线程池
介绍



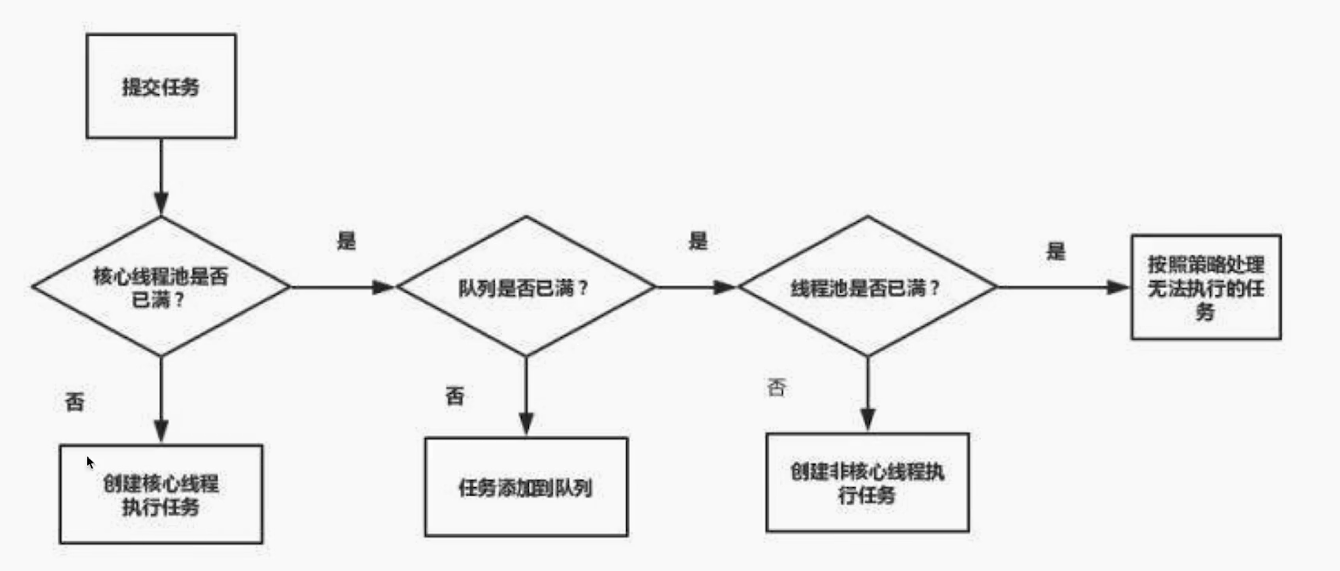
增减时机

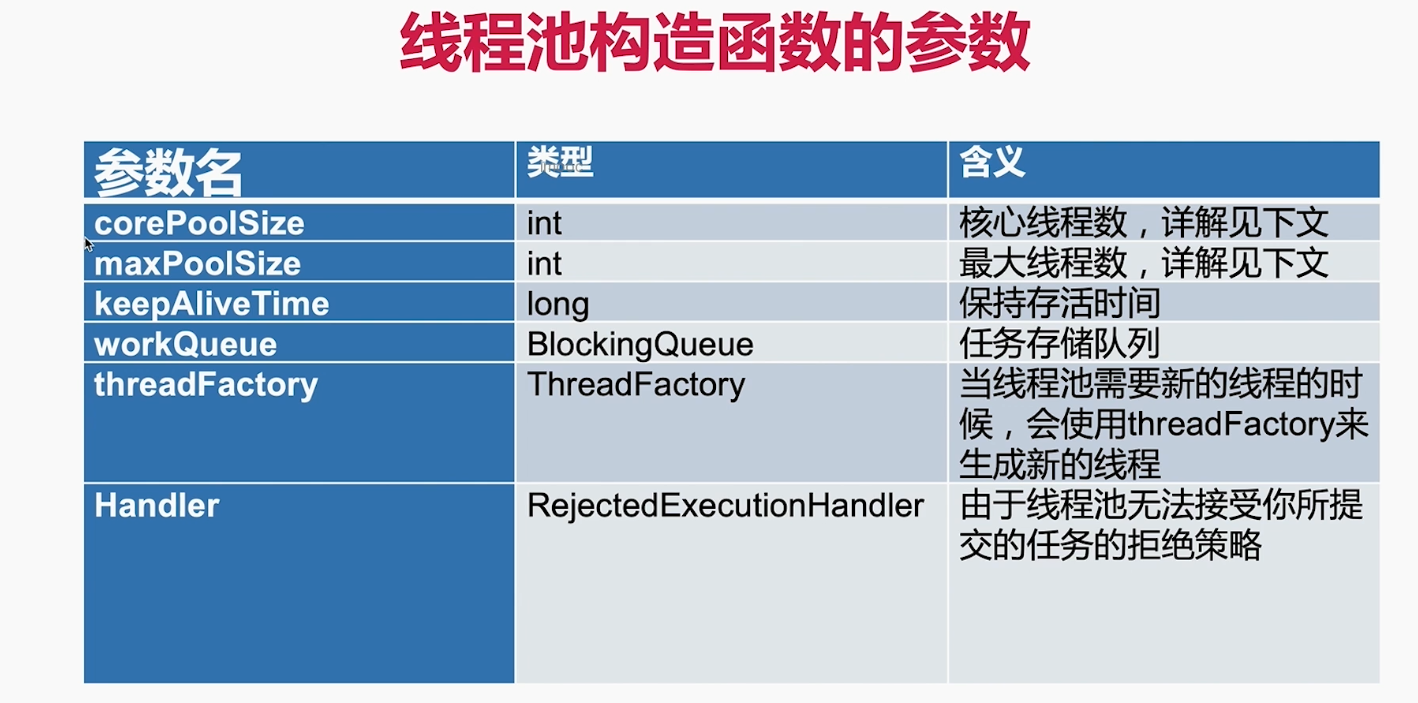



keepAlive 和线程工厂



线程池用法


线程池特点

停止线程池



任务前后执行(可暂停的线程池)
public class PausePool extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
public PausePool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
}
@Override
protected void beforeExecute(Thread t, Runnable r) {
super.beforeExecute(t, r);
lock.lock();
try {
while (isPaused){
unpaused.await();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private boolean isPaused;
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition unpaused = lock.newCondition();
private void pause(){
lock.lock();
try {
isPaused = true;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public void resume(){
lock.lock();
try {
isPaused = false;
unpaused.signalAll();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
PausePool pausePool = new PausePool(10,20,101,TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>());
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("执行");
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
pausePool.execute(runnable);
}
Thread.sleep(1500);
pausePool.pause();
