from typing import Tuple
import torch
def reshape_for_broadcast(freqs_cis: torch.Tensor, x: torch.Tensor):
"""
Helper function to reshape frequency tensor to have the same shape as the target tensor 'x'
for the purpose of broadcasting the frequency tensor during element-wise operations.
Args:
freqs_cis (torch.Tensor): Frequency tensor to be reshaped.
x (torch.Tensor): Target tensor for broadcasting compatibility.
Returns:
torch.Tensor: Reshaped frequency tensor.
Raises:
AssertionError: If the frequency tensor doesn't match the expected shape.
AssertionError: If the target tensor 'x' doesn't have the expected number of dimensions.
"""
ndim = x.ndim
assert 0 <= 1 < ndim
assert freqs_cis.shape == (x.shape[1], x.shape[-1])
shape = [d if i == 1 or i == ndim - 1 else 1 for i, d in enumerate(x.shape)]
return freqs_cis.view(shape)
#########填充维度,方便计算
def apply_rotary_emb(
query: torch.Tensor,
key: torch.Tensor,
head_dim: int,
max_seq_len: int,
theta: float = 10000.0,
) -> Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]:
"""
Apply rotary embeddings to input tensors using the given frequency tensor.
Args:
query (torch.Tensor): Query tensor to apply rotary embeddings. Shape: (batch_size, seqlen, n_local_heads, head_dim)
key (torch.Tensor): Key tensor to apply rotary embeddings. Shape: (batch_size, seqlen, n_local_kv_heads, head_dim)
head_dim (int): Dimension of each attention head.
max_seq_len (int): Maximum sequence length supported by model.
Returns:
Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]: Tuple of modified query tensor and key tensor with rotary embeddings.
"""
_, seqlen, _, _ = query.shape # 获取查询张量的形状参数
device = query.device # 获取查询张量的设备信息(如在 CPU 或 GPU 上)
seq_len, batch_size, num_heads = query.size(1), query.size(0), query.size(2) # 获取序列长度、批次大小和头部数量
# reshape xq and xk to match the complex representation
query_real, query_imag = query.float().reshape(query.shape[:-1] + (-1, 2)).unbind(-1) # 将查询张量重塑并分为实部和虚部
