看到 c++11 中 enum 的两个新用法,记录一下。
1,限制枚举变量值大小
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum DEV_TYPE: unsigned char
{
DEV_A,
DEV_B,
DEV_C,
DEV_D = 255
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}
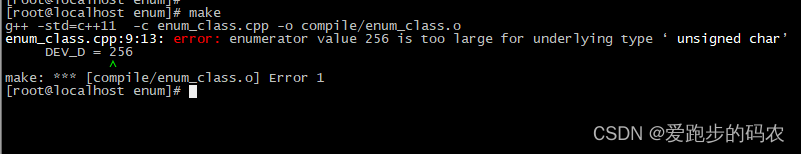
类似于 class 中的继承的语法,这里的作用是限制了 enum 元素的最大值,如上 DEV_D 的最大值就是 255,如果赋值大于 255 会怎样呢?
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum DEV_TYPE: unsigned char
{
DEV_A,
DEV_B,
DEV_C,
DEV_D = 256
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}
编译失败:
2,枚举类
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
enum class COLOR
{
white,
red,
black,
gray,
green
};
int main()
{
return 0;
}
这样用有什么好处----限制了枚举的变量的作用域。如果没有这个作用域是怎样的呢?如:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
enum COLOR
{
white,
red,
black,
gray,
green
};
bool red = true;
return 0;
}
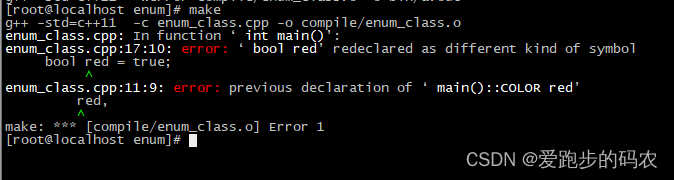
编译错误,因为这个main作用域内已经有了一个枚举类型值 red。改用枚举类就不一样了:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main()
{
enum class COLOR
{
white,
red,
black,
gray,
green
};
bool red = true;
//使用域限定符
COLOR color = COLOR::red;
return 0;
}
有了枚举类限定了枚举类型的作用域,减少了命名空间的冲突。





 文章介绍了C++11对enum的两个新特性:一是可以限制枚举变量的值大小,例如通过`enumDEV_TYPE:unsignedchar`限制最大值;二是引入了枚举类(enumclass),这可以限制枚举的作用域,避免命名冲突。通过枚举类,可以更安全地使用枚举,比如在示例中防止了与全局变量red的冲突。
文章介绍了C++11对enum的两个新特性:一是可以限制枚举变量的值大小,例如通过`enumDEV_TYPE:unsignedchar`限制最大值;二是引入了枚举类(enumclass),这可以限制枚举的作用域,避免命名冲突。通过枚举类,可以更安全地使用枚举,比如在示例中防止了与全局变量red的冲突。
















 1482
1482

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