System.out.println("pause");
Thread.sleep(1500);
pausePool.resume();
System.out.println("start");
}
}
线程池原理
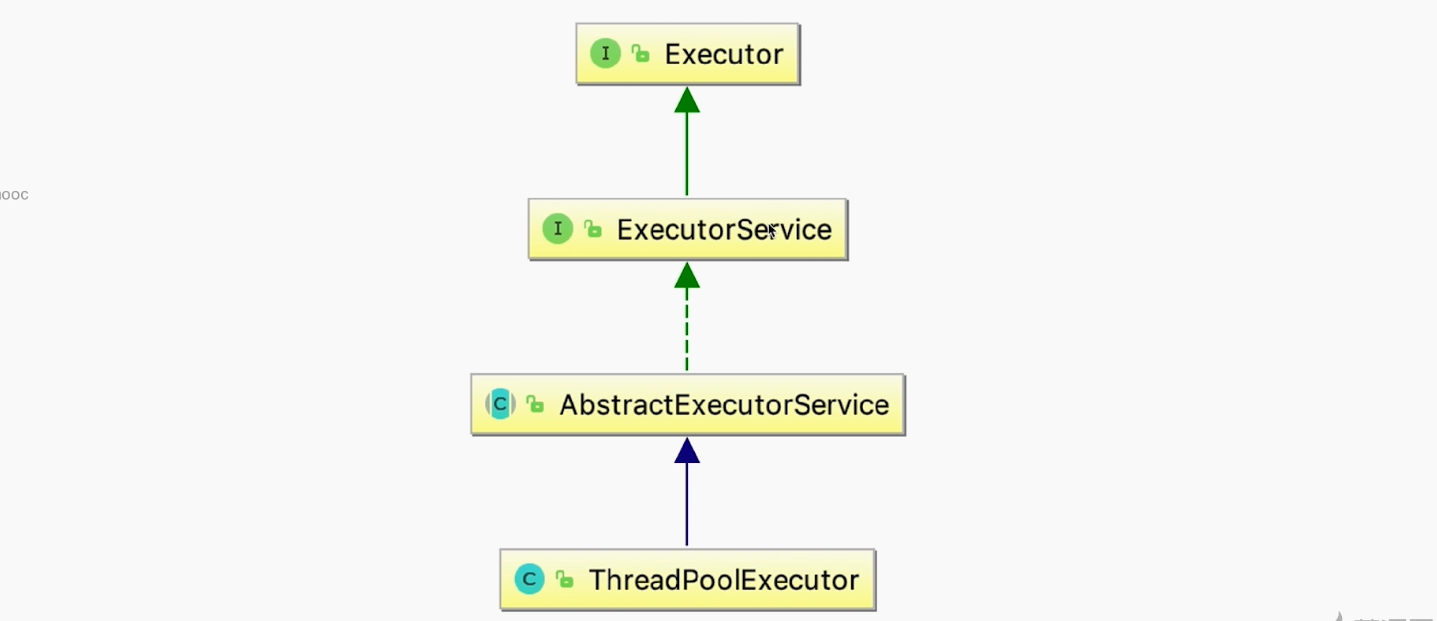
线程池任务复用:相同线程执行不同任务
线程池状态


ThreadLocal
使用场景

场景1


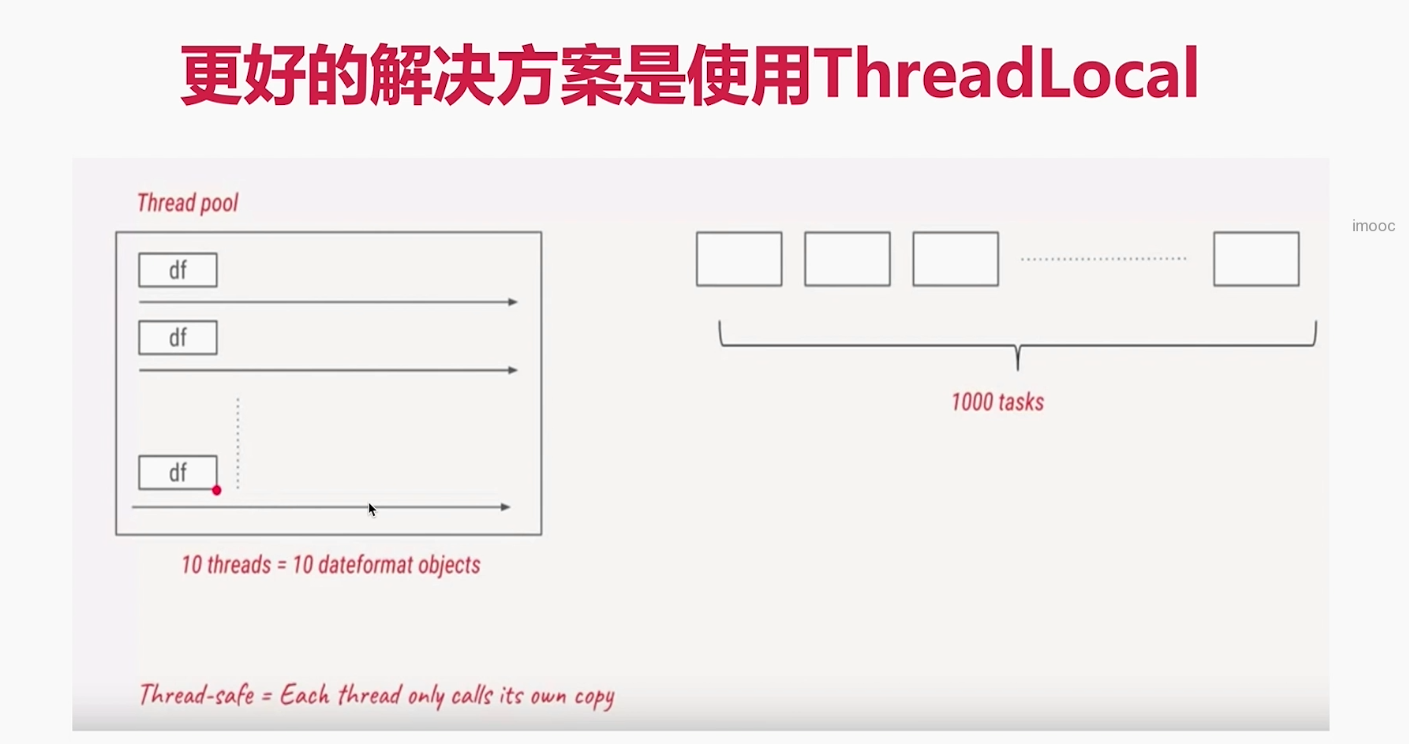
/**
* 描述: 利用ThreadLocal,给每个线程分配自己的dateFormat对象,保证了线程安全,高效利用内存
*/
public class ThreadLocalNormalUsage05 {
public static ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
int finalI = i;
threadPool.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
String date = new ThreadLocalNormalUsage05().date(finalI);
System.out.println(date);
}
});
}
threadPool.shutdown();
}
public String date(int seconds) {
//参数的单位是毫秒,从1970.1.1 00:00:00 GMT计时
Date date = new Date(1000 * seconds);
// SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = ThreadSafeFormatter.dateFormatThreadLocal.get();
return dateFormat.format(date);
}
}
class ThreadSafeFormatter {
public static ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>
dateFormatThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<SimpleDateFormat>(){
@Override
protected SimpleDateFormat initialValue() {
return new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
}
};
}
场景2



