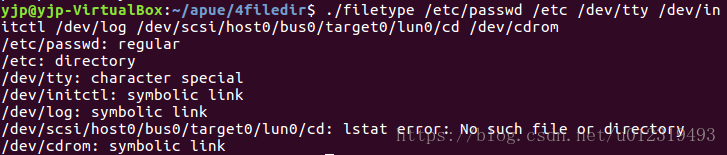
对每个命令函参数打印文件类型
#include "apue.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
struct stat buf;
char *ptr;
for(i=1; i<argc; i++)
{
printf("%s: ", argv[i]);
/*
int lstat(const char *restrict pathname, struct stat *restrict buf);
返回改符号链接的有关信息
struct stat
{
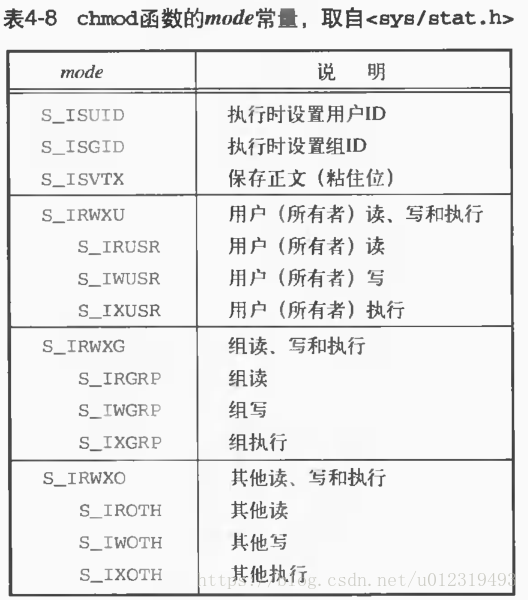
mode_t st_mode; file type & mode (permissions)
ino_t st_ino; i-node number (serial number)
dev_t st_dev; device number (file system)
dev_t st_rdev; device nummber for special files
nlink_t st_nlink; number of links
uid_t st_uid; user ID of owner
gid_t st_gid; group ID of owner
off_t st_size; size in bytes, for regular files
time_t st_atime; time of last modification
time_t st_mtime; time of last modification
time_t st_ctime; time of last file status change
blksize_t st_blksize; best I/O block size
blkcnt_t st_blocks; number of disk blocks allocated
}
*/
if(lstat(argv[i], &buf) < 0)
{
err_ret("lstat error");
continue;
}
if(S_ISREG(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "regular";
else if (S_ISDIR(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "directory";
else if(S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "character special";
else if(S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "block special";
else if(S_ISFIFO(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "fifo";
else if(S_ISLNK(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "symbolic link";
else if(S_ISSOCK(buf.st_mode))
ptr = "socket";
else
ptr = "** unkown mode **";
printf("%s\n", ptr);
}
exit(0);
}
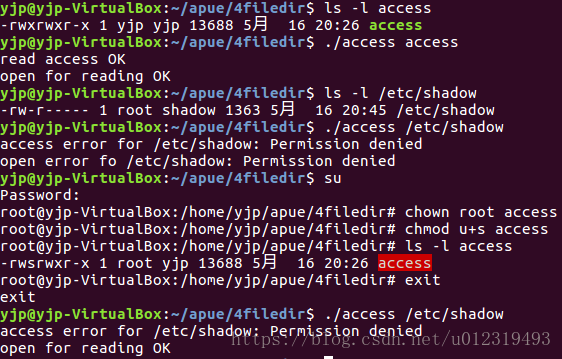
access函数实例
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if(argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: a.out <pathname>");
/*
int access(const char *pathname, int mode);
按实际用户ID和实际组ID进行访问权限测试
mode:
R_OK 测试读权限
W_OK 测试写权限
X_OK 测试执行权限
F_OK 测试文件是否存在
*/
if(access(argv[1], R_OK)< 0)
err_ret("access error for %s", argv[1]);
else
printf("read access OK\n");
/*
open按进程的有效用户ID和有效组ID进程访问权限测试
*/
if(open(argv[1], O_RDONLY) < 0)
err_ret("open error fo %s", argv[1]);
else
printf("open for reading OK\n");
exit(0);
}
umask函数实例
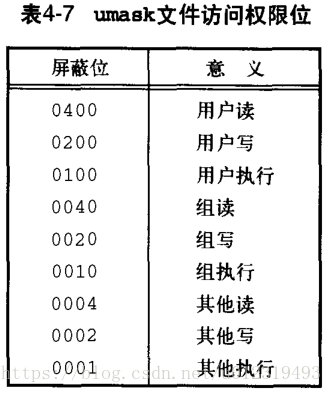
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
#define RWRWRW (S_IRUSR|S_IWUSR|S_IRGRP|S_IWGRP|S_IROTH|S_IWOTH)
int main(void)
{
/*
mode_t umask(mode_t cmask);
为进程设置“文件模式创建”屏蔽字,并返回以前的值
*/
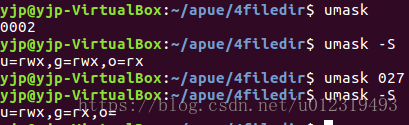
umask(0);
if(creat("foo", RWRWRW) < 0)
err_sys("create error for foo");
/* 禁止所有组和其他用户的访问权限 */
umask(S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH);
if(creat("bar", RWRWRW) < 0)
err_sys("create error for bar");
exit(0);
}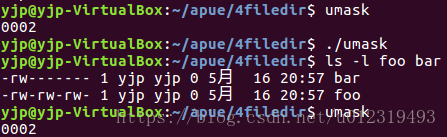
更改进程的文件模式创建屏蔽字不影响父进程的屏蔽字
chmod函数实例
