1.实现多线程的方法有多少种:
实现runnable接口, 继承thread类
runnable方法更好,:
1)从代码架构角度和thread类解耦,
2)不需要新建线程节省资源,
3)java单继承,影响继承其他类
区别:runnable接口是调用传入的target的run,继承thread是重写了run
总结:创建线程只有一种方法就是构造thread类,实现线程的执行单元有两种方式:
方式一:实现runnable接口的run方法,并把runnable实例传给thread类
方式二:重写thread类的run方法
2.正确的线程启动方式:
两次调用start方法会出现什么:异常,start有状态检查Threadstatus = 0,
为什么不直接调用run:start是真正启动了,native start0, 经历生命周期,run只是方法
3.如何停止线程:
使用interrupt通知
两种最佳实践:
1)catch了之后的优先选择:在方法签名中抛出异常,那么在run方法中就会强制try catch
public class Right implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
System.out.println("go");
try {
throwInMethod();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void throwInMethod() throws InterruptedException {
Thread.sleep(2000);
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Right());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
2)在catch子语句中调用Thread.currentThread().interrupt()来恢复设置中断状态,以便于在后续的执行中,依然能够检查到刚才发生了中断,
public class Right2 implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
while (true){
if(Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()){
System.out.println("end");
break;
}
throwInMethod();
}
}
private void throwInMethod() {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new Right2());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
thread.interrupt();
}
}
错误的方法:stop, suspend, resume
volatile 设置boolean标记,无法处理长时间阻塞:
例如:生产者生产的快,消费者消费的慢,队列满了以后生产者会阻塞
package thread.stopThread.volatileDemo;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class WrongWayCant {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ArrayBlockingQueue<Object> storage = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(10);
Producer producer = new Producer(storage);
Thread producerThread = new Thread(producer);
producerThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(storage);
while (consumer.need()){
System.out.println(consumer.storage.take()+"被消费了");
Thread.sleep(100);
}
System.out.println("不再需要");
producer.canceled = true;
}
}
class Producer implements Runnable{
volatile boolean canceled = false;
BlockingQueue storage;
public Producer(BlockingQueue storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
int num = 0;
try {
while (num <= 100000 && !canceled) {
if (num % 100 == 0) {
storage.put(num);
System.out.println(num + "是100的倍数放到仓库");
}
num++;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
System.out.println("producer end");
}
}
}
class Consumer {
BlockingQueue storage;
public Consumer(BlockingQueue storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