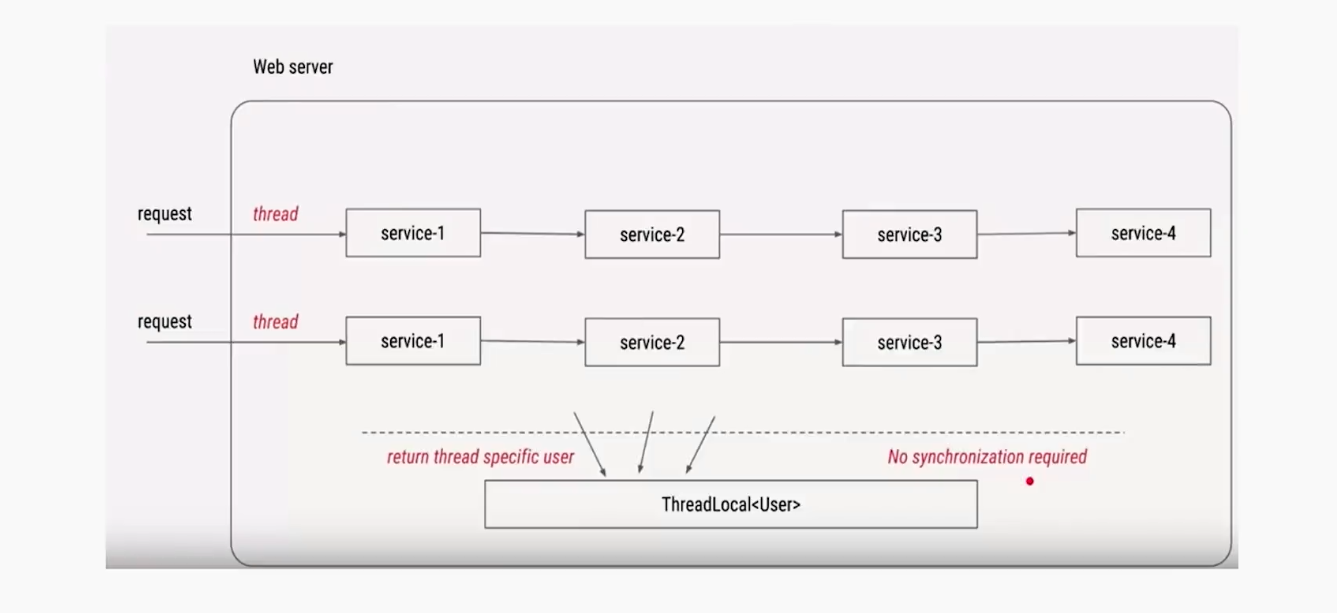
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Service1().process();
}
}
class Service1{
public void process(){
User user = new User("test");
UserHolder.holder.set(user);
new Service2().process();
}
}
class Service2{
public void process(){
System.out.println(UserHolder.holder.get());
new Service3().process();
}
}
class Service3{
public void process(){
System.out.println(UserHolder.holder.get());
}
}
class UserHolder{
public static ThreadLocal<User> holder = new ThreadLocal<>();
}
class User{
String name;
public User(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
总结
两个作用:
1、让需要用到的对象在线程捡隔离,每个线程都有自己的独立的对象
2、在任何方法中都可以轻松获取到该对象
根据对象生成实际不同选择不同而方法
1、initialvalue
在Threadlocal第一次get的时候把对象初始化出来,对象的初始化时机由我们控制
2、set
如果需要保存到threadlocal里的对象的生成时机不被我们控制,用set放到threadlocal中去。

