多线程
main( )方法是主线程入口,关键词Thread
一、线程改名
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t=new Thread("线程1");
Thread th=Thread.currentThread();
th.setName("主线程");
System.out.println(th.getName());
System.out.println(t.getName());
}
二、线程创建
线程的创建方式:
1. 继承Thread类
2. 实现Runnable接口
3. 实现Callable接口
方法1:
继承Thread类
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <=100 ; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TestThread t1=new TestThread();
// t1.setName("线程1");
// TestThread t2=new TestThread();
// t2.setName("线程2");
// t1.start();
// t2.start();
TestThread t=new TestThread();
Thread th1=new Thread(t);
th1.setName("线程1");
Thread th2=new Thread(t);
th2.setName("线程2");
th1.start();
th2.start();
}
方法2:
使用Runnable接口
public class TestRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 1; i <=100 ; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+":"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestRunnable runnable= new TestRunnable();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"线程1");
Thread t2=new Thread(runnable,"线程2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
方法3:
使用Callable接口
public class TestCallable implements Callable<Integer> {
@Override
public Integer call() {
for (int i = 0; i <10 ; i++) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":"+(i+1));
}
return 3;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
TestCallable t=new TestCallable();
FutureTask<Integer> f=new FutureTask<>(t);
Thread th=new Thread(f);
th.start();
System.out.println(f.get());
}
}
区别:
- 继承Thread类
编写简单,可直接操作线程
适用于单继承 - 实现Runnable接口
避免单继承局限性
便于共享资源
Callable接口与Runnable接口类似,多一个返回值
三、线程的状态及调度
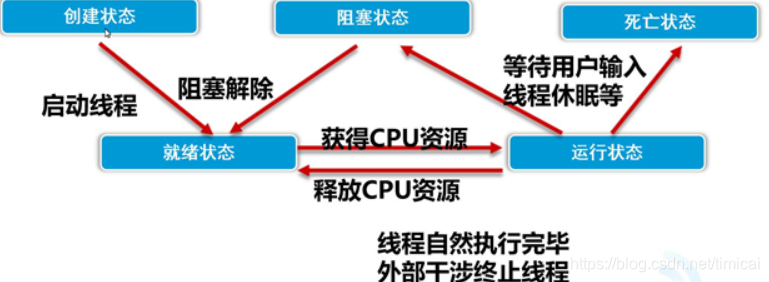
线程调度:
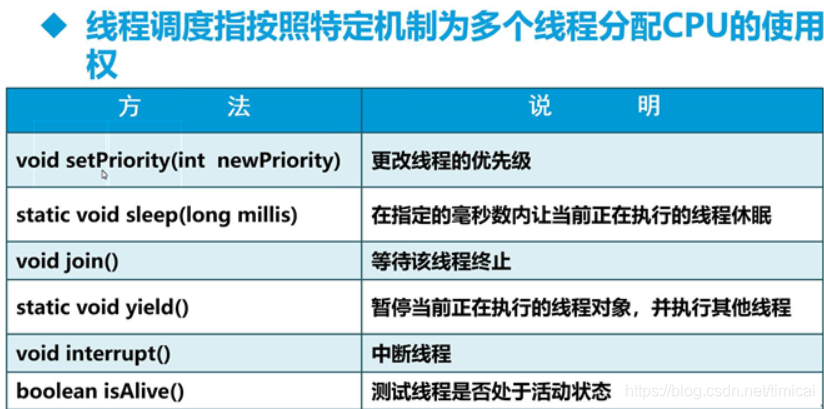
setPriority( ) 线程优先级,1-10,默认5
sleep( ) 一般在run( )中用,表示线程休眠
join( ) 一般加在主线程中,主线程等待需要执行的子程执行完后再继续执行
yield( ) 在run( )方法中添加,表示执行一次后礼让,之后再次抢资源,(只会提供一种可能,不保证一定会礼让)
例:
需求说明
某科室一天需看普通号50个,特需号10个,
特需号看病时间是普通号的2倍,
开始时普通号和特需号并行叫号,叫到特需号的概率比普通号高,
当普通号叫完第10号时,要求先看完全部特需号,再看普通号,
使用多线程模拟这一过程
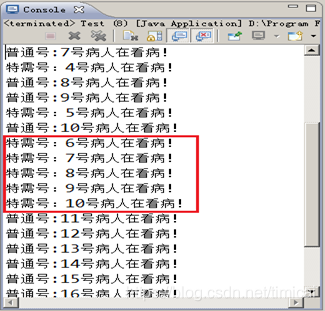
public class Call implements Runnable{
public void run(){
for (int i = 1; i <=10 ; i++) {
System.out.println("特需号"+i+"看病中");
try {
Thread.sleep(20);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable runnable=new Call();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"普通号");
t1.setPriority(8);
t1.start();
for (int i = 1; i <=50 ; i++) {
System.out.println("普通号"+i);
Thread.sleep(10);
if (i==10){
t1.join();
}
}
}
}
四、线程同步
synchronized( )方法: -->线程安全
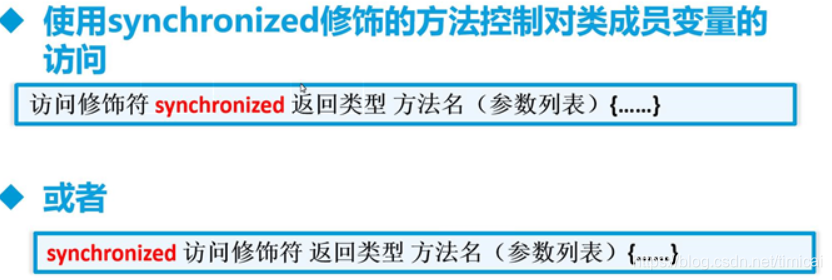

例:
模拟抢票
public class TestTicket implements Runnable{
int ticket=100;
int sale=0;
@Override
public void run() {
while(ticket>0){
synchronized (this){
ticket--;
sale++;
if (ticket<0)return;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买到了第"
+sale+"张票,还剩"+ticket);
try {
Thread.sleep(30);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable=new TestTicket();
Thread t1=new Thread(runnable,"水友1");
Thread t2=new Thread(runnable,"水友2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}





 本文主要介绍了Java中的多线程,包括线程改名、创建线程的三种方式(Thread继承、Runnable接口实现、Callable接口实现)、线程状态与调度(如线程优先级、休眠、等待和礼让),以及线程同步的概念和synchronized关键字的应用。
本文主要介绍了Java中的多线程,包括线程改名、创建线程的三种方式(Thread继承、Runnable接口实现、Callable接口实现)、线程状态与调度(如线程优先级、休眠、等待和礼让),以及线程同步的概念和synchronized关键字的应用。
















 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