public boolean need() {
if (Math.random() > 0.95) {
return false;
} else return true;
}
}
面试题:
如何停止线程:
用中断来请求,要请求方、被停止方、子方法被调用方相互配合,最后说错误的方法
如何处理不可中断的阻塞:
根据不同的类调用不同的方法
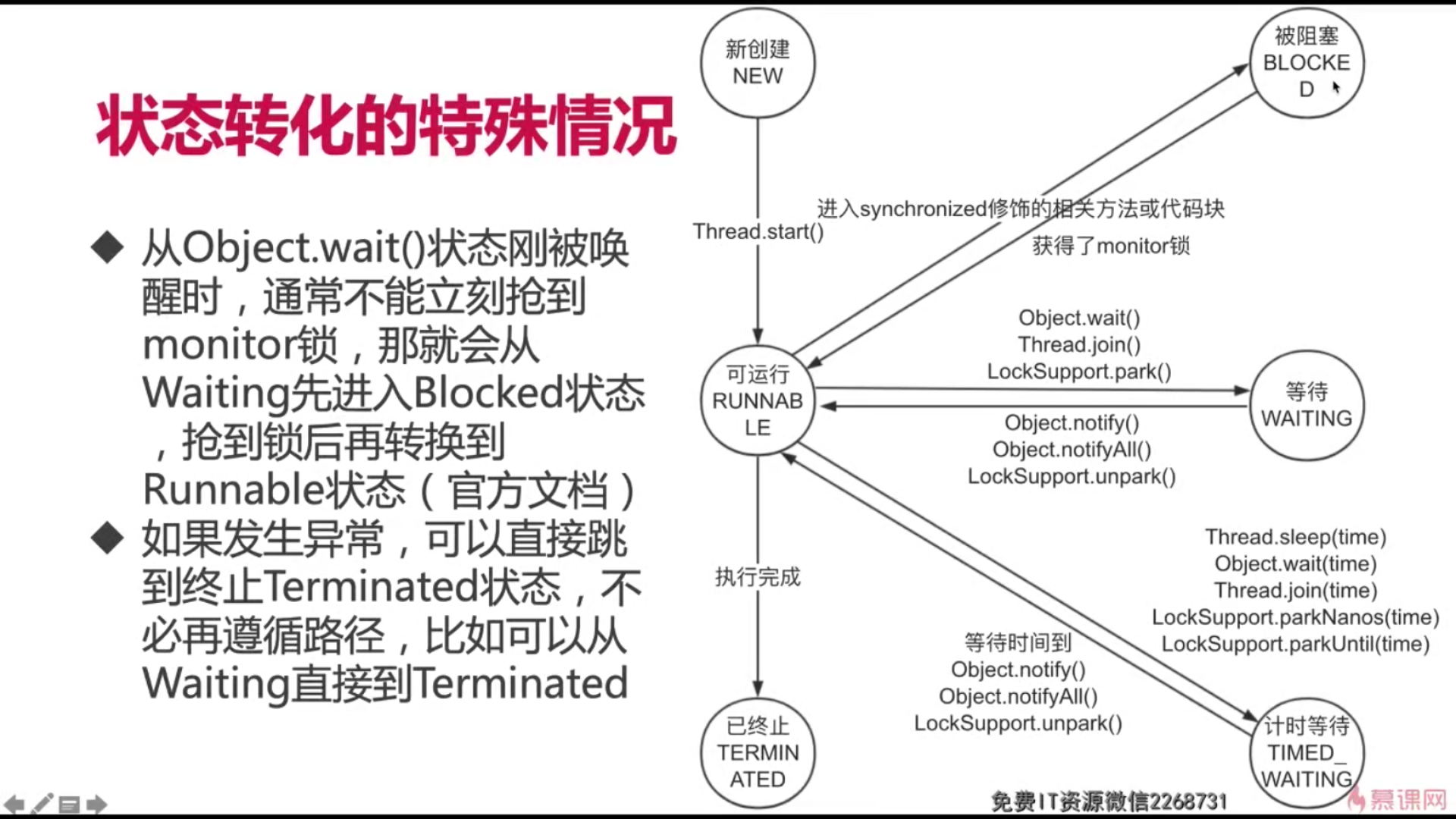
4.线程生命周期:
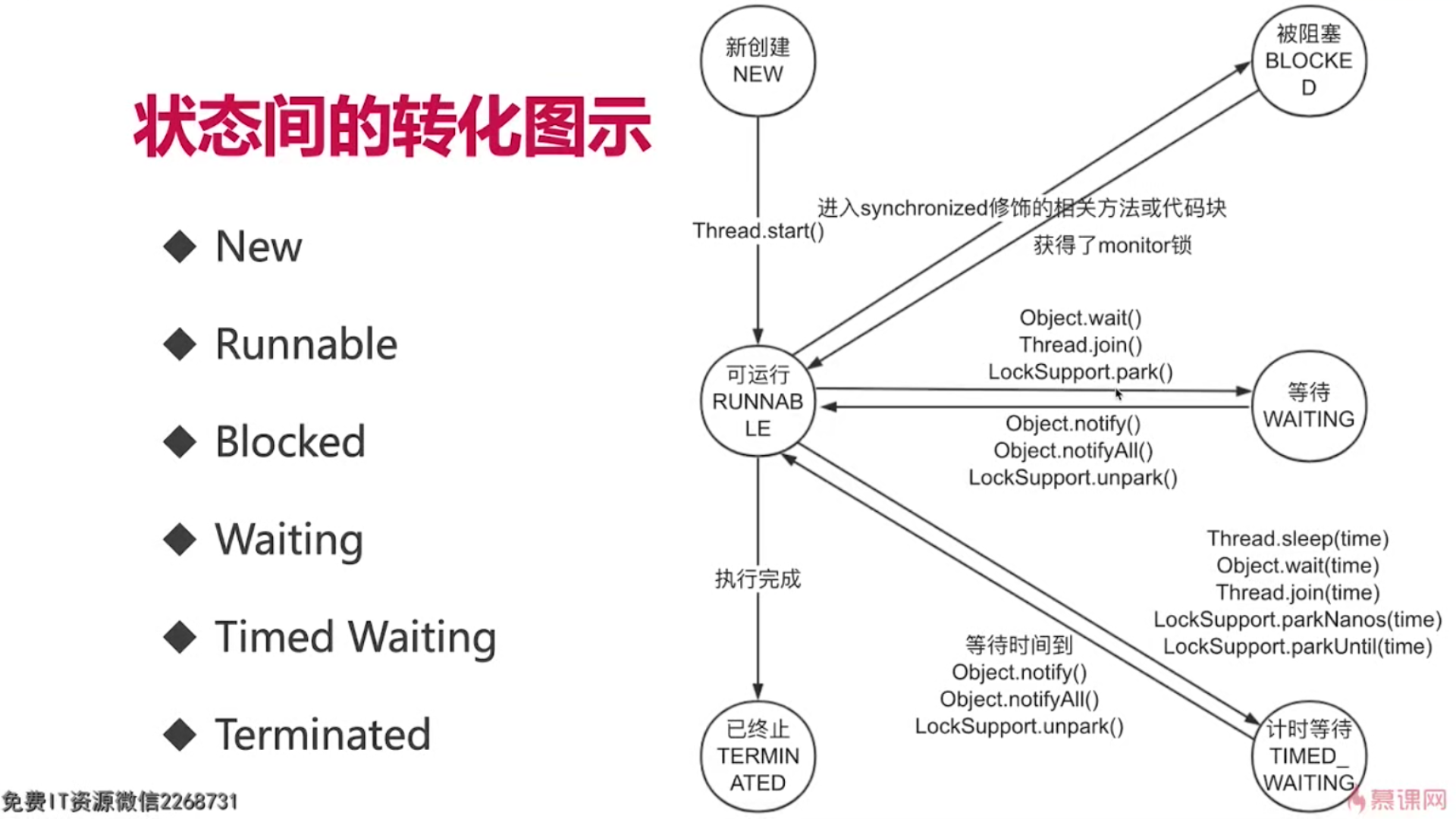
习惯把右边三种称为阻塞状态
面试题:
线程状态,生命周期
5.Thread和Object类的方法:
wait方法, notify方法:wait释放了锁
public class Wait {
public static final Object object = new Object();
static class Thread1 extends Thread{
public void run(){
synchronized (object){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"开始执行");
try {
object.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到了锁");
}
}
}
static class Thread2 extends Thread{
public void run(){
synchronized (object){
object.notify();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" notify");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1();
Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2();
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread2.start();
}
}
notify和notifyall:
public class WaitAll implements Runnable {
public static final Object resourceA = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get A");
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" start");
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
WaitAll runna = new WaitAll();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runna);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(runna);
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (resourceA) {
resourceA.notifyAll();
System.out.println("c notify");
}
}
});
thread2.start();
thread1.start();
Thread.sleep(200);
thread3.start();
}
}
wait只释放当前的锁:
package thread.Wait;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/29
*/
public class WaitAll2 implements Runnable {
public static final Object resourceA = new Object();
public static final Object resourceB = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get A");
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"get B");
try {
resourceA.wait();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" A end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
WaitAll2 runna = new WaitAll2();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(runna);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (resourceA){
System.out.println("rel A");
synchronized (resourceB){
System.out.println("rel B");
}
}
}
});
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
}
wait原理:
生产者消费者:
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class ProModel {
static class EventStorage{
private int maxSize;
