找工作刷题中···
其实这个学数据结构与算法的时候就刷过了,但是!又忘记了呜呜呜。
首先中序遍历指的是先左节点再根节点,再右节点。
题目一,中序遍历
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> sta = new Stack<TreeNode>();
//这里要用栈,可以用Stack
//也可以用双端队列实现,Deque<TreeNode> sta = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();这里底层用链表实现
while(!sta.isEmpty() || root != null ){
while(root != null){
sta.push(root);
root = root.left;
}//一直找到最左边的节点才开始遍历,
root = sta.pop();
arr.add(root.val);//左边放入
root = root.right;//开始遍历右子树
}
return arr;
}
}其实我大致还是有点迷惑没看懂,多做几遍吧。
题目二
这个题不算中序遍历···是我以为是中序的
错误答案
一开始发现,如果对称的话,中序遍历获得的数组是对称的。
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root.left == null || root.right == null){
return true;
}
//中序遍历后判断是否对称
List<Integer> arr = new ArrayList<Integer>();//后面要写ArrayList
Deque<TreeNode> st = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
st.push(root);
while(!st.isEmpty() && root != null){
while(root != null){
st.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = st.pop();
arr.add(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
int len = arr.size() - 1;
for(int i = 0; i <= len / 2 ; i ++){
int j = len - i;
if(arr.get(j)!= arr.get(i)){//用get(i)获取数据,不是中括号
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}但是这个答案只对了一半
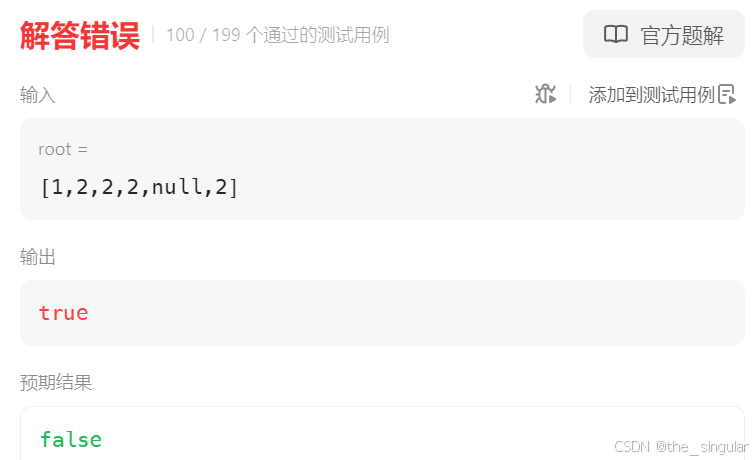
从这个样例也能看出来,如果是下面这样,中序遍历的数组依旧是对称的【2,2,1,2,2】
太狗了真的
正确答案
思路
如果一个树的左子树与右子树镜像对称,那么这个树是对称的。
如果同时满足下面的条件,两个树互为镜像:
- 它们的两个根结点具有相同的值
- 每个树的右子树都与另一个树的左子树镜像对称
递归方法
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
return check(root, root);
//当然这样写也可以
return check(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean check(TreeNode p, TreeNode q){
if (p == null && q == null){
return true;
}
if(p == null || q == null){
return false;
}
return p.val == q.val && check(p.left, q.right) && check(p.right, q.left);
}
}比较好理解,当现在遍历的这两个节点实现相等的,就看下左右节点是否一致,且一个往左走一个往右走。
迭代法
待写


























 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