原理
方法





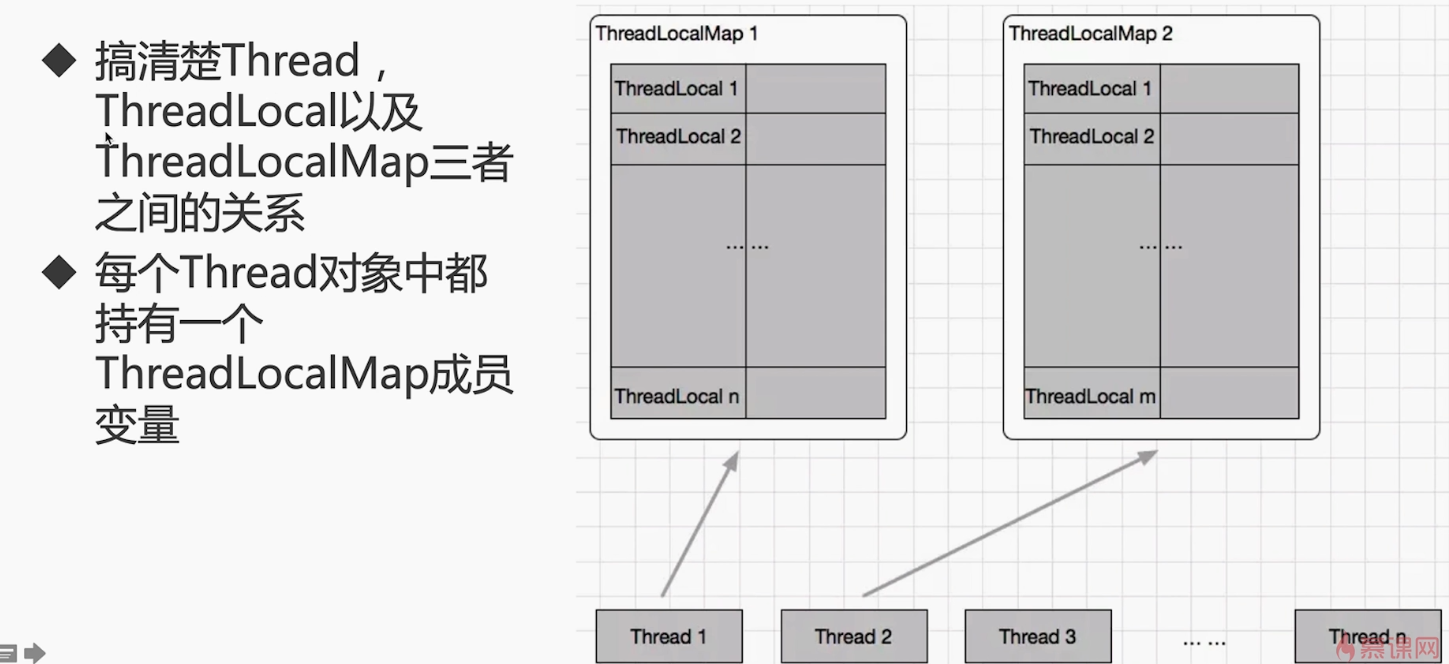
ThreadLocalMap


注意点
内存泄漏



空指针

直接返回基本类型long,会因为拆箱装箱将Null转化为Long空指针异常
public class ThreadPoolNPE {
ThreadLocal<Long> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<Long>();
void set(){
threadLocal.set(Thread.currentThread().getId());
}
Long get(){
return threadLocal.get();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolNPE threadPoolNPE = new ThreadPoolNPE();
System.out.println(threadPoolNPE.get());
// new Thread(new Runnable() {
// @Override
// public void run() {
// threadPoolNPE.set();
// System.out.println(threadPoolNPE.get());
// }
// }).start();
}
}


锁
lock







public class LockInterruptibly implements Runnable {
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
LockInterruptibly lockInterruptibly = new LockInterruptibly();
Thread thread0 = new Thread(lockInterruptibly);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(lockInterruptibly);
thread0.start();
thread1.start();
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
thread1.interrupt();
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "尝试获取锁");
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获取到了锁");
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "睡眠期间被中断了");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "释放了锁");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "获得锁期间被中断了");
}
}
}
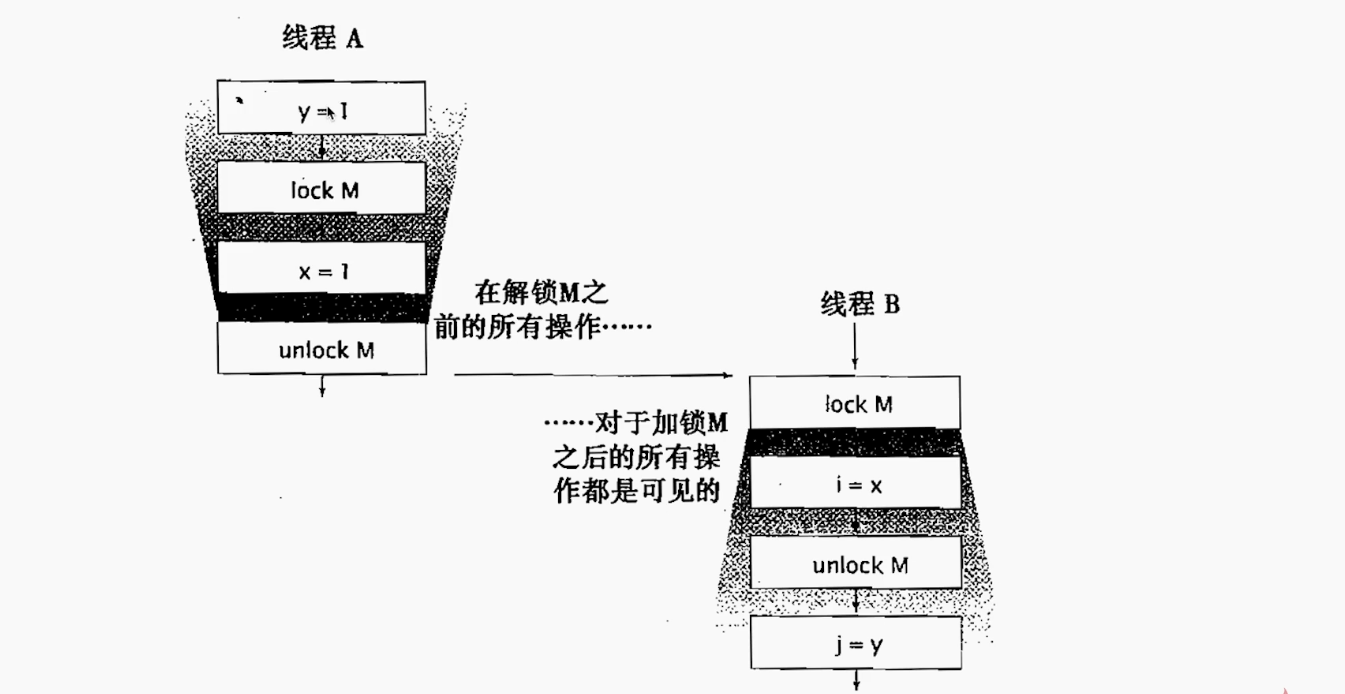
可见性