private LinkedList<Date> storage;
public EventStorage() {
this.maxSize = 10;
this.storage = new LinkedList<>();
}
synchronized void put(){
while (storage.size() == maxSize){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
storage.add(new Date());
System.out.println("有了"+storage.size()+"个");
notify();
}
synchronized void take(){
while (storage.size() == 0){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println("取到了"+storage.poll());
System.out.println("剩下了"+storage.size()+"个");
notify();
}
}
static class Producer implements Runnable{
private EventStorage storage;
public Producer(EventStorage storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
storage.put();
}
}
}
static class Consumer implements Runnable{
private EventStorage storage;
public Consumer(EventStorage storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
storage.take();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventStorage storage = new EventStorage();
Producer producer = new Producer(storage);
Consumer consumer = new Consumer(storage);
Thread thread1 = new Thread(producer);
Thread thread = new Thread(consumer);
thread.start();
thread1.start();
}
}
面试:交替打印0-100
package thread.Wait;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/29
*/
public class PrintOddEven implements Runnable{
private static int count;
private static final Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Thread(new PrintOddEven(), "偶数").start();
new Thread(new PrintOddEven(), "奇数").start();
}
public void run() {
while (count <= 100) {
synchronized (lock) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()
+ ":" + count++);
lock.notify();
if (count <= 100)
{
try {
lock.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
}
面试:生产者消费者
为什么wait需要在同步代码块中使用,sleep不需要:通信可靠,防止死锁
为什么wait三个定义在object,sleep定义在thread: 每个类都是一把锁,对象头保存了monitor预留
调用Thread.wait会怎样:
sleep方法让线程进入waiting,不释放锁,休眠期间被中断抛出异常并清除中断。
面试题:wait, sleep,异同
相同:阻塞,响应中断
不同:wait在同步方法中,释放锁,指定时间,所属类
join:新的线程加入了我们,所以要等他执行完再出发。
用法:main等待子线程执行完毕
join期间线程处于waiting状态
yield方法:释放我的cpu时间片
6.线程的各个属性:
守护线程和普通线程:整体无区别,是否影响jvm退出,作用不同
是否需要设置为守护线程:不应该
7.未捕获异常:
主线程可以发现异常,子线程不可以:
子线程异常无法用传统方法捕获
解决方法:
1)手动在每个run里try
2)uncaughtExceptionHandler:
自己实现处理异常:
public class MyUncaughtException implements Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler {
private String name;
public MyUncaughtException(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void uncaughtException(Thread t, Throwable e) {
Logger logger = Logger.getAnonymousLogger();
logger.log(Level.WARNING, "异常"+t.getName(), e);