#include "apue.h"
int main(void)
{
struct stat statbuf;
/* turn on set-group-ID and turn off group-execute */
if(stat("foo", &statbuf) < 0)
err_sys("stat error for foo");
/*
int chmod(const char *pathname, mode_t mode);
更改文件访问权限
进程的有效用户ID必须等于文件的所有者ID,或该进程必须具有超级用户权限
*/
if(chmod("foo", (statbuf.st_mode & ~S_IXGRP) | S_ISGID) < 0)
err_sys("chmod error for foo");
/* set absolute mode to "rw-r--r--" */
if(chmod("bar", S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IRGRP | S_IROTH) < 0)
err_sys("chmod error for bar");
exit(0);
}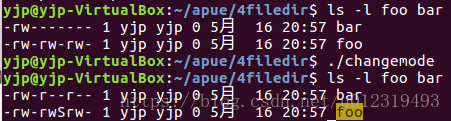
组执行位为S,表示设置组ID位已设置,同时,组执行位则未设置
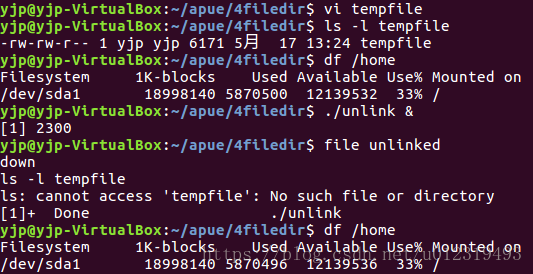
打开一个文件,然后unlink
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
int main(void)
{
if(open("tempfile", O_RDWR) < 0)
err_sys("open error");
/*
int unlink(const char *pathname);
删除一个现有的目录项
当打开文件进程数为0, 链接计数等于0时,才可被删除
*/
if(unlink("temfile") < 0)
err_sys("unlink error");
printf("file unlinked\n");
sleep(2);
printf("down\n");
exit(0);
}
utime函数实例
目的:将文件长度截段为0,但并不更改起访问时间及修改时间
#include "apue.h"
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <utime.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i, fd;
struct stat statbuf;
struct utimbuf timebuf;
for(i=1; i<argc; i++)
{
/* fetch current times */
if(stat(argv[i], &statbuf) < 0)
{
err_ret("%s: stat error", argv[i]);
continue;
}
/* truncate */
if((fd = open(argv[i], O_RDWR | O_TRUNC)) < 0)
{
err_ret("%s: open error", argv[i]);
continue;
}
close(fd);
timebuf.actime = statbuf.st_atime; /* access time */
timebuf.modtime = statbuf.st_mtime; /* modification time */
/*
int utime(const char *pathname, const struct utimbuf *times);
修改文件的访问和修改时间
struct utimebuf
{
time_t actime; access time
time_t modtime; modification time
}
*/
if(utime(argv[i], &timebuf) < 0)
{
err_ret("%s: utime error", argv[i]);
continue;
}
}
exit(0);
}yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ls -l changemode 查看长度和最后修改时间
-rwxr-x--- 1 yjp yjp 13712 5月 16 21:18 changemode
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ls -lu changemode 查看最后访问时间
-rwxr-x--- 1 yjp yjp 13712 5月 16 21:19 changemode
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ date 打印当天日期
2018年 05月 17日 星期四 13:45:18 CST
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ./utime changemode 运行程序
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ls -l changemode 检查最后修改时间
-rwxr-x--- 1 yjp yjp 0 5月 16 21:18 changemode
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ls -lu changemode 检查最后访问时间
-rwxr-x--- 1 yjp yjp 0 5月 16 21:19 changemode
yjp@yjp-VirtualBox:~/apue/4filedir$ ls -lc changemode 检查更改状态时间
-rwxr-x--- 1 yjp yjp 0 5月 17 13:45 changemode
递归降序遍历目录层次结构,并按文件类型计数
#include "apue.h"
#include <dirent.h>
#include <limits.h>