锁分类
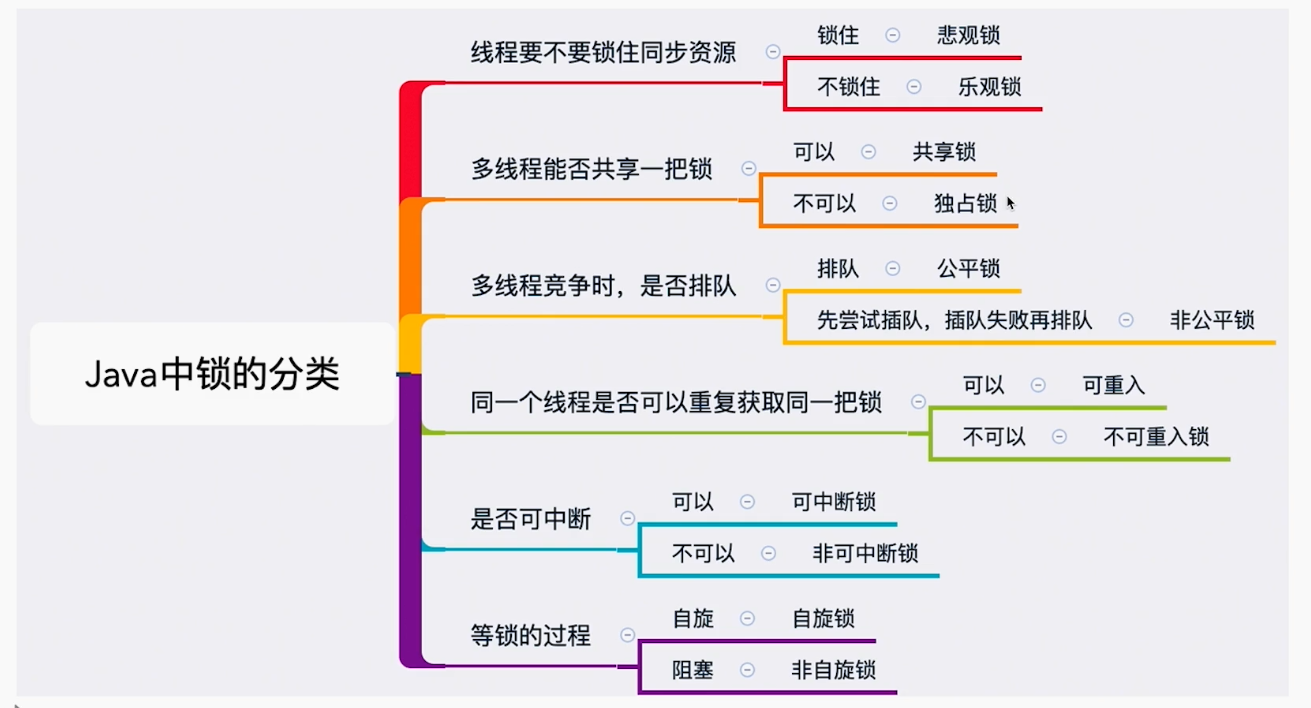
乐观锁和悲观锁



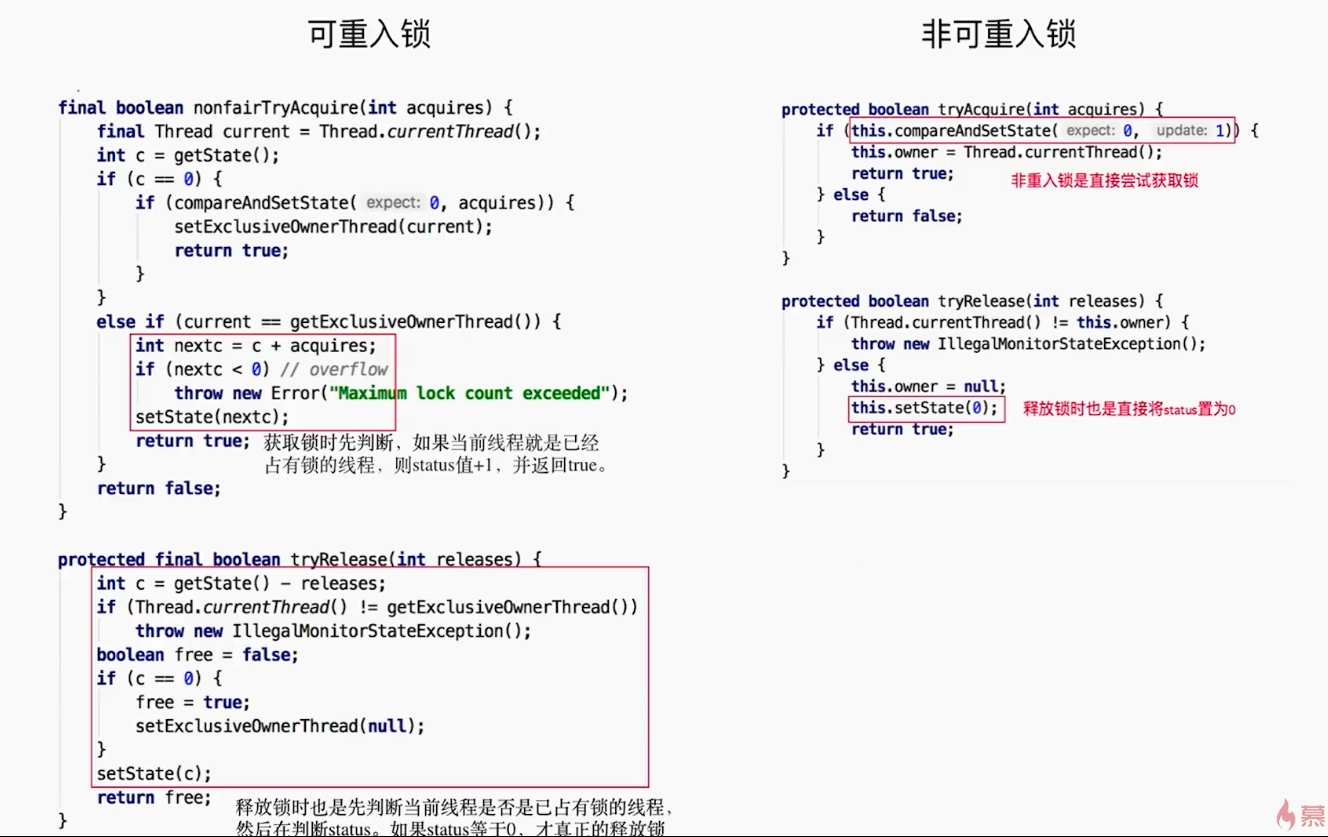
重入锁
例子:预定电影院座位
public class SeatLock {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
static void bookSeat(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始预定");
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"预定完成");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(()->bookSeat()).start();
new Thread(()->bookSeat()).start();
new Thread(()->bookSeat()).start();
}
}
性质源码
public class ReentrantLockTest {
static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void access() {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("处理");
if (lock.getHoldCount() < 5){
System.out.println(lock.getHoldCount());
access();
System.out.println(lock.getHoldCount());
}
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
access();
}
}
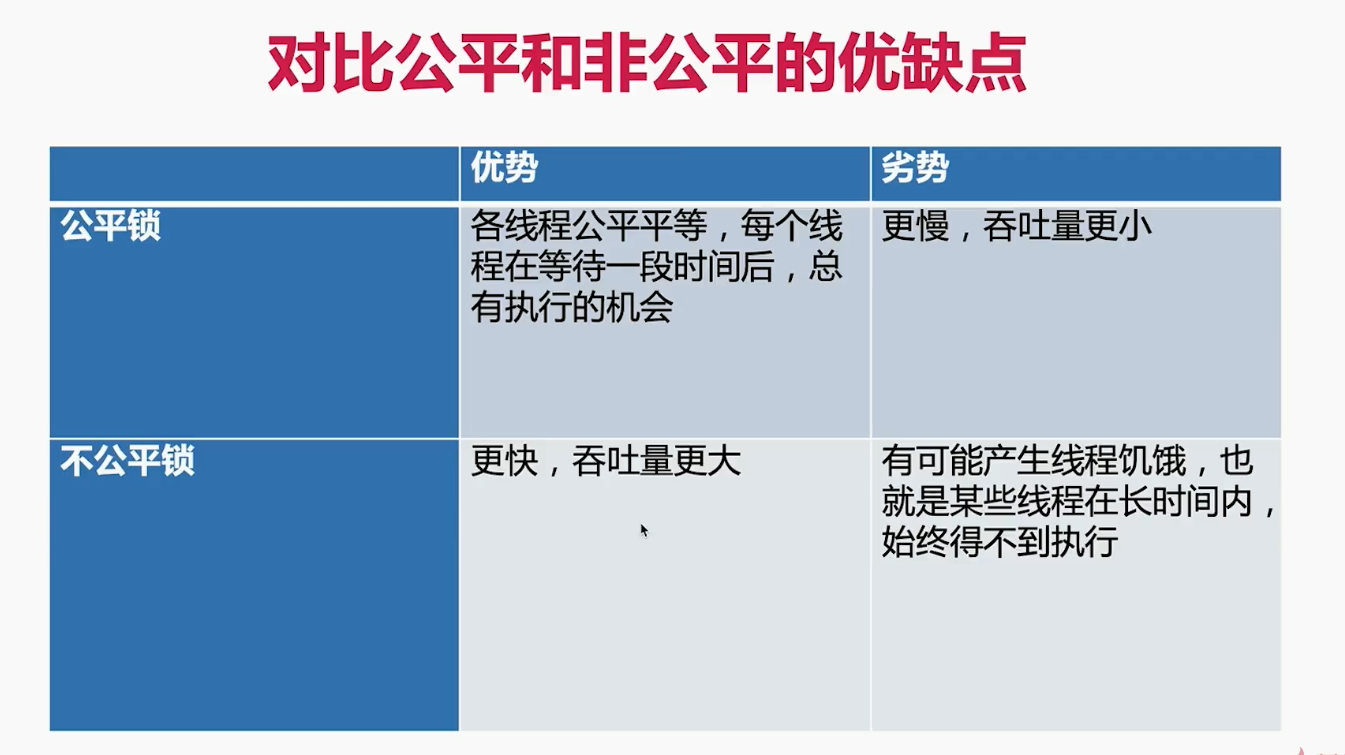
公平锁

避免唤醒带来的空档期

/**
* 描述: 演示公平和不公平两种情况
*/
public class FairLock {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintQueue printQueue = new PrintQueue();
Thread thread[] = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
thread[i] = new Thread(new Job(printQueue));
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
thread[i].start();
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
class Job implements Runnable {
PrintQueue printQueue;
public Job(PrintQueue printQueue) {
this.printQueue = printQueue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "开始打印");
printQueue.printJob(new Object());
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "打印完毕");
}
}
class PrintQueue {
private Lock queueLock = new ReentrantLock(true);
public void printJob(Object document) {
queueLock.lock();
try {
int duration = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "第一次正在打印,需要" + duration);
Thread.sleep(duration * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
queueLock.unlock();
}
queueLock.lock();
try {
int duration = new Random().nextInt(10) + 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "第二次正在打印,需要" + duration+"秒");
Thread.sleep(duration * 1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
queueLock.unlock();
}
}
}


共享锁和排他锁



public class ReadWriteLock {
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantReadWriteLock
= new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock
= reentrantReadWriteLock.readLock();
private static ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock
= reentrantReadWriteLock.writeLock();
private static void read(){
readLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"读");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放读");
readLock.unlock();
}
}
private static void write(){
writeLock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"写");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"释放写");
writeLock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(ReadWriteLock::read, "t1").start();
new Thread(ReadWriteLock::read, "t2").start();
new Thread(ReadWriteLock::write, "t3").start();
new Thread(ReadWriteLock::write, "t4").start();
}
}