System.out.println(name + "捕获了异常"+t.getName()+"异常"+e);
}
}
public class Use implements Runnable{
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new MyUncaughtException("捕获器1"));
new Thread(new Use(), "MyThread-1").start();
Thread.sleep(300);
new Thread(new Use(), "MyThread-2").start();
Thread.sleep(300);
new Thread(new Use(), "MyThread-3").start();
Thread.sleep(300);
new Thread(new Use(), "MyThread-4").start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
8.多线程导致的问题:
线程安全:
线程不安全:
1、运行结果错误:a++多线程消失请求现象
public class Multi implements Runnable{
static Multi instance = new Multi();
int index;
static AtomicInteger realIndex = new AtomicInteger();
static AtomicInteger wrongCount = new AtomicInteger();
final boolean[] marked = new boolean[100000];
static volatile CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier1 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
static volatile CyclicBarrier cyclicBarrier2 = new CyclicBarrier(2);
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(instance);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("表面:"+instance.index);
System.out.println("real : " + realIndex.get());
System.out.println("error : " + wrongCount.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
marked[0]=true;
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
try {
cyclicBarrier2.reset();
cyclicBarrier1.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
index++;
try {
cyclicBarrier1.reset();
cyclicBarrier2.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | BrokenBarrierException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
realIndex.incrementAndGet();
synchronized (instance){
if (marked[index] && marked[index-1]){
System.out.println("发生错误"+index);
wrongCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
marked[index] = true;
}
}
}
2、活跃性问题:死锁、活锁、饥饿
public class Multi2 implements Runnable{
int flag;
static Object o1 = new Object();
static Object o2 = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) {
Multi2 r1 = new Multi2();
Multi2 r2 = new Multi2();
r1.flag = 1;
r2.flag = 0;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(r1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(r2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag==1){
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("flag = "+flag);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("1");
}
}
}
if (flag==0){
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("flag = "+flag);
try {
Thread.sleep(500);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("0");