/* function type that is called for each filename */
typedef int Myfunc(const char *, const struct stat *, int);
static Myfunc myfunc;
static int myftw(char *, Myfunc *);
static int dopath(Myfunc *);
static long nreg, ndir, nblk, nchr, nfifo, nslink, nsock, ntot;
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int ret;
if(argc != 2)
err_quit("usage: ftw <starting-pathname>");
ret = myftw(argv[1], myfunc);
ntot = nreg + ndir + nblk + nchr + nfifo + nslink + nsock;
if(ntot == 0)
ntot = 1; /* avoid divide by 0; print 0 for all counts */
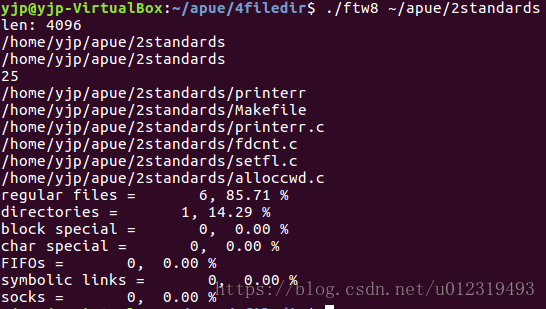
printf("regular files = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nreg, nreg*100.0/ntot);
printf("directories = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", ndir, ndir*100.0/ntot);
printf("block special = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nblk, nblk*100.0/ntot);
printf("char special = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nchr, nchr*100.0/ntot);
printf("FIFOs = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nfifo, nfifo*100.0/ntot);
printf("symbolic links = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nslink, nslink*100.0/ntot);
printf("socks = %7d, %5.2f %%\n", nsock, nsock*100.0/ntot);
exit(ret);
}
/*
Descend through the hierarchy, starting at "pathname".
The caller's func() is called for every file.
*/
#define FTW_F 1 /* file other than directory */
#define FTW_D 2 /* directory */
#define FTW_DNR 3 /* directory that can't be read */
#define FTW_NS 4 /* file that we can't stat */
static char *fullpath; /* contains full pathname for every file */
static int myftw(char *pathname, Myfunc *func)
{
int len = 4096;
/* malloc's for PATH_MAX+1 bytes
用来存放整个路径,包括子文件夹
*/
fullpath = malloc(len);
strncpy(fullpath, pathname, len); /* protect against */
fullpath[len-1] = 0;
printf("len: %d\n", len);
printf("%s\n", pathname);
printf("%s\n", fullpath);
printf("%d\n", strlen(fullpath));
return(dopath(func));
}
/*
Descend through the hierarchy, starting at "fullpath".
If "fullpath" is anyting other than a directory, we lstat() it,
call func(), and return. For a directory, we call ourself
recursively for each name in the directory.
*/
static int dopath(Myfunc *func)
{
struct stat statbuf;
/*
struct dirent
{
ino_t d_ino; i-node number
char d_name[NAME_MAX+1] null-terminated filename
}
*/
struct dirent *dirp;
DIR *dp;
int ret;
char *ptr;
if(lstat(fullpath, &statbuf) < 0) /* stat error */
return (func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_NS));
if(!S_ISDIR(statbuf.st_mode)) /* not a directory */
return (func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_F));
/*
It's a directory. First call func() for the directory,
then process each filename in the directory.
