创新扩散理论, 美国学者Rogers提出的关于推广传播新观点新技术的理论。
创新扩散,会经历五个阶段: Knowledge, Persuasion, Decision, Implementation, Confirmation:
| Stage | Definition |
|---|---|
| Knowledge | In this stage the individual is first exposed to an innovation but lacks information about the innovation. During this stage of the process the individual has not been inspired to find more information about the innovation. |
| Persuasion | In this stage the individual is interested in the innovation and actively seeks information/detail about the innovation. |
| Decision | In this stage the individual takes the concept of the change and weighs the advantages/disadvantages of using the innovation and decides whether to adopt or reject the innovation. Due to the individualistic nature of this stage Rogers notes that it is the most difficult stage to acquire empirical evidence (Rogers 1964, p. 83). |
| Implementation | In this stage the individual employs the innovation to a varying degree depending on the situation. During this stage the individual determines the usefulness of the innovation and may search for further information about it. |
| Confirmation | In this stage the individual finalizes his/her decision to continue using the innovation. This stage is both intrapersonal (may cause cognitive dissonance) and interpersonal, confirmation the group has made the right decision. |
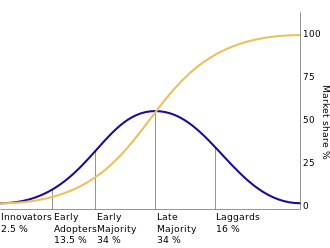
而在这个过程中, 创新扩散的对象, Rogers划分为5类: Innovators, Early adopters, Early Majority, Late Majority, Laggards.
| Adopter category | Definition |
|---|---|
| Innovators | Innovators are the first individuals to adopt an innovation. Innovators are willing to take risks, youngest in age, have the highest social class, have great financial liquidity, are very social and have closest contact to scientific sources and interaction with other innovators. Risk tolerance has them adopting technologies which may ultimately fail. Financial resources help absorb these failures. (Rogers 1962 5th ed, p. 282) |
| Early adopters | This is the second fastest category of individuals who adopt an innovation. These individuals have the highest degree of opinion leadership among the other adopter categories. Early adopters are typically younger in age, have a higher social status, have more financial liquidity, advanced education, and are more socially forward than late adopters. More discrete in adoption choices than innovators. Realize judicious choice of adoption will help them maintain central communication position (Rogers 1962 5th ed, p. 283). |
| Early Majority | Individuals in this category adopt an innovation after a varying degree of time. This time of adoption is significantly longer than the innovators and early adopters. Early Majority tend to be slower in the adoption process, have above average social status, contact with early adopters, and seldom hold positions of opinion leadership in a system (Rogers 1962 5th ed, p. 283) |
| Late Majority | Individuals in this category will adopt an innovation after the average member of the society. These individuals approach an innovation with a high degree of skepticism and after the majority of society has adopted the innovation. Late Majority are typically skeptical about an innovation, have below average social status, very little financial liquidity, in contact with others in late majority and early majority, very little opinion leadership. |
| Laggards | Individuals in this category are the last to adopt an innovation. Unlike some of the previous categories, individuals in this category show little to no opinion leadership. These individuals typically have an aversion to change-agents and tend to be advanced in age. Laggards typically tend to be focused on "traditions", likely to have lowest social status, lowest financial liquidity, be oldest of all other adopters, in contact with only family and close friends. |
在传播早期, 采用者很少, 进展很缓慢。 但采用者比例扩大到10% - 25%时, 进展开始加速;等到了饱和期之后, 增长空间变小, 趋势变得缓和。
The diffusion of innovations according to Rogers. With successive groups of consumers adopting the new technology (shown in blue), its market share (yellow) will eventually reach the saturation level. In mathematics the S curve is known as the
logistic function
.
整个创新扩散能否成功, 关键在于能否从早期市场(Innovators, Early adopters)跨越到主流市场(Early Majority, Late Majority), 这是成败的关键。Rogers 认为影响创新能否成功被采纳接受的关键因素为: Reletive Advantage(相对优越性), Compatibility(兼容性), Complexity or Simplicity(复杂性), Trialability(可试用性), Observability(可观察性)
| Factor | Definition |
|---|---|
| Relative Advantage | How improved an innovation is over the previous generation. |
| Compatibility | The level of compatibility that an innovation has to be assimilated into an individual’s life. |
| Complexity or Simplicity | If the innovation is perceived as complicated or difficult to use, an individual is unlikely to adopt it. |
| Trialability | How easily an innovation may be experimented. If a user is able to test an innovation, the individual will be more likely to adopt it. |
| Observability | The extent that an innovation is visible to others. An innovation that is more visible will drive communication among the individual’s peers and personal networks and will in turn create more positive or negative reactions. |
参考文献
























 812
812

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