key_real, key_imag = key.float().reshape(key.shape[:-1] + (-1, 2)).unbind(-1) # 将键张量重塑并分为实部和虚部
inv_freq = 1.0 / (theta ** (torch.arange(0, head_dim, 2.0, device=device) / head_dim))
pos_seq = torch.arange(0, seqlen, device=device)
sinusoid_inp = torch.einsum("i,j->ij", pos_seq, inv_freq) #
sin = torch.sin(sinusoid_inp)
cos = torch.cos(sinusoid_inp)
# Use the reshape_for_broadcast function to reshape cos and sin terms for broadcasting
cos_rotations = reshape_for_broadcast(cos, query_real) # 调整余弦值张量的形状以进行广播
sin_rotations = reshape_for_broadcast(sin, query_imag) # 调整正弦值张量的形状以进行广播
# Apply the rotations to the real and imaginary parts
query_rot_real = cos_rotations * query_real - sin_rotations * query_imag # 应用旋转到查询张量的实部
query_rot_imag = sin_rotations * query_real + cos_rotations * query_imag # 应用旋转到查询张量的虚部
key_rot_real = cos_rotations * key_real - sin_rotations * key_imag # 应用旋转到键张量的实部
key_rot_imag = sin_rotations * key_real + cos_rotations * key_imag # 应用旋转到键张量的虚部
# Reassemble the real and imaginary parts back into the original format
# query_out = torch.cat([query_rot_real, query_rot_imag], dim=-1).view_as(query) # 重新组合并调整查询张量的形状
# key_out = torch.cat([key_rot_real, key_rot_imag], dim=-1).view_as(key) # 重新组合并调整键张量的形状
query_out = torch.stack((query_rot_real, query_rot_imag), dim=-1).flatten(-2)
key_out = torch.stack((key_rot_real, key_rot_imag), dim=-1).flatten(-2)
return query_out, key_out # 返回包含旋转位置嵌入的查询和键张量
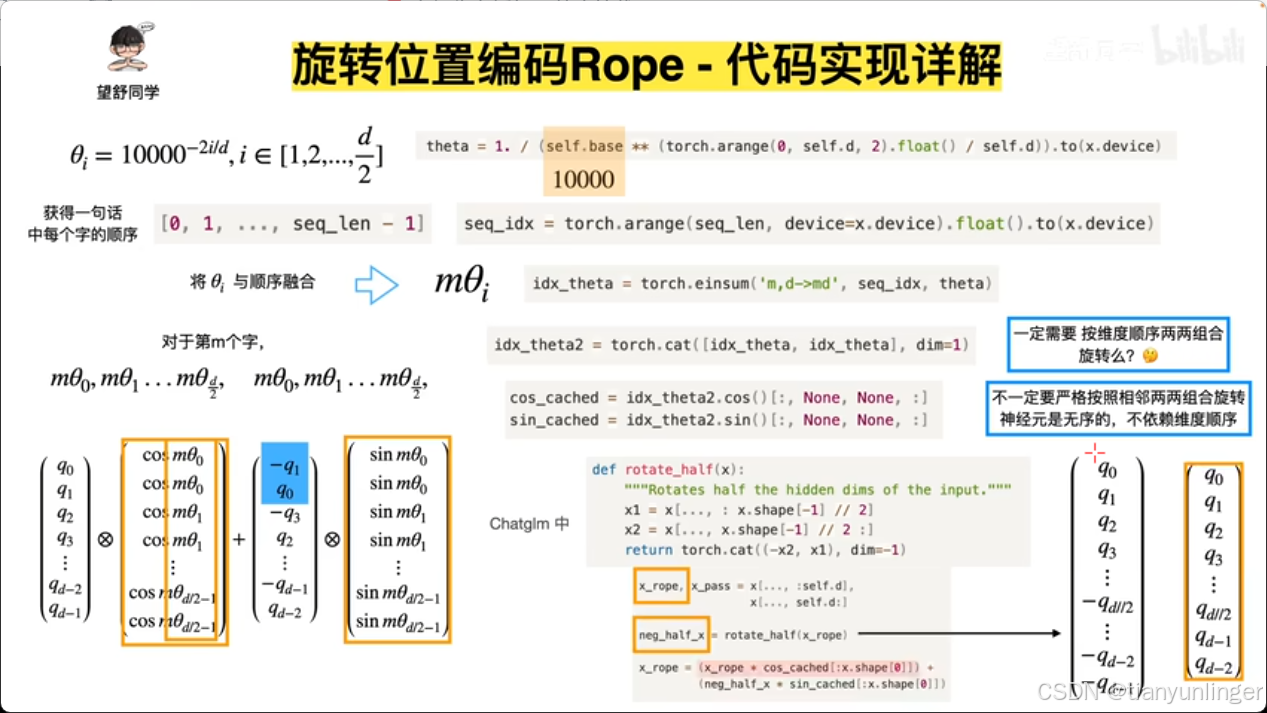
上述代码和b站这个up讲的,或者一般的rope代码有两点不同
1,q0,q1,q2,q3…和用两个相同cos,sin张量堆叠起来的新张量点乘的操作,变成先将张量q分离成q0,q2,q4…和q1,q3,q5…两个张量去和相同的cos,sin张量点乘
2,补全张量维度由代码
cos_cached idx_theta2.cos()[:,None,None,:]
sin_cached idx_theta2.sin()[:,None,None,:]
变成
cos_rotations = reshape_for_broadcast(cos, query_real) # 调整余弦值张量的形状以进行广播
sin_rotations = reshape_for_broadcast(sin, query_imag) # 调整正弦值张量的形状以进行广播





















 437
437










