz in and claim the crown to replace NVIDIA, they lack the hardware prowess. On the flip side, hardware manufacturers can’t wade into the software territory without struggling. This has made CUDA the winning ingredient for NVIDIA in AI.
软件公司不能只是跳华尔兹并夺取取代 NVIDIA 的桂冠,他们缺乏硬件实力。另一方面,硬件制造商如果不费力气就涉足软件领域。这使得 CUDA 成为 NVIDIA 在 AI 领域的制胜要素。
Undisputed but vulnerable 无可争议但脆弱
NVIDIA built CUDA in 2006 with parallel computing for processing on multiple GPUs simultaneously. Earlier, developers were using models like Microsoft’s Direct3D or Linux’s OpenGL for computational purposes on GPUs, but lacked parallel computing capabilities. After the launch of CUDA, businesses began tailoring their strategies to adopt the software. OpenCL by Khronos Group was the only potential competitor released in 2009. But by then all companies had already started leveraging CUDA, leaving no room or need for it.
NVIDIA 于 2006 年构建了具有并行计算功能的 CUDA,可同时在多个 GPU 上进行处理。早些时候,开发人员使用 Microsoft 的 Direct3D 或 Linux 的 OpenGL 等模型在 GPU 上进行计算,但缺乏并行计算能力。CUDA 推出后,企业开始调整采用该软件的策略。Khronos Group 的 OpenCL 是 2009 年发布的唯一潜在竞争对手。但到那时,所有公司都已经开始利用 CUDA,没有留下任何空间或需求。
NVIDIA’s current strategy sounds all great, but there are some major drawbacks in it as well. Though CUDA is a moat for NVIDIA, the company’s pursuit of an upmarket strategy, focusing on high-priced data centre offerings, might let other companies be able to catch up with their software.
NVIDIA 目前的策略听起来不错,但也有一些主要缺点。尽管 CUDA 是 NVIDIA 的护城河,但该公司追求高端战略,专注于高价数据中心产品,可能会让其他公司赶上他们的软件。
Moreover, the market is rife with a GPU shortage that feels almost mythical, but a few are willing to forsake NVIDIA’s wares for alternatives like AMD or Intel. It’s almost as if tech aficionados would rather gnaw on cardboard than consider a GPU from another company.
此外,市场上充斥着 GPU 短缺,这感觉几乎是神话,但少数人愿意放弃 NVIDIA 的产品,转而选择 AMD 或 Intel 等替代品。就好像科技爱好者宁愿啃纸板也不愿考虑其他公司的 GPU。
NVIDIA’s maintenance of its current dominance is rooted in removing the RAM constraints within its consumer grade GPUs. This situation is likely to change as necessity drives the development of software that efficiently exploits consumer-grade GPUs, potentially aided by open-source solutions or offerings from competitors like AMD and Intel.
NVIDIA 保持其当前主导地位的根源在于消除其消费级 GPU 中的 RAM 限制。这种情况可能会改变,因为需求推动了有效利用消费级 GPU 的软件开发,并可能得到开源解决方案或 AMD 和 Intel 等竞争对手的产品的帮助。
Both Intel and AMD stand a chance at challenging NVIDIA’s supremacy, provided they shift away from mimicking NVIDIA’s high-end approach and instead focus on delivering potent, yet cost-effective GPUs, and build open source solutions. Crucially, they should differentiate themselves by avoiding artificial constraints that limit GPU capabilities, which NVIDIA employs to steer users towards their pricier data centre GPUs.
Intel 和 AMD 都有机会挑战 NVIDIA 的霸主地位,前提是它们不再模仿 NVIDIA 的高端方法,而是专注于提供强大且经济高效的 GPU,并构建开源解决方案。至关重要的是,他们应该通过避免限制 GPU 功能的人为限制来区分自己,NVIDIA 利用这些限制来引导用户使用价格更高的数据中心 GPU。
Even after these existing constraints, a lot of developers choose NVIDIA’s consumer grade GPUs over Intel or AMD for ML development. A lot of recent development in these smaller GPUs has led to people shifting to them for deploying models.
