直接如题,从brpc开源的文档中看到brpc既支持同步调用,同时也支持异步调用。这里直接给出同步、异步的例子,同时对其进行分析。
1、brpc同步调用
brcp的同步调用是之前的echo的简单例子,所谓同步就是client对远端的server进行调用,同时自己原地等待,等待rpc返回之后,在进行之后的操作。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <gflags/gflags.h>
#include <butil/logging.h>
#include <butil/time.h>
#include <brpc/channel.h>
#include "echo.pb.h"
using namespace std;
DEFINE_string(attachment, "", "Carry this along with requests");
DEFINE_string(protocol, "baidu_std", "Protocol type. Defined in src/brpc/options.proto");
DEFINE_string(connection_type, "", "Connection type. Available values: single, pooled, short");
DEFINE_string(server, "0.0.0.0:8000", "IP Address of server");
DEFINE_string(load_balancer, "", "The algorithm for load balancing");
DEFINE_int32(timeout_ms, 100, "RPC timeout in milliseconds");
DEFINE_int32(max_retry, 3, "Max retries(not including the first RPC)");
DEFINE_int32(interval_ms, 1000, "Milliseconds between consecutive requests");
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
// Parse gflags. We recommend you to use gflags as well.
GFLAGS_NS::ParseCommandLineFlags(&argc, &argv, true);
// A Channel represents a communication line to a Server. Notice that
// Channel is thread-safe and can be shared by all threads in your program.
brpc::Channel channel;
// Initialize the channel, NULL means using default options.
brpc::ChannelOptions options;
options.protocol = FLAGS_protocol;
options.connection_type = FLAGS_connection_type;
options.timeout_ms = FLAGS_timeout_ms/*milliseconds*/;
options.max_retry = FLAGS_max_retry;
if (channel.Init(FLAGS_server.c_str(), FLAGS_load_balancer.c_str(), &options) != 0) {
LOG(ERROR) << "Fail to initialize channel";
return -1;
}
// Normally, you should not call a Channel directly, but instead construct
// a stub Service wrapping it. stub can be shared by all threads as well.
example::EchoService_Stub stub(&channel);
// Send a request and wait for the response every 1 second.
int log_id = 0;
while (!brpc::IsAskedToQuit()) {
// We will receive response synchronously, safe to put variables
// on stack.
example::EchoRequest request;
example::EchoResponse response;
brpc::Controller cntl;
request.set_message("hello world");
cntl.set_log_id(log_id ++); // set by user
// Set attachment which is wired to network directly instead of
// being serialized into protobuf messages.
cntl.request_attachment().append(FLAGS_attachment);
// Because `done'(last parameter) is NULL, this function waits until
// the response comes back or error occurs(including timedout).
//注意这里是同步调用,因为回调函数done被设置为NULL
//同步表示stub调用rpc,返回之后才会进行后面的语句
stub.Echo(&cntl, &request, &response, NULL);
cout << "after stub_method 0 " << endl;
if (!cntl.Failed()) {
LOG(INFO) << "Received response from " << cntl.remote_side()
<< " to " << cntl.local_side()
<< ": " << response.message() << " (attached="
<< cntl.response_attachment() << ")"
<< " latency=" << cntl.latency_us() << "us";
} else {
LOG(WARNING) << cntl.ErrorText();
}
cout << "after stub_method 1 " << endl;
usleep(FLAGS_interval_ms * 1000L);
}
LOG(INFO) << "EchoClient is going to quit";
return 0;
}
注意
1、stub.Echo调用可以看到回调函数被设置为NULL,那么此时调用被设置为同步操作,原地等待。
2、同步访问中的response/controller不会在CallMethod后被框架使用,它们都可以分配在栈上。注意,如果request/response字段特别多字节数特别大的话,还是更适合分配在堆上。
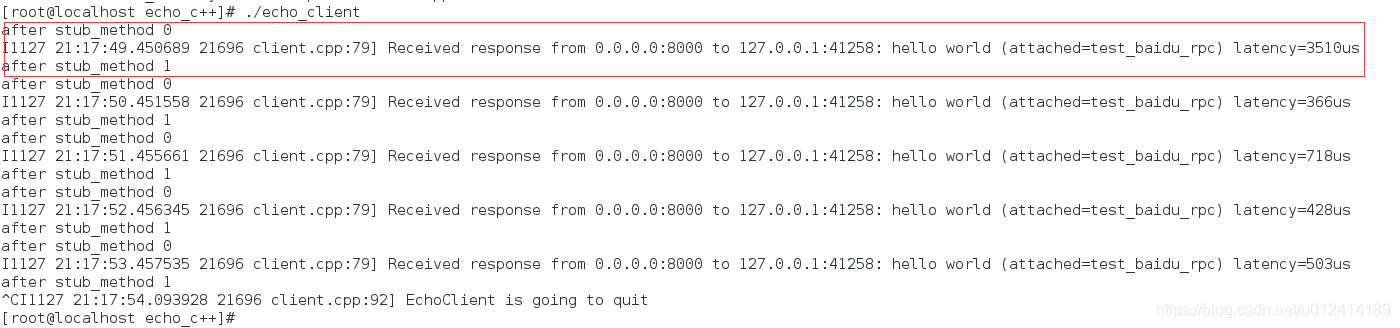
运行结果
同步进行,按照操作流程一步步打印
2、brpc异步调用
brpc的异步调用指的是和同步调用相比,在进行rpc调用之后,此时callmethod就结束了,进行继续执行后续的动作,等到rpc返回之后,会调用事先注册的回调函数,回调函数进行后面rpc返回之后的操作。
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <gflags/gflags.h>
#include <butil/logging.h>
#include <butil/time.h>
#include <brpc/channel.h>
#include "echo.pb.h"
using namespace std;
DEFINE_bool(send_attachment, true, "Carry attachment along with requests");
DEFINE_string(protocol, "baidu_std", "Protocol type. Defined in src/brpc/options.proto");
DEFINE_string(connection_type, "", "Connection type. Available values: single, pooled, short");
DEFINE_string(server, <







 本文详细介绍了brpc框架中同步、异步、半同步RPC调用的实现和注意事项,包括同步调用的原地等待特性、异步调用的回调函数机制、半同步调用的等待机制以及如何取消RPC调用。通过代码示例和运行结果展示了各种调用方式的特点。
本文详细介绍了brpc框架中同步、异步、半同步RPC调用的实现和注意事项,包括同步调用的原地等待特性、异步调用的回调函数机制、半同步调用的等待机制以及如何取消RPC调用。通过代码示例和运行结果展示了各种调用方式的特点。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
















 1283
1283

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