总结:只能降级,不能升级,适合读多写少的场合
自旋和阻塞



可中断锁

原子类

public class AtomicInteger1 implements Runnable{
private static final AtomicInteger ato
= new AtomicInteger();
private static final AtomicInteger ato1
= new AtomicInteger();
void incre(){
ato.getAndIncrement();
ato1.getAndAdd(2);
}
static volatile int basicCount = 0;
void increBasic(){
basicCount++;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
incre();
increBasic();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicInteger1 r = new AtomicInteger1();
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(r);
thread.start();
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(ato.get());
System.out.println(ato1.get());
System.out.println(basicCount);
}
}
数组和引用
class Dece implements Runnable{
private AtomicIntegerArray array;
public Dece(AtomicIntegerArray array) {
this.array = array;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) {
array.getAndDecrement(i);
}
}
}
class Ince implements Runnable{
private AtomicIntegerArray array;
public Ince(AtomicIntegerArray array) {
this.array = array;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) {
// array.getAndIncrement(i);
// }
}
}
public class AtomicInteger2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
AtomicIntegerArray array = new AtomicIntegerArray(1000);
Ince ince = new Ince(array);
Dece dece = new Dece(array);
Thread[] threads2 = new Thread[10];
Thread[] threads1 = new Thread[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads1[i] = new Thread(dece);
threads2[i] = new Thread(ince);
threads1[i].start();
threads2[i].start();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
threads1[i].join();
threads2[i].join();
}
for (int i = 0; i < array.length(); i++) {
// if (array.get(i) != 0){
// System.out.println("error"+i);
// }
System.out.println(array.get(i));
}
System.out.println("success");
}
}

升级原子类
public class AtomiciUpdate implements Runnable{
static Candidate tom;
static Candidate peter;
static AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater<Candidate> sco
= AtomicIntegerFieldUpdater.newUpdater(Candidate.class, "score");
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
peter.score++;
sco.getAndIncrement(tom);
}
}
public static class Candidate{
volatile int score;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
tom = new Candidate();
peter = new Candidate();
AtomiciUpdate atomiciUpdate = new AtomiciUpdate();
new Thread(atomiciUpdate).start();
new Thread(atomiciUpdate).start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(tom.score);
System.out.println(peter.score);
}
}
Adder累加器



CAS

public class CASTest implements Runnable
{
private volatile int value;
synchronized int compareAndSwap(int expect, int newValue){
int old = value;
if (old == expect){
value = newValue;
}
return old;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CASTest r = new CASTest();
r.value = 0;
Thread t1 = new Thread(r);
Thread t2 = new Thread(r);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println(r.value);
}
@Override
public void run() {
compareAndSwap(0, 1);
}
}



不变性
final




并发容器
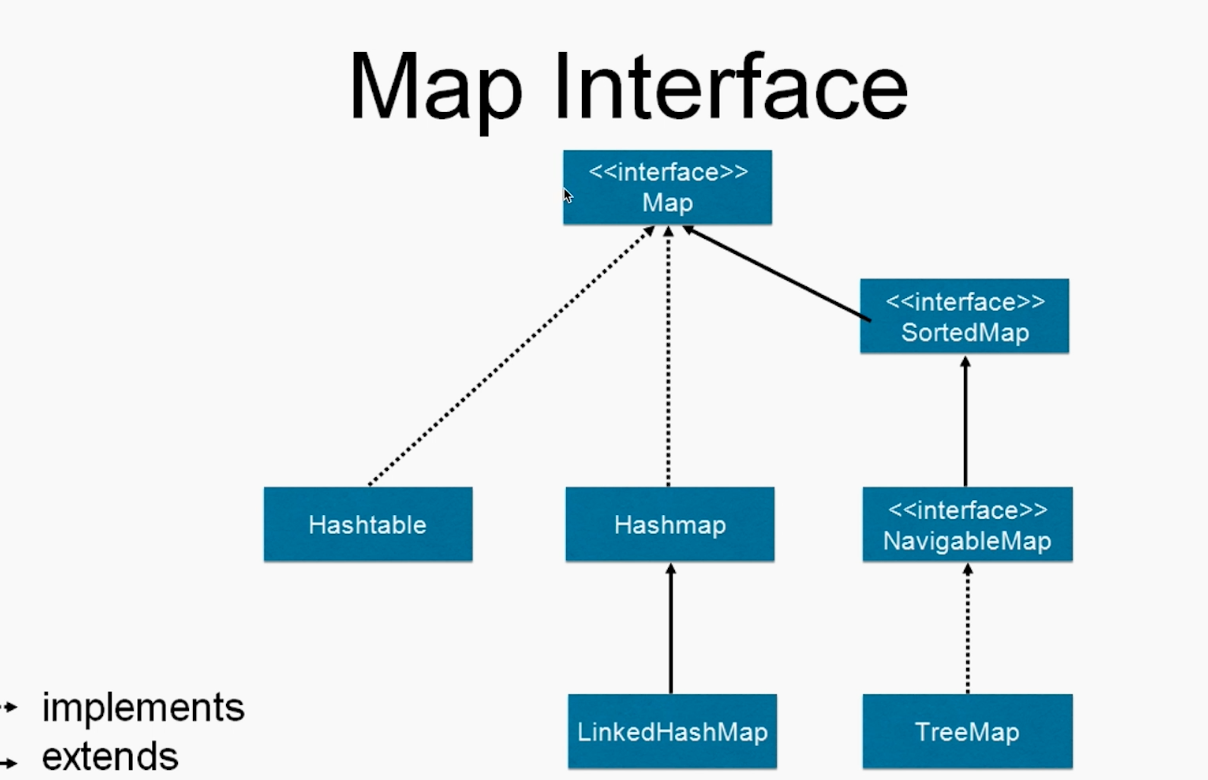
map


concurrenthashmap



为什么把1.7的结构改为1.8?
数据结构不同,提高了并发性,
hash碰撞,8有红黑树
并发安全,7segment,lock,8 cas+syn
复杂度,7链表n,8红黑树logn
为什么超过8转为红黑树:默认链表,占用内存更少,想要达到8概率很低
组合操作线程不安全:replace方法
copyonwriteArrayList




add方法用lock加锁
阻塞队列

ArrayBlockingQueue 有界,容量限制 put方法Lock锁 LinkedBlockingQueue 无界,容量为最大值 Put方法lock锁和原子类锁


