承接上文Spring源码-AnnotationConfigApplicationContext分析
在AnnotationConfigApplicationContext构造函数中,调用了register(componentClasses)将配置类转换为BeanDefinition注册到了Spring 容器中,在执行refresh()方法前beanDefinitionMap中内容如下,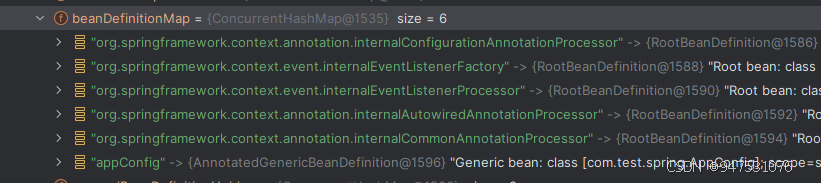
那其他的BeanDefinition什么时候解析呢?比如还有如下类
@Data
@Component
public class Cat {private String name;}
@Data
public class Dog {private String name;}
@Data
public class Person {private String name;}
@ComponentScan
@Configuration
@Import(Dog.class)
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public Person myPerson() {return new Person();}
}
答案是在refresh方法的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)中,该方法用来调用实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口和实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类。ConfigurationClassPostProcessor就实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,并且优先级最高。它就是专门负责将满足条件的类解析为BeanDefinition的。从源码注释可以看出这两个接口的作用。
BeanFactoryPostProcessor与BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口
BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口:用于在Spring加载BeanDefinition之后、实例化Bean之前对BeanDefinition进行修改,可以参考PropertyResourceConfigurer其具体实现。
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口:用于注册新的bean定义,这个bean也可以是BeanFactoryPostProcessor。也不限于只注册1个,可以参考mybatis-spring中的MapperScannerConfigurer类,直接扫描指定包下的所有Mapper封装成 BeanDefinition 并加载到 BeanFactory 中。
两个接口的区别
BeanFactoryPostProcessor用于修改bean定义;
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor用于新增bean定义,比BeanFactoryPostProcessor更早调用,继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
两个接口的注册方式
① 硬编码。比如通过BeanConfigurableApplicationContext的addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor)方法;该方式Order失效(也就是不会排序)。另外也有其他方式,比如调用registerBean方法。
② 通过bean定义(配置的方式),Spring会自动检测,并在创建任何其他 bean 之前调用。比如:
@Component
public class MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法执行了");
}
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
BeanDefinition person = registry.getBeanDefinition("myPerson");
person.setScope("prototype");
registry.registerBeanDefinition("myPerson",person);
System.out.println("MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessBeanFactory方法执行了");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE;
}
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法源码解析
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (!NativeDetector.inNativeImage() && beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()
//beanFactoryPostProcessors为通过调用addBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
//存放已经执行过的PostProcessor
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
//beanFactory是DefaultListableBeanFactory,实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
//BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承自BeanFactoryPostProcessor
//将实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的类分开保存到对应的list中
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//如果是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,直接调用
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//这里调用的是容器中已解析为BeanDefinition的且实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的PostProcessor
//调用顺序:PriorityOrdered、Ordered、剩下的
//如果未向容器中手动注册实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的BeanDefinition,这里满足条件的就只有ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,
//这是因为在AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader对象创建时注册了internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor对应的BeanDefinition,
//此时其他的类尚未解析为BeanDefinition,ConfigurationClassPostProcessor就是专门来做这个的。
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
//先调用实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//注册Bean,这里已经实例化了,后面可以直接用了
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
//此时ConfigurationAnnotationProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法得到调用,
//执行完成后,所有符合条件的类都会被解析为BeanDefinition,注册到Spring容器中
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
//其次调用实现Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,因为上一步已经注册了所有的BeanDefinition,
//所有通过配置的方式注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接下来就可以被调用了
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
//最后调用剩下的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry, beanFactory.getApplicationStartup());
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
//调用BeanFactoryPostProcessors的postProcessBeanFactory方法,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors先执行
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
//接下来执行通过配置方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,同样调用顺序为:PriorityOrdered、Ordered、剩下的
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(orderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.size());
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
}
总结
1、在refresh方法的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)中,实现了BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类都会被调用。
2、ConfigurationClassPostProcessor实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口,并且优先级最高,除了硬编码的之外,它最先得到执行,执行完后所有满足条件的类都将被解析为BeanDefinition并注册到Spring容器中。
3、BeanFactoryPostProcessor用于修改bean定义,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor用于新增bean定义,对于动态添加或修改 bean 定义非常有用。
4、注册BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor可以通过硬编码,此种方式执行顺序得不到保证;也可以通过Bean定义(配置)方式,Spring自动检测,有执行顺序。
5、BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor执行顺序
① 调用硬编码的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
② 调用配置的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法,优先级:PriorityOrdered>Ordered>剩余的
③ 到这里BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor自己的方法调完了,开始调用父接口BeanFactoryPostProcessors的postProcessBeanFactory方法
④ 调用硬编码的BeanFactoryPostProcessors接口的postProcessBeanFactory方法
⑤ 调用配置的BeanFactoryPostProcessors接口的postProcessBeanFactory方法,优先级:PriorityOrdered>Ordered>剩余的
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