}
}
}
}
}
3、对象发布和初始化:
1)、方法返回一个private对象
public class Multi3 {
private Map<String , String > states;
public Multi3() {
this.states = new HashMap<>();
states.put("1", "周一");
}
public Map<String , String > getStates(){
return states;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Multi3 multi3 = new Multi3();
Map<String, String> states = multi3.getStates();
states.remove("1");
System.out.println(states.get("1"));
}
}
2)、未完成初始化把对象提供给外界
构造函数没初始化
class Point{
private final int x, y;
public Point(int x, int y) throws InterruptedException {
this.x = x;
Multi4.point = this;
Thread.sleep(10);
this.y = y;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Point{" +
"x=" + x +
", y=" + y +
'}';
}
}
public class Multi4 {
static Point point;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Thread thread = new Thread(new PointMaker());
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(5);
if (point != null) System.out.println(point);
}
}
class PointMaker implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
try {
new Point(1, 1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注册监听
public class MultiThreadsError5 {
int count;
public MultiThreadsError5(MySource source) {
source.registerListener(new EventListener() {
@Override
public void onEvent(Event e) {
System.out.println("\n我得到的数字是" + count);
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
count = 100;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySource mySource = new MySource();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySource.eventCome(new Event() {
});
}
}).start();
MultiThreadsError5 multiThreadsError5 = new MultiThreadsError5(mySource);
}
static class MySource {
private EventListener listener;
void registerListener(EventListener eventListener) {
this.listener = eventListener;
}
void eventCome(Event e) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onEvent(e);
} else {
System.out.println("还未初始化完毕");
}
}
}
interface EventListener {
void onEvent(Event e);
}
interface Event {
}
}
构造函数中运行线程
public class Multi6 {
private Map<String , String > states;
public Multi6() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
states = new HashMap<>();
states.put("1", "周一");
}
}).start();
}
public Map<String , String > getStates(){
return states;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Multi6 multi6 = new Multi6();
Thread.sleep(100);
String s = multi6.getStates().get("1");
System.out.println(s);
}
}
解决方法:
1、返回副本,解决(方法返回一个private对象)
public Map<String , String > getImStates(){