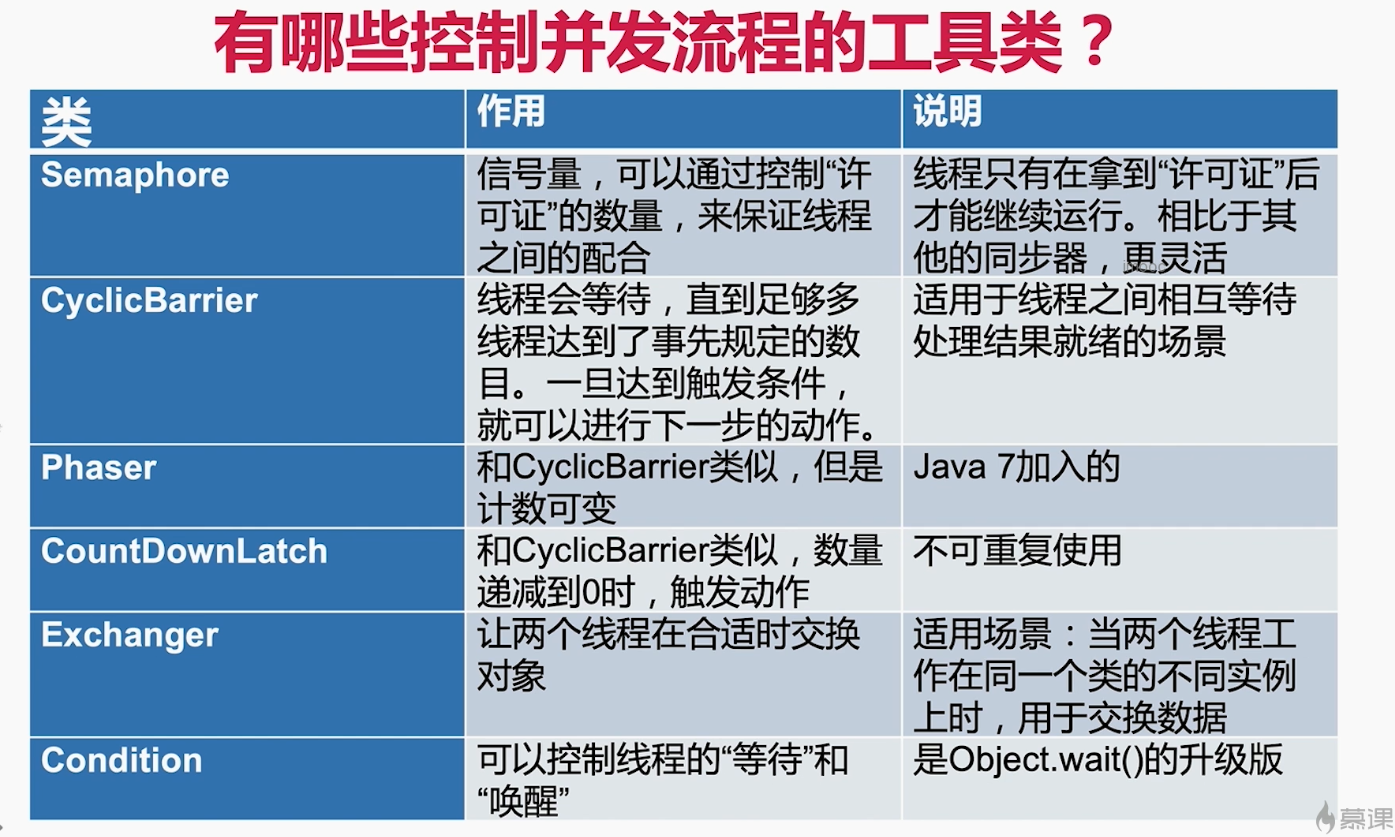
并发流程
countdown

//多等1
public class CountDownTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(5);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int n = i+1;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
System.out.println(n+"end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
latch.countDown();
}
}
};
service.submit(runnable);
}
System.out.println("start");
latch.await();
System.out.println("all end");
}
}
// 多等1
public class CountDownTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int n = i+1;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(n+"wait");
try {
latch.await();
System.out.println(n+"start");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};
service.submit(runnable);
}
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("can");
latch.countDown();
}
}
//多等一和一等多结合
public class CountDownTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(1);
CountDownLatch count = new CountDownLatch(5);
ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
final int n = i+1;
Runnable runnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println(n+"等待跑");
try {
latch.await();
System.out.println(n+"开始跑");
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
System.out.println(n+"到终点");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
count.countDown();
}
}
};
service.submit(runnable);
}
Thread.sleep(500);
System.out.println("比赛开始");
latch.countDown();
count.await();
System.out.println("所有都到了");
}
}
信号量



condition


public class Conditiontest {
private ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
void method1() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("wait");
condition.await();
System.out.println("start");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
void method2() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("complete");
condition.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Conditiontest r1 = new Conditiontest();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
r1.method2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
r1.method1();
}
}
生产消费者案例:

/**
* 描述: 演示用Condition实现生产者消费者模式
*/
public class ConditionDemo2 {
private int queueSize = 10;
private PriorityQueue<Integer> queue = new PriorityQueue<Integer>(queueSize);
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
private Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConditionDemo2 conditionDemo2 = new ConditionDemo2();
Producer producer = conditionDemo2.new Producer();
Consumer consumer = conditionDemo2.new Consumer();
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
class Consumer extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
consume();
}
private void consume() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == 0) {
System.out.println("队列空,等待数据");
try {
notEmpty.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.poll();
notFull.signalAll();
System.out.println("从队列里取走了一个数据,队列剩余" + queue.size() + "个元素");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
class Producer extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
produce();
}
private void produce() {
while (true) {
lock.lock();
try {
while (queue.size() == queueSize) {
System.out.println("队列满,等待有空余");
try {
notFull.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
queue.offer(1);
notEmpty.signalAll();
System.out.println("向队列插入了一个元素,队列剩余空间" + (queueSize - queue.size()));
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
}
循环栅栏


AQS










future callable




 深入理解Java线程池:原理、使用与实践
深入理解Java线程池:原理、使用与实践





















 1659
1659

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








