项目说明
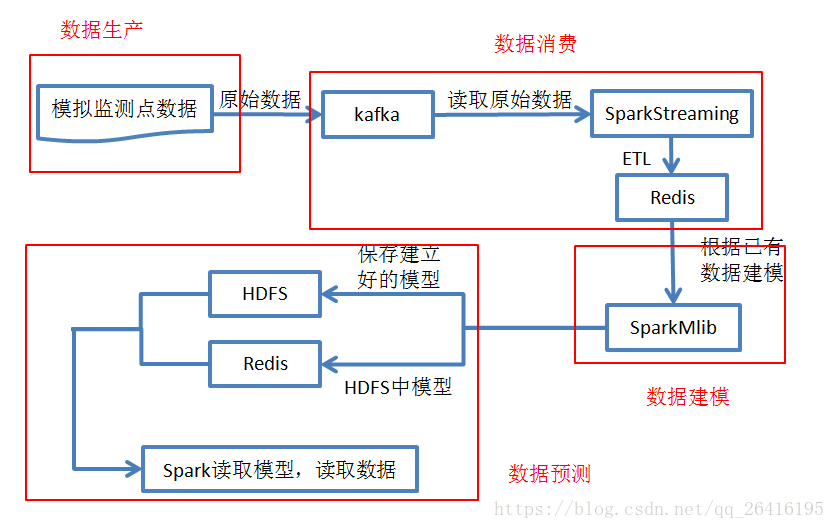
这是一个依据尚硅谷公开课(智慧出行)搭建的项目,仅实现了三个模块,包括“数据生产、消费、建模”。
开发工具及环境说明:Intellij IDEA,Scala,Redis,Kafka
kafka
生产者生产数据:
字段:卡口id,车速
kafka外部配置文件kafka.properties
# 设置生产者属性
# 9092 kafka默认server端口
# bootstrap.servers
# TYPE list DEFAULT localhost:9092
# 用于建立与kafka集群连接的host/port组。
# A list of host/port pairs to use for establishing the initial connection to the Kafka cluster.
bootstrap.servers = 10.25.34.103:9092, 10.25.34.104:9092, 10.25.34.105:9092
# 消息以“键-值”形式存入消息队列
# 在使用Kafka发送接收消息时,producer端需要序列化,consumer端需要反序列化
# 设置“键-值”的序列化方式(涉及跨进程通讯,一定要序列化)
# (在External Libraries的maven的kafka依赖库中查找,copy reference)
# key.serializer(value.serializer):
# TYPE class
# Serializer class for key(value) that implements the Serializer interface.
key.serializer = org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value.serializer = org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
# kafka为了避免信息丢失,会备份信息
# acks :
# producer要求在leader在判定某条消息是否写入完成之前需要收到的确认写入的个数。这个值控制了发送消息的可用性。
# The number of acknowledgments the producer requires the leader to have received before considering a request complete.
# This controls the durability of records that are sent.
# The following settings are allowed:
# acks=0 If set to zero then the producer will not wait for any acknowledgment from the server at all.
# 如果设置为0,则表明producer不要等待server的任何写入确认。记录会立刻添加到socket buffer,然后认为是发送了。
# 这种情况下,无法保证server是否确实收到了消息,同时retries这个配置不起作用,请求返回应答中的offset通常设置为-1
# acks=1 This will mean the leader will write the record to its local log but will respond without awaiting full acknowledgement from all followers.
# 只要leader确认写入本地日志了就可以返回应答了,不需要等待所有follower同步成功。
# 这种情况下,如果leader写入本地之后立马返回确认应答,但是此时follower没有同步这条消息,同时leader如果挂掉,则这条消息丢失了
# acks=all This means the leader will wait for the full set of in-sync replicas to acknowledge the record.
# 这种情况下要求leader在收到所有活跃备份节点确认写入的消息之后才能回馈确认写入的消息给producer。
# 这种方式可以保证只要有一个备份节点活跃,消息就不会丢。这是最强的保证。这个和acks=-1相同
acks = all
# retries:
# 设置重试次数可以在发送失败时进行重试,提高发送的可靠性。
# 注意,这个重试和客户端发生接受错误的重试没有区别。
# 允许重试,而不设置max.in.flight.request.per.connection为1的话,将可能调整消息的发送次序,
# 例如两组批量消息发送到同一个partition,第一个失败了然后重试,但是第二个发送成功了,实际的结果可能是第二个小组在partition中出现的更早。
retries = 0
# 设置主题
kafka.topics = traffic
# 设置消费者属性
# Consumer端核心的配置是group.id(必需)、zookeeper.connect
# group.id
# TYPE String
# 决定该Consumer归属的唯一组ID
# A unique string that identifies the consumer group this consumer belongs to.
# This property is required if the consumer uses either the group management functionality by using subscribe(topic) or the Kafka-based offset management strategy.
group.id = g_traffic1
# enable.auto.commit:
# TYPE boolean DEFAULT true
# If true the consumer's offset will be periodically committed in the background.
enable.auto.commit = true
# 每过30s自动保存
# auto.commit.interval.ms:
# TYPE int DEFAULT 5000
# The frequency in milliseconds that the consumer offsets are auto-committed to Kafka if enable.auto.commit is set to true.
auto.commit.interval.ms = 30000
# 设置follower和leader的同步时间
# zookeeper.sync.time.ms
# DEFAULT 2000
# How far a ZK follower can be behind a ZK leader
zookeeper.sync.time.ms = 250
# num.io.threads
# TYPE int DEFAULT 8 VALID VALUES [1,...]
# The number of io threads that the server uses for carrying out network requests
num.io.threads = 12
# batch.size:
# TYPE int DEFAULT 16384 VALID VALUES [0,...]
# The producer will attempt to batch records together into fewer requests whenever multiple records are being sent to the same partition.
# This helps performance on both the client and the server.
# This configuration controls the default batch size in bytes.
batch.size = 65536
# buffer.memory
# TYPE long DEFAULT 33554432 VALID VALUES [0,...]
# The total bytes of memory the producer can use to buffer records waiting to be sent to the server.
# If records are sent faster than they can be delivered to the server the producer will block for max.block.ms after which it will throw an exception.
buffer.memory = 524288
# 日志默认保存时间168小时
# log.retention.hours
# TYPE int DEFAULT 168
# The number of hours to keep a log file before deleting it (in hours), tertiary to log.retention.ms property
log.retention.hours = 5
启动集群的zookeeper服务 (全部节点都要启动)
zkServer.sh start