return new HashMap<>(states);
}
2、工厂模式修复(注册监听)
/**
* 描述: 用工厂模式修复刚才的初始化问题
*/
public class MultiThreadsError7 {
int count;
private EventListener listener;
private MultiThreadsError7(MySource source) {
listener = new EventListener() {
@Override
public void onEvent(MultiThreadsError5.Event e) {
System.out.println("\n我得到的数字是" + count);
}
};
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
System.out.print(i);
}
count = 100;
}
public static MultiThreadsError7 getInstance(MySource source) {
MultiThreadsError7 safeListener = new MultiThreadsError7(source);
source.registerListener(safeListener.listener);
return safeListener;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MySource mySource = new MySource();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
mySource.eventCome(new MultiThreadsError5.Event() {
});
}
}).start();
MultiThreadsError7 multiThreadsError7 = new MultiThreadsError7(mySource);
}
static class MySource {
private EventListener listener;
void registerListener(EventListener eventListener) {
this.listener = eventListener;
}
void eventCome(MultiThreadsError5.Event e) {
if (listener != null) {
listener.onEvent(e);
} else {
System.out.println("还未初始化完毕");
}
}
}
interface EventListener {
void onEvent(MultiThreadsError5.Event e);
}
interface Event {
}
}
四种情况总结:
1、访问共享的变量资源
2、所有依赖时序的操作
3、数据之间存在捆绑关系 ip和端口号
4、使用其他类的时候,对方没有声明线程安全 hashmap
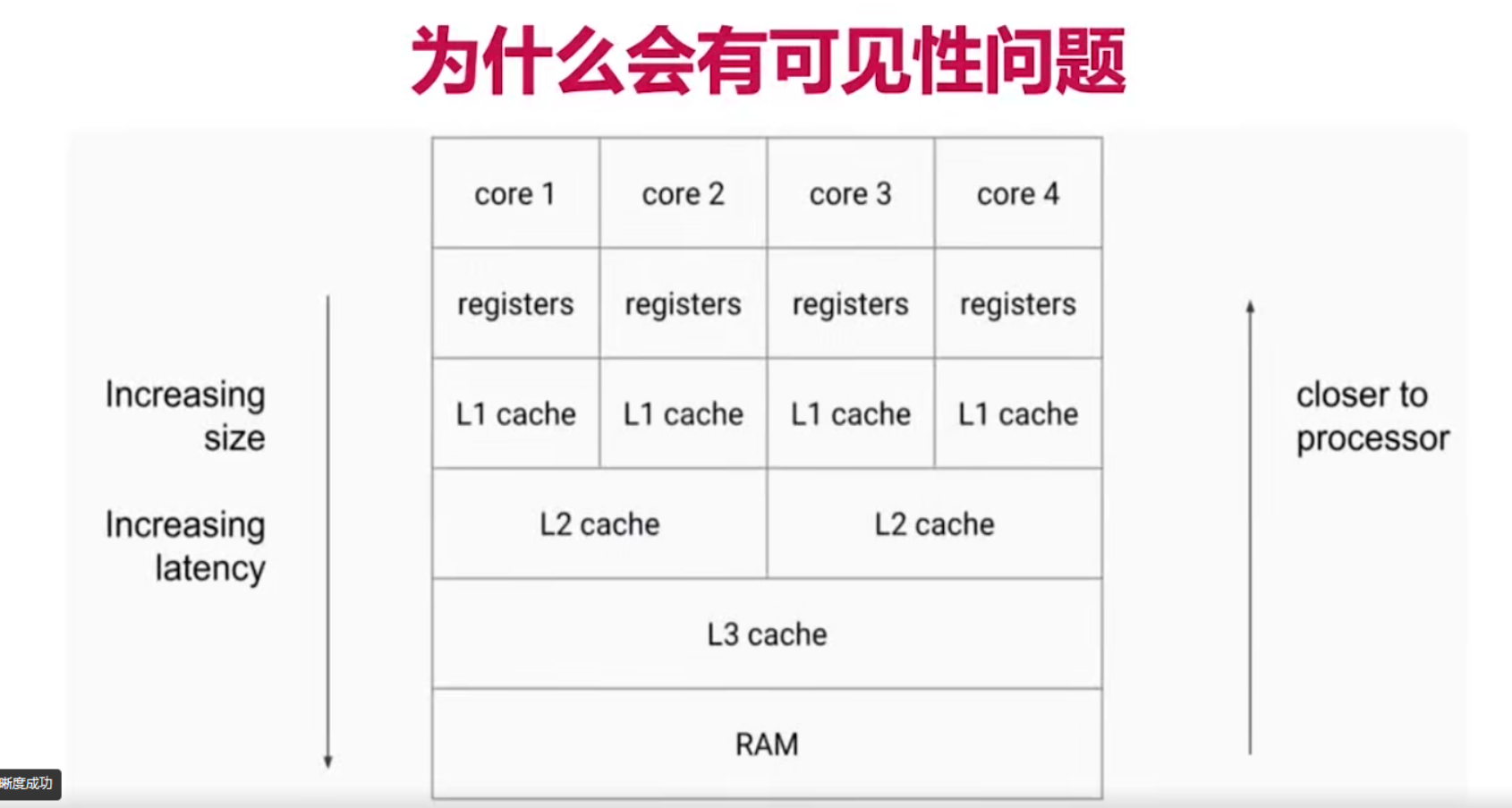
多线程性能
调度:上下文切换:内核再cpu上对于进程线程进行
1)存储进程状态 2)检索恢复进程状态 3)跳转程序计数器指向的位置
-
上下文:保存现场
-
缓存开销:缓存失效
-
密集上下文切换时机:抢锁,io
面试总结:





java内存模型

1、jvm内存结构 ,java内存模型,java对象模型
jvm内存结构和java虚拟机的运行时区域有关
java内存模型和并发有关
java对象模型和java对象在虚拟机中的表现形式有关
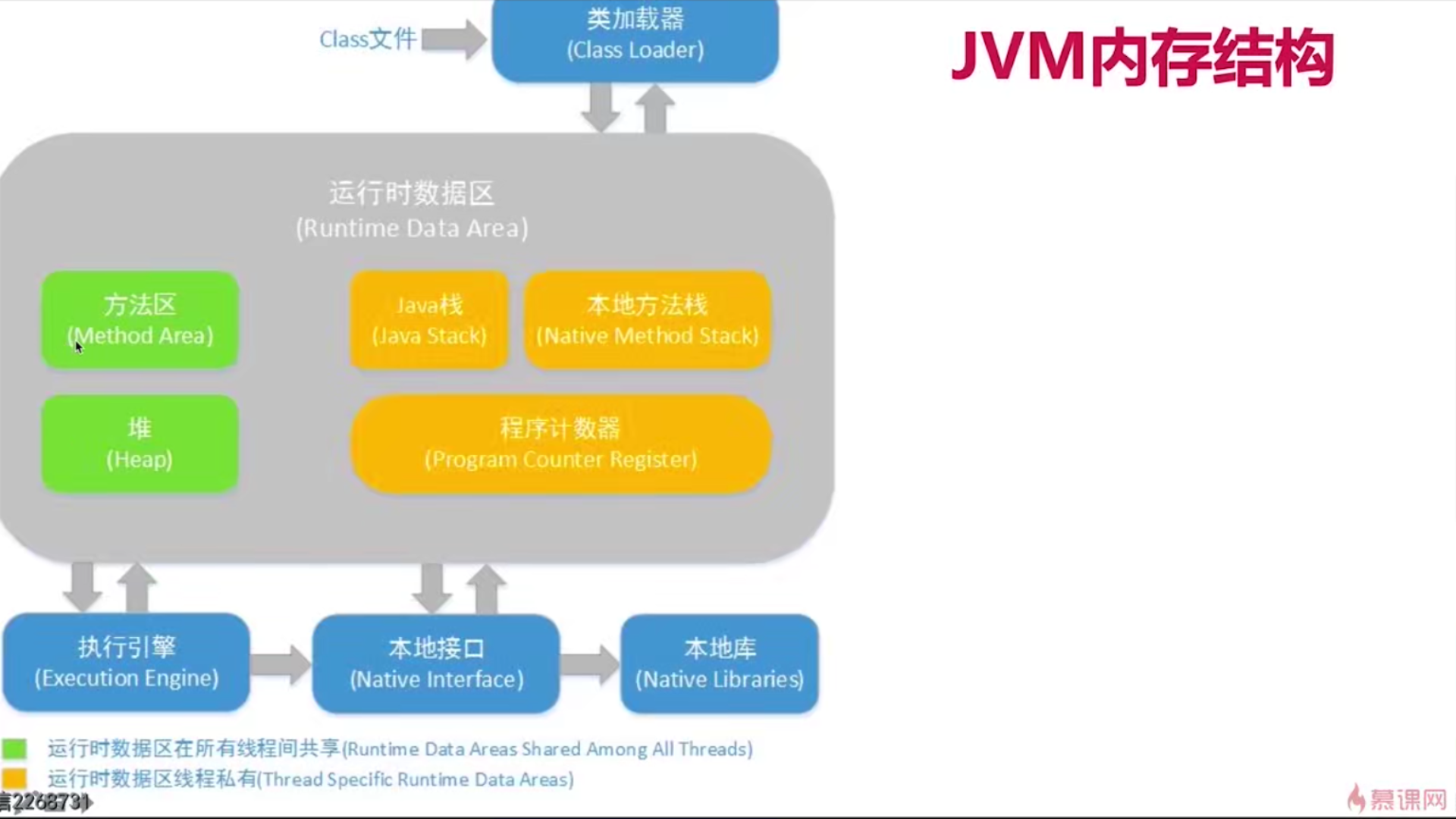
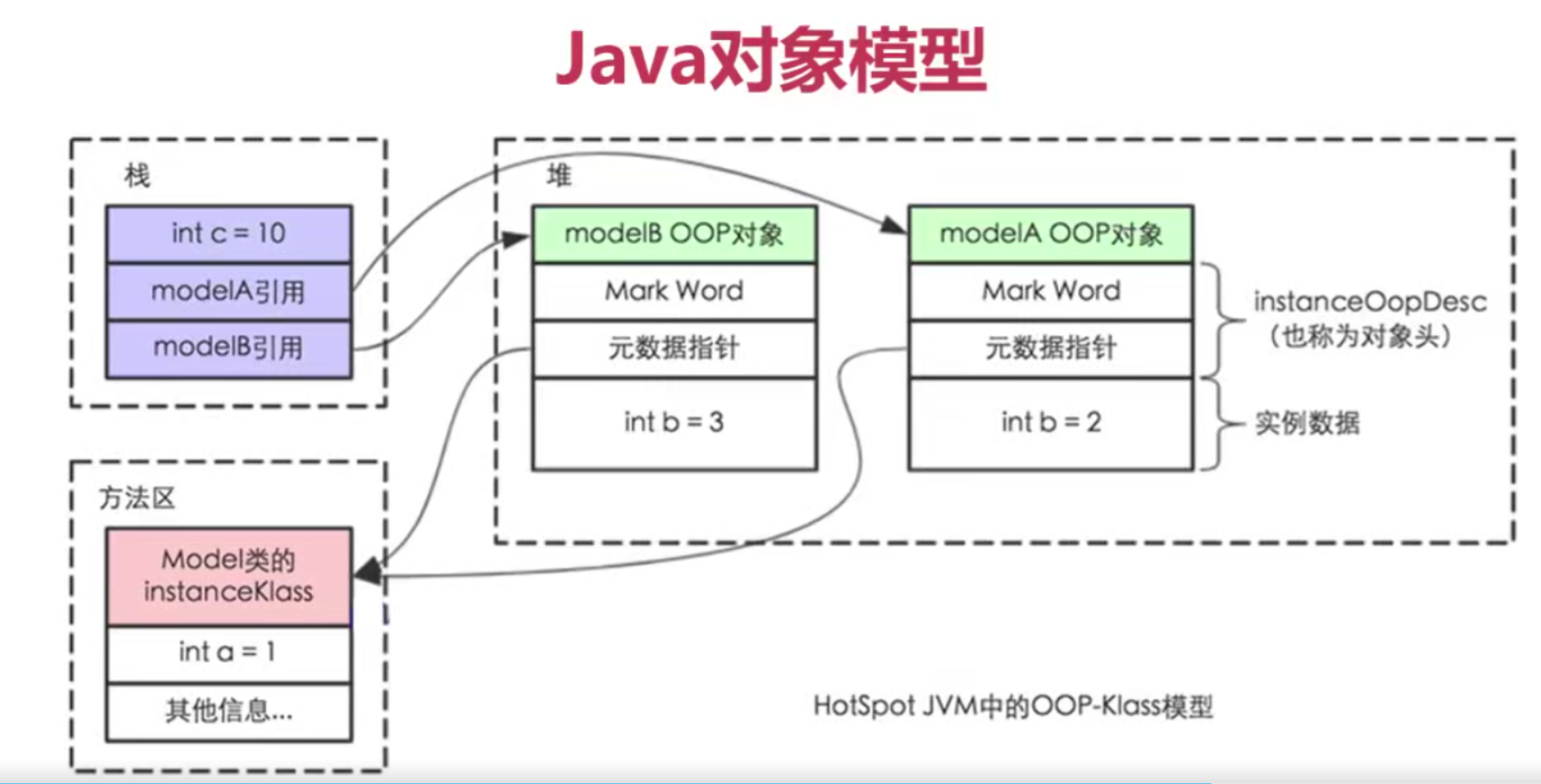

JMM规范
重排序
代码
*/
public class OutOfOrderExecution {
private static int x = 0, y = 0;
private static int a = 0, b = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
int i = 0;
for (; ; ) {
i++;
x = 0;
y = 0;
a = 0;
b = 0;
CountDownLatch latch = new CountDownLatch(3);
Thread one = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
latch.countDown();
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
a = 1;
x = b;
}
});
Thread two = new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
latch.countDown();
latch.await();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
b = 1;
y = a;
}
});
two.start();
one.start();
latch.countDown();
one.join();
two.join();
String result = "第" + i + "次(" + x + "," + y + ")";
if (x == 1 && y == 1) {
System.out.println(result);
break;
