LDA: Linear Discriminant Analysis
LDA分类的一个目标是使得不同类别间的距离越远越好,同一类别中的距离越近越好。
每类样例的均值为:
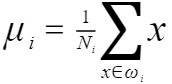








代码地址:https://github.com/create-info/ML_DL_resources/blob/master/TF-IDF_LDA_NB/LDA.ipynb
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""LDA.ipynb
Automatically generated by Colaboratory.
Original file is located at
https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1FdTAEoYCtcELdB3qeN6vABszRomWvfLD
"""
# 线性判别分析
# https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/
# 指定特征名
feature_dict = {i:label for i, label in zip(range(4),
('sepal length in cm',
'sepal width in cm',
'petal length in cm',
'petal width in cm',))}
# print(feature_dict)
import pandas as pd
df = pd.io.parsers.read_csv(
filepath_or_buffer = 'https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learning-databases/iris/iris.data',
header = None,
sep = ',',
)
df.columns = [l for i,l in sorted(feature_dict.items())] + ['class_label']
df.dropna(how = 'all', inplace=True)
df.tail()
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
X = df[['sepal length in cm',
'sepal width in cm',
'petal length in cm',
'petal width in cm']].values
y = df['class_label'].values
# print(X)
# 类别向量化
enc = LabelEncoder()
label_encoder = enc.fit(y)
y = label_encoder.transform(y) + 1
# print(y)
label_dict = {1: 'Setosa', 2: 'Versicolor', 3:'Virginica'}
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(precision=4)
# 计算每个类别中每个特征列的均值
mean_vectors = []
for c1 in range(1,4):
# print(c1) 1 2 3
mean_vectors.append(np.mean(X[y==c1], axis=0))
print('Mean vector class %s: %s\n' %(c1, mean_vectors[c1-1]))
# print(mean_vectors)
# 计算两个4*4矩阵:类内散布矩阵和类间散布矩阵
S_W = np.zeros((4,4))
# print(S_W)
for c1, mv in zip(range(1,4), mean_vectors):
class_sc_mat = np.zeros((4,4))
for row in X[y==c1]:
# print(row)
row, mv = row.reshape(4,1), mv.reshape(4,1)
class_sc_mat += (row-mv).dot((row-mv).T)
S_W += class_sc_mat
print('with-class Scatter Matrix:\n', S_W)
# 计算类间散布矩阵
# 全局均值
overall_mean = np.mean(X, axis=0)
print(overall_mean)
S_B = np.zeros((4,4))
for i,mean_vec in enumerate(mean_vectors):
n = X[y==i+1,:].shape[0]
# print(n) 50,每个类别中样本都是50个
mean_vec = mean_vec.reshape(4,1)
S_B += n * (mean_vec - overall_mean).dot((mean_vec - overall_mean).T)
print('between-class Scatter Mattrix:\n', S_B)
# 求矩阵的特征值,np.linalg.inv(S_W)表示求逆
# np.linalg.eig:计算特征值,特征向量
eig_vals, eig_vecs = np.linalg.eig(np.linalg.inv(S_W).dot(S_B))
for i in range(len(eig_vals)):
eigvec_sc = eig_vecs[:,i].reshape(4,1)
# 输出特征向量
print('\nEigenvector {}:\n{}'.format(i+1, eigvec_sc.real))
# 输出特征值
print('Eigenvalue {}: {:.2e}'.format(i+1, eig_vals[i].real))
# 特征向量:表示映射方向
# 特征值:特征向量的重要程度
# 对特征值进行降序排序
eig_pairs = [(np.abs(eig_vals[i]), eig_vecs[:,i]) for i in range(len(eig_vals))]
eig_pairs = sorted(eig_pairs, key=lambda k: k[0], reverse=True)
print('Eigenvalues in decreasing order:\n')
for i in eig_pairs:
print(i[0])
# 输出各个特征占总体方差的百分比
print('Variance explained:\n')
eigv_sum = sum(eig_vals)
for i,j in enumerate(eig_pairs):
print('eigenvalue {0:}: {1:.2%}'.format(i+1,(j[0]/eigv_sum).real))
# 选择前两维特征
W = np.hstack((eig_pairs[0][1].reshape(4,1), eig_pairs[1][1].reshape(4,1)))
print('Matrix W :\n',W.real)
# 由150*4变成了150*2
X_lda = X.dot(W)
assert X_lda.shape == (150,2), 'The matrix is not 150*2 dimensional'
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def plot_step_lda():
# 其中参数111,指的是将图像分成1行1列,此图是第一个图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
for label, marker, color in zip(
range(1,4), ('^', 's', 'o'),('blue','red','green')):
plt.scatter(x=X_lda[:,0].real[y==label],
y=X_lda[:,1].real[y==label],
marker=marker,
color=color,
alpha=0.5,
label=label_dict[label]
)
plt.xlabel('LD1')
plt.ylabel('LD2')
leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True)
leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)
plt.title('LDA Iris projection onto first 2 linear discriminants')
# hidden axis ticks
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='both', bottom='off',
labelbottom='on', left='off', right='off', labelleft='on')
# remove axis spines
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout
plt.show()
# 画图
plot_step_lda()
# 下面使用sklearn实现LDA
from sklearn.discriminant_analysis import LinearDiscriminantAnalysis as LDA
sklearn_LDA = LDA(n_components=2)
X_lda = sklearn_LDA.fit_transform(X, y)
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def plot_sklearn_lda(X, title):
# 其中参数111,指的是将图像分成1行1列,此图是第一个图
ax = plt.subplot(111)
for label, marker, color in zip(
range(1,4), ('^', 's', 'o'),('blue','red','green')):
plt.scatter(x=X[:,0][y==label],
y=X[:,1][y==label]*-1,
marker=marker,
color=color,
alpha=0.5,
label=label_dict[label]
)
plt.xlabel('LD1')
plt.ylabel('LD2')
leg = plt.legend(loc='upper right', fancybox=True)
leg.get_frame().set_alpha(0.5)
plt.title(title)
# hidden axis ticks
plt.tick_params(axis='both', which='both', bottom='off',
labelbottom='on', left='off', right='off', labelleft='on')
# remove axis spines
ax.spines['top'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['right'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['bottom'].set_visible(False)
ax.spines['left'].set_visible(False)
plt.grid()
plt.tight_layout
plt.show()
# 画图
plot_sklearn_lda(X_lda,'LDA Iris projection onto first 2 linear discriminants')



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