即使在这些现有限制之后,许多开发人员仍选择 NVIDIA 的消费级 GPU 而不是 Intel 或 AMD 进行 ML 开发。这些较小的 GPU 最近的许多发展导致人们转向它们来部署模型。
There is another competitor coming up 还有另一个竞争对手即将出现
Interestingly, OpenAI’s Triton emerges as a disruptive force against NVIDIA’s closed-source stronghold with CUDA. Triton, taking Meta’s PyTorch 2.0 input via PyTorch Inductor, carves a path by sidestepping NVIDIA’s CUDA libraries and favouring open-source alternatives like CUTLASS.
有趣的是,OpenAI 的 Triton 成为对抗 NVIDIA 的 CUDA 闭源据点的颠覆性力量。Triton 通过 PyTorch Inductor 获取 Meta 的 PyTorch 2.0 输入,通过避开 NVIDIA 的 CUDA 库并支持 CUTLASS 等开源替代方案来开辟一条道路。
While CUDA is an accelerated computing mainstay, Triton broadens the horizon. It bridges languages, enabling high-level ones to match the performance of lower-level counterparts. Triton’s legible kernels empower ML researchers, automating memory management and scheduling while proving invaluable for complex operations like Flash Attention.
虽然 CUDA 是加速计算的支柱,但 Triton 拓宽了视野。它桥接了语言,使高级语言能够与较低级别的语言的性能相匹配。Triton 清晰的内核为 ML 研究人员提供支持,实现内存管理和调度的自动化,同时证明对 Flash Attention 等复杂操作非常有价值。
Triton is currently only being powered on NVIDIA GPUs, the open-source reach might soon extend beyond, marking the advent of a shift. Numerous hardware vendors are set to join the Triton ecosystem, reducing the effort needed to compile for new hardware.
Triton 目前仅在 NVIDIA GPU 上提供支持,开源范围可能很快就会扩展到之外,这标志着转变的到来。许多硬件供应商将加入 Triton 生态系统,从而减少为新硬件编译所需的工作量。
NVIDIA, with all its might, overlooked a critical aspect – usability. This oversight allowed OpenAI and Meta to craft a portable software stack for various hardware, questioning why NVIDIA didn’t simplify CUDA for ML researchers. The absence of their hand in initiatives like Flash Attention raises eyebrows.
NVIDIA 竭尽全力忽视了一个关键方面——可用性。这种疏忽使 OpenAI 和 Meta 能够为各种硬件制作一个可移植的软件堆栈,质疑 NVIDIA 为什么不为 ML 研究人员简化 CUDA。他们在 Flash Attention 等倡议中的缺席引起了人们的注意。
NVIDIA has indeed had the upper hand when it comes to product supremacy. But let’s not underestimate the giants of tech. Cloud providers have rolled up their sleeves, designing their own chips that could give NVIDIA’s GPUs a run for their transistors.
NVIDIA 在产品霸权方面确实占据了上风。但我们不要低估科技巨头。云提供商已经卷起袖子,设计了自己的芯片,这些芯片可以让 NVIDIA 的 GPU 与他们的晶体管竞争。
Still, all of this is just wishful thinking as of now.
尽管如此,到目前为止,所有这些都只是一厢情愿。
Mohit Pandey
Mohit dives deep into the AI world to bring out information in simple, explainable, and sometimes funny words.
via:
-
AMD 上直接跑 CUDA 程序,英伟达护城河没了?张玄 EDN 电子技术设计 2024 年 07 月 18 日 15:47 中国香港
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/9ceqZjZqkuClvRkZ5o3p8Q -
SCALE documentation
https://docs.scale-lang.com/ -
How AMD May Get Across the CUDA Moat By Doug Eadline 作者:Doug Eadline October 5, 2023 10 月 5,2023
https://www.hpcwire.com/2023/10/05/how-amd-may-get-across-the-cuda-moat/ -
SCALEing the CUDA Castle By Doug Eadline 作者:Doug Eadline July 18, 2024 7 月 18,2024
https://www.hpcwire.com/2024/07/18/scaleing-the-cuda-castle/ -
NVIDIA’s AI Supremacy is All About CUDA
https://analyticsindiamag.com/ai-origins-evolution/nvidias-ai-supremacy-is-all-about-cuda/






















 1522
1522

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