} else {
System.out.println(result);
}
}
}
}





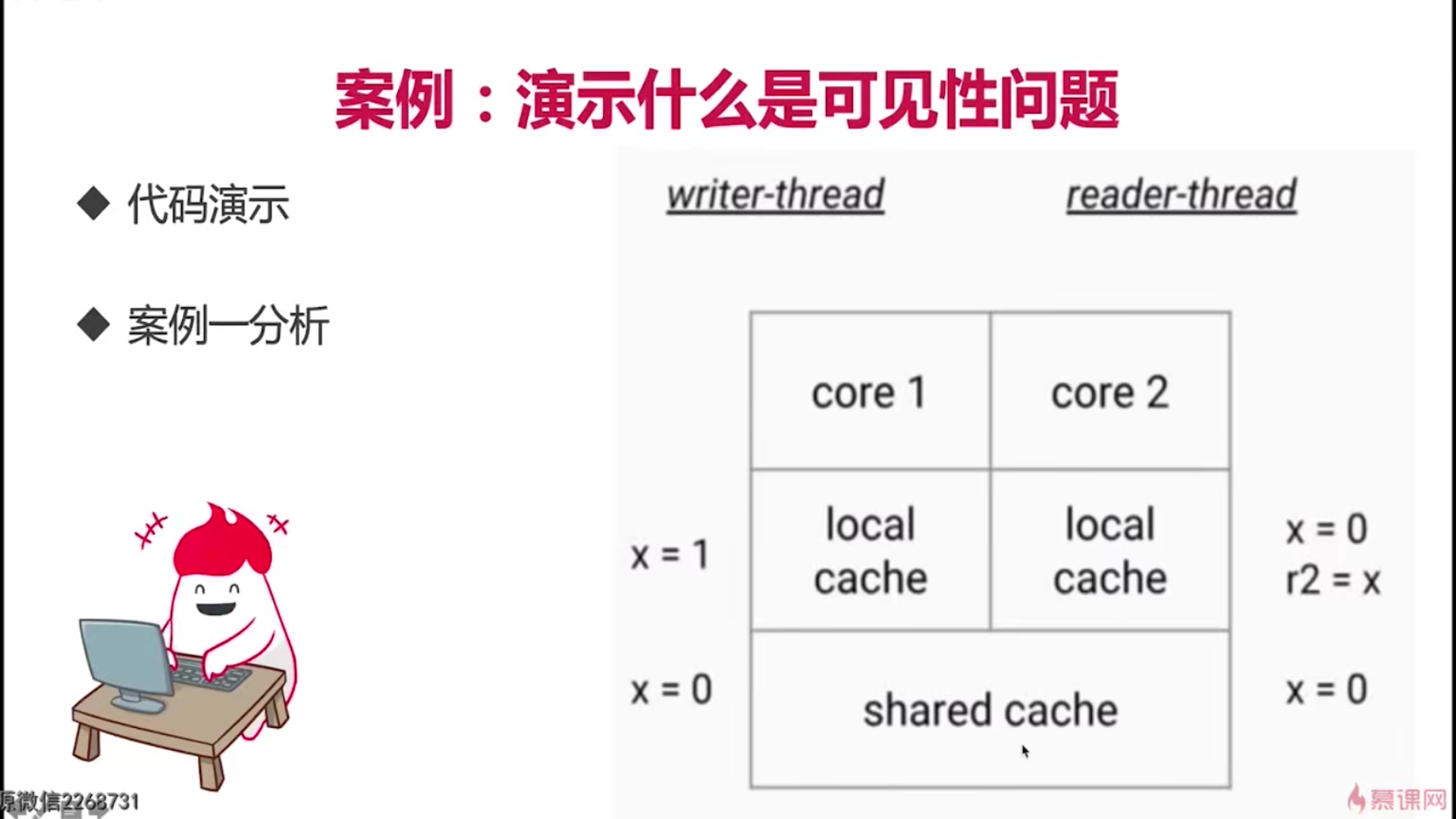
可见性
/**
* 描述: 演示可见性带来的问题
*/
public class FieldVisibility {
//错误的b=3;a=1
int a = 1;
int b = 2;
private void change() {
a = 3;
b = a;
}
private void print() {
System.out.println("b=" + b + ";a=" + a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
FieldVisibility test = new FieldVisibility();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
test.change();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
test.print();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
volatile 强制线程看到更改的变量
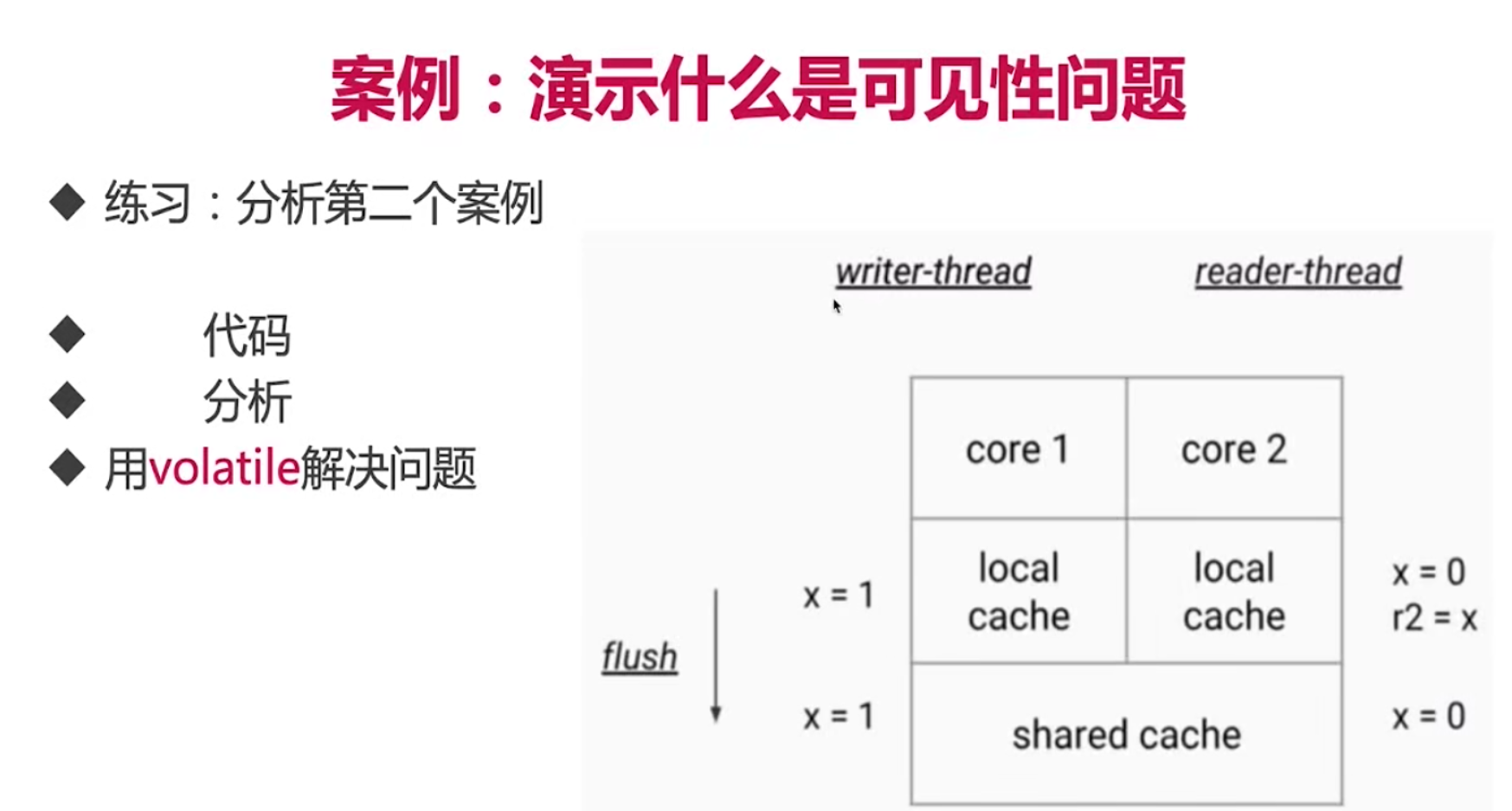


主内存和本地内存

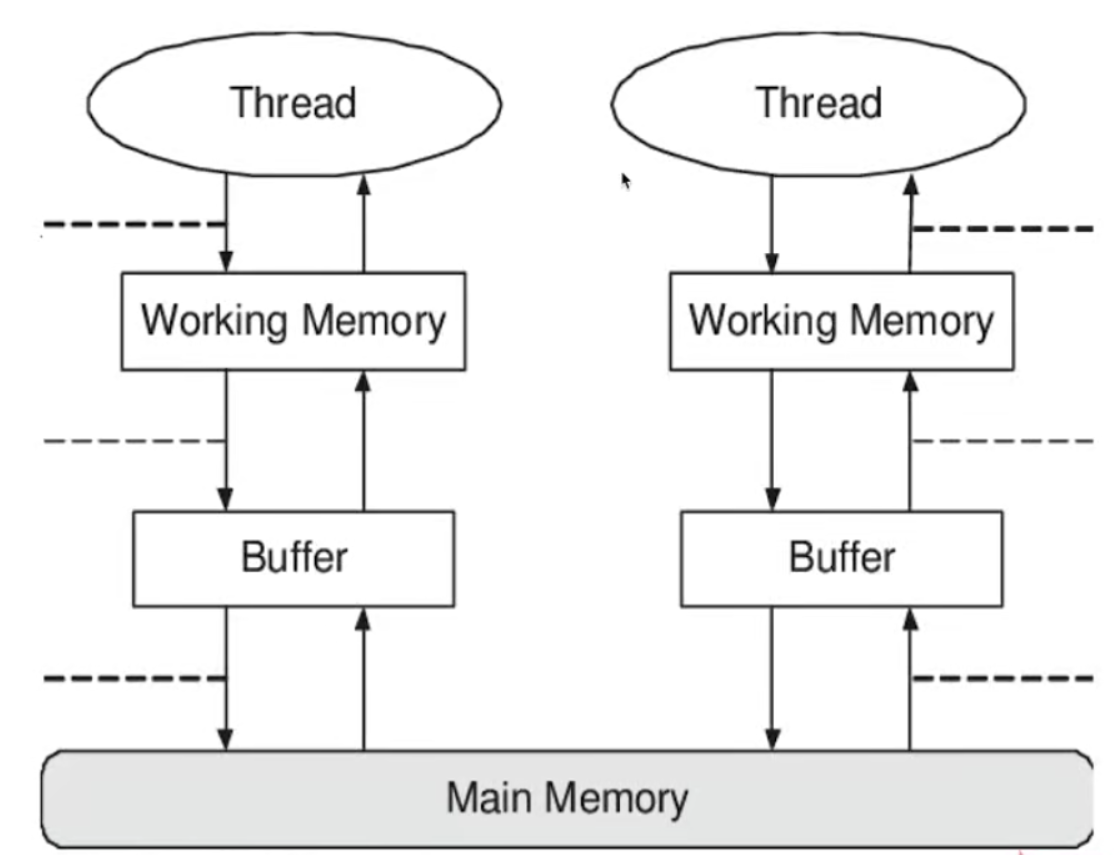
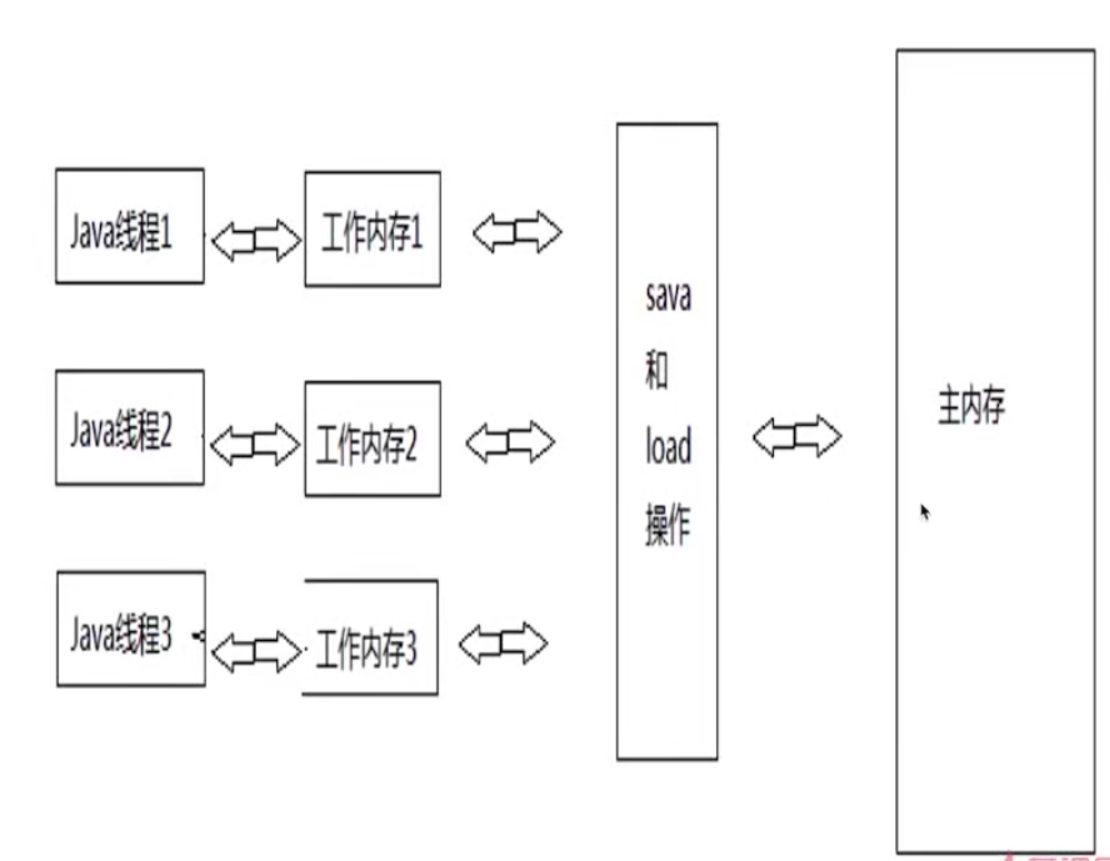

happens-before

原则:锁操作,volatile,join

volatile


不适用a++:
/**
* 描述: 不适用于volatile的场景
*/
public class NoVolatile implements Runnable {
volatile int a;
AtomicInteger realA = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable r = new NoVolatile();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(r);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(r);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(((NoVolatile) r).a);
System.out.println(((NoVolatile) r).realA.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
a++;
realA.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
不适用于依赖于之前的状态
/**
* 描述: volatile不适用的情况2
*/
public class NoVolatile2 implements Runnable {
volatile boolean done = false;
AtomicInteger realA = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable r = new NoVolatile2();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(r);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(r);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(((NoVolatile2) r).done);
System.out.println(((NoVolatile2) r).realA.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
flipDone();
realA.incrementAndGet();
}
}
private void flipDone() {
done = !done;
}
}
适用纯赋值:
/**
* 描述: volatile适用的情况1
*/
public class UseVolatile1 implements Runnable {
volatile boolean done = false;
AtomicInteger realA = new AtomicInteger();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Runnable r = new UseVolatile1();
Thread thread1 = new Thread(r);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(r);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println(((UseVolatile1) r).done);
System.out.println(((UseVolatile1) r).realA.get());
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
setDone();
realA.incrementAndGet();
}
}
private void setDone() {
done = true;
}