*/
if((ret = func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_D)) != 0)
return ret;
ptr = fullpath + strlen(fullpath); /* point to end of fullpath */
*ptr++ = '/';
*ptr = 0;
/*
DIR *opendir(const char *pathname);
执行初始化操作,时第一个readdir读目录的第一个目录项
*/
if((dp = opendir(fullpath)) == NULL) /* can't read directory */
return(func(fullpath, &statbuf, FTW_DNR));
/*
struct dirent *readdir(DIR *dp);
*/
while((dirp = readdir(dp)) != NULL)
{
if(strcmp(dirp->d_name, ".") == 0 ||
strcmp(dirp->d_name, "..") == 0)
continue; /* ignore dot and dot-dot */
strcpy(ptr, dirp->d_name); /* append name after slash */
printf("%s\n", fullpath);
if((ret = dopath(func)) != 0) /* recursive */
break; /* time to leave */
}
ptr[-1] = 0; /* erase everything from slash onwards */
/*
int closedir(DIR *dp);
*/
if(closedir(dp) < 0)
err_ret("can't close directory %s", fullpath);
return ret;
}
static int myfunc(const char *pathname, const struct stat *statptr, int type)
{
switch(type)
{
case FTW_F:
switch(statptr->st_mode & S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFREG: nreg++; break;
case S_IFBLK: nblk++; break;
case S_IFCHR: nchr++; break;
case S_IFIFO: nfifo++; break;
case S_IFLNK: nslink++; break;
case S_IFDIR: err_dump("for S_IFDIR for %s", pathname);
/* directories should have type = FTW_D */
default:
err_dump("wrong type %d for pathname %s", type, pathname);
break;
}
break;
case FTW_D:
ndir++;
break;
case FTW_DNR:
err_ret("can't read directory %s", pathname);
break;
case FTW_NS:
err_ret("stat error for %s", pathname);
break;
default:
err_dump("unkown type %d for pathname %s", type, pathname);
break;
}
return 0;
}
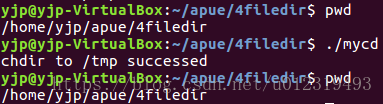
chdir函数实例
当前工作目录是进程的一个属性,所以只影响调用chdir的进程本身,不影响其他进程,即调用该程序不会得到希望的结果
#include "apue.h"
int main(void)
{
/*
int chdir(const char *pathname);
更改工作目录
*/
if(chdir("/tmp") < 0)
err_sys("chdir failed");
printf("chdir to /tmp successed\n");
exit(0);
}
getcwd函数实例
#include "apue.h"
int main(void)
{
char *ptr;
int size;
if(chdir("/tmp") < 0)
err_sys("chdir failed");
ptr = path_alloc(&size); /* our own function */
/*
char *getcwd(char *buf, size_t size);
得到当前工作目录
从当前工作目录.开始,用..目录找上一级目录,然后读目录项,
直到该目录项中的i节点编号与工作目录i节点编号相同,这就找到了对应的文件名
buf: 容纳绝对路径名+null终止字符
size: buf长度
*/
if(getcwd(ptr, size) == NULL)
err_sys("getcwd failed");
printf("cwd = %s\n", ptr);
exit(0);
}
打印st_dev和st_rdev值
#include "apue.h"
#ifdef SOLAPRIS
#include <sys/mkdev.h>
#endif
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
struct stat buf;
for(i=1; i<argc; i++)
{
printf("%s: ", argv[i]);
if(stat(argv[i], &buf) < 0)
{
err_ret("stat error");
continue;
}
/* 打印主设备号和从设备号 */
printf("dev = %d/%d", major(buf.st_dev), minor(buf.st_dev));
if(S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode) || S_ISBLK(buf.st_mode))
{
printf("(%s) rdev = %d/%d",
(S_ISCHR(buf.st_mode)) ? "character" : "block",
major(buf.st_rdev), minor(buf.st_rdev));
}
printf("\n");
}
exit(0);
}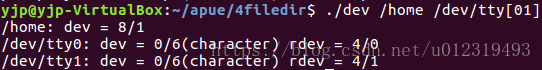
第一个是目录,后两个是设备
设备号不同,说明位于不同的文件系统
两个终端设备(st_dev)的文件名和i节点在设备0/6上(devfs伪文件系统),实际设备号是4/0和4/1





 本文通过多个示例程序介绍如何使用C语言进行文件类型的判断、文件权限的设置与查询、目录遍历等操作,深入理解文件系统的工作原理。
本文通过多个示例程序介绍如何使用C语言进行文件类型的判断、文件权限的设置与查询、目录遍历等操作,深入理解文件系统的工作原理。
















 317
317

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