启动hadoop服务(主节点启动)
start-all.sh
启动kafka集群(全部节点都要启动)
kafka-server-start.sh /home/hadoop/kafka_2.11/config/server.properties
创建kafka主题traffic(一个节点执行)
kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper centosa:2181 --topic traffic --create --replication-factor 1 --partitions 3
检查主题
kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper centosa:2181
创建kafka的控制台消费者
kafka-console-consumer.sh --zookeeper centosa:2181 --topic traffic --from-beginning
(如果kafka.properties中的bootstrap.servers中使用的是ip地址,则需要将名称改为ip地址)
–from-beginning可以去掉
Scala生产数据代码
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.its</groupId>
<artifactId>tf_producer</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.kafka/kafka-clients -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId>
<version>1.1.0</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/com.alibaba/fastjson -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.47</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
创建读取配置属性kafka.properties的工具类,object PropertyUtil
package utils
import java.util.Properties
// PropertyUtil读取配置文件的工具类
object PropertyUtil {
// 1 import java.util.Properties
val properties = new Properties
// 4 异常处理,加try catch语句(ctrl Alt + t)
try {
// 2 加载配置文件,将其转换为输入流
val inputStream = ClassLoader.getSystemResourceAsStream("kafka.properties")
// 3 加载配置文件属性
properties.load(inputStream)
} catch {
// 5
case e: Exception => e.getStackTrace
} finally {}
// 6 封装一个方法用于快速获取“key-value”
def getProperty(key: String): String = properties.getProperty(key)
}
完整的Producer.scala代码:
package main
import java.text.DecimalFormat
import java.util
import java.util.Calendar
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON
import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.{KafkaProducer, ProducerRecord}
import utils.PropertyUtil
import scala.util.Random
object Producer {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
// 1 读取kafka配置信息
// import utils.PropertyUtil
val props = PropertyUtil.properties
// 2 创建kafka生产者对象
// import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.KafkaProducer
val producer = new KafkaProducer[String, String](props)
// 3 模拟生产实时数据,每5分钟切换一次车辆速度
// import java.util.Calendar
// getTimeInMillis得到当前毫秒数, / 1000 得到当前“秒”
var startTime = Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis / 1000
// 4 定义切换周期(单位:s)
val trafficCycle = 10
// 5 利用循环,不停的开始产生模拟数据
while (true) {
// 6 模拟产生监测点(模拟20个监测点id)
// import java.text.DecimalFormat
val randomMonitorID = new DecimalFormat("0000").format(Random.nextInt(20) + 1)
// 7 定义随机速度
var randomSpeed = ""
// 8 当前时间获取(数据产生时间)
val currentTime = Calendar.getInstance().getTimeInMillis / 1000
// 9 速度切换判断,模拟(堵车)切换周期:5分钟
if (currentTime - startTime > trafficCycle - 1) {
// 10 产生随机速度数据[0, 16)(单位:km/h)
randomSpeed = new DecimalFormat("000").format(Random.nextInt(16))
// 11 在堵车5分钟后,结束堵车状态
if (currentTime - startTime > (trafficCycle - 1) * 2) {
startTime = currentTime
}
} else {
// 12 产生随机速度数据[30, 61)(单位:km/h)
randomSpeed = new DecimalFormat("000").format(Random.nextInt(31) + 30)
}
// 13 打印模拟数据,测试
// println(randomMonitorID + "," + randomSpeed)
// 15 json序列化数据后,再上传数据到kafka中
// import java.util(貌似与scala中的HashMap冲突,scala允许无缝连接java的api)
val jsonMap = new util.HashMap[String, String]()
// 16 monitor_id到json
jsonMap.put("monitor_id", randomMonitorID)
// 17 Speed到json
jsonMap.put("speed", randomSpeed)
// 18 序列化json
// import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON
val event = JSON.toJSON(jsonMap)
// 19 查看序列化后结果,json字符串
println(event)
// 20 将消息传送到kafka
// import org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.ProducerRecord
producer.send(new ProducerRecord[String, String](props.getProperty("kafka.topics"), event.toString))
// 14 减缓线程,便于观察
//Thread.sleep(200)
}
}
}
运行 scala Producer.scala
数据生成完成








 该博客介绍了基于尚硅谷公开课的智慧出行项目,项目涵盖了数据生产、消费和建模。使用Intellij IDEA、Scala、Redis和Kafka作为开发工具和环境。详细步骤包括启动Zookeeper、Hadoop、Kafka集群,创建Kafka主题traffic,以及用Scala编写数据生产代码并运行。
该博客介绍了基于尚硅谷公开课的智慧出行项目,项目涵盖了数据生产、消费和建模。使用Intellij IDEA、Scala、Redis和Kafka作为开发工具和环境。详细步骤包括启动Zookeeper、Hadoop、Kafka集群,创建Kafka主题traffic,以及用Scala编写数据生产代码并运行。
















 2054
2054

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