}
适用触发器:
/**
* 描述:
*/
public class FieldVisibility {
int a = 1;
volatile int b = 2;
private void change() {
a = 3;
b = a;
}
private void print() {
System.out.println("b=" + b + ";a=" + a);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true) {
FieldVisibility test = new FieldVisibility();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
test.change();
}
}).start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
test.print();
}
}).start();
}
}
}
对比syn:






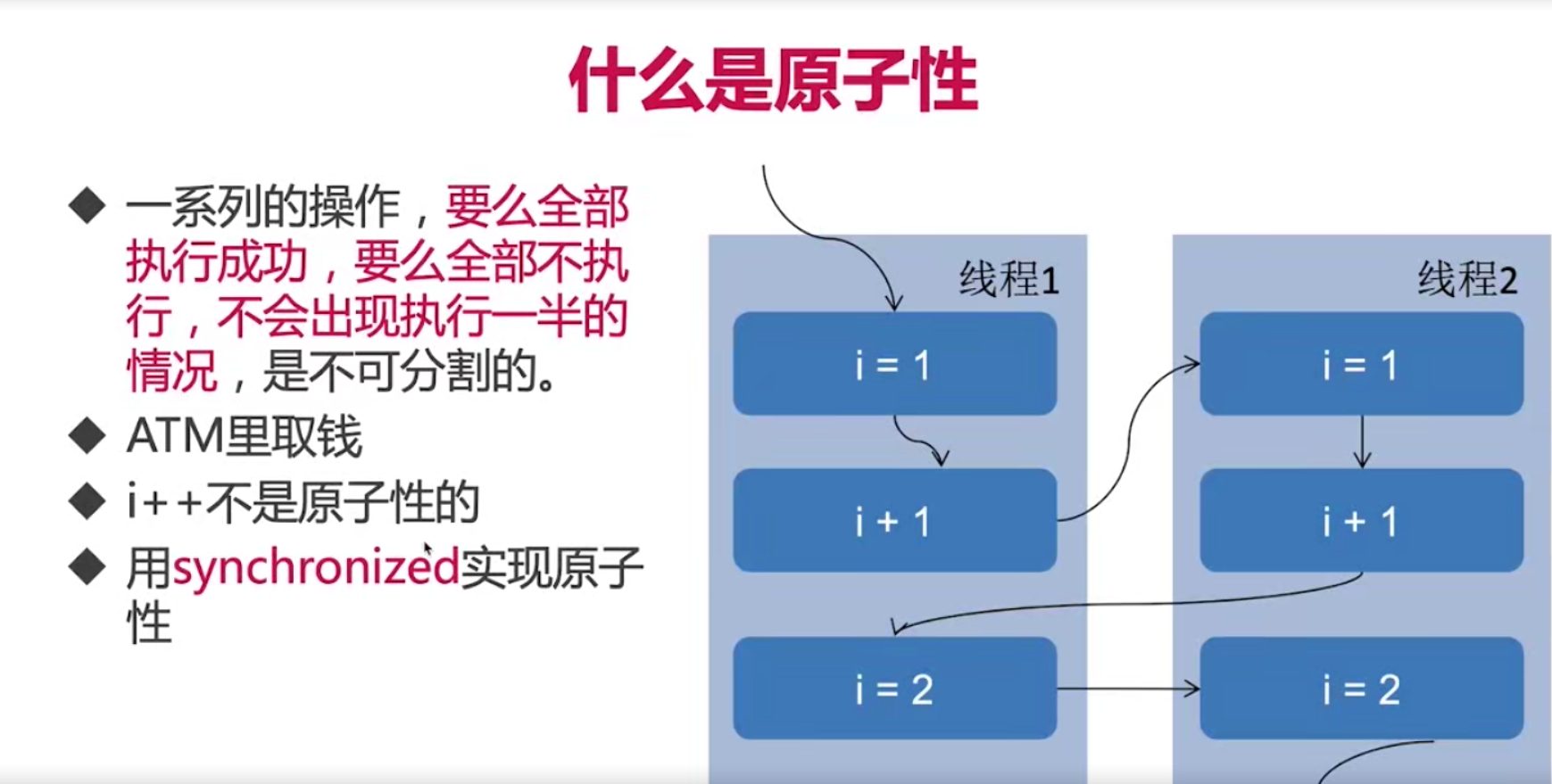
原子性



单例模式


饿汉式:jvm保证线程安全,类一加载就完成了
public class Singleton1 {
private final static Singleton1 INSTANCE = new Singleton1();
private Singleton1(){
}
public static Singleton1 getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
public class Singleton2 {
private final static Singleton2 INSTANCE;
static {
INSTANCE = new Singleton2();
}
private Singleton2(){
}
public static Singleton2 getInstance(){
return INSTANCE;
}
}
懒汉式:
线程安全,性能不好
public class Singleton3 {
private static Singleton3 INSTANCE;
private Singleton3(){
}
public synchronized static Singleton3 getInstance(){
if (INSTANCE == null){
INSTANCE = new Singleton3();
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}
线程不安全
public class Singleton4 {
private static Singleton4 INSTANCE;
private Singleton4(){
}
public static Singleton4 getInstance(){
if (INSTANCE == null){
INSTANCE = new Singleton4();
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}
public class Singleton5 {
private static Singleton5 INSTANCE;
private Singleton5(){
}
// 解锁后其余线程会继续创建覆盖
public static Singleton5 getInstance(){
if (INSTANCE == null){
synchronized (Singleton5.class){
INSTANCE = new Singleton5();
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}
推荐使用:双重检查,
public class Singleton6 {
private volatile static Singleton6 INSTANCE;
private Singleton4(){
}
public static Singleton6 getInstance(){
if (INSTANCE == null){
synchronized (Singleton6.class){
if (INSTANCE == null)
INSTANCE = new Singleton6();
}
}
return INSTANCE;
}
}

一次检查,第四种会创建多次实例,第三种安全但是性能不好
最安全的,volatile可见性保证第二个线程能看到第一个线程给Instance做的改变,禁止重排序保证创建对象不会返回空指针
静态内部类:
public class Singleton7 {
private volatile static Singleton7 INSTANCE;
private Singleton7(){
}
private static class SingletonInstance{
private static final Singleton7 INSTANCE = new Singleton7();
}
public static Singleton7 getInstance(){
return SingletonInstance.INSTANCE;
}
}
枚举:推荐用
public enum Singleton8 {
INSTANCE;
public void whatever(){
}
}
总结:
饿汉:简单,但是没有懒加载
懒汉:有线程安全问题
静态内部类:可用
双重检查:面试用
枚举:最好,写法简单,线程安全,反编译是静态对象,避免反序列化破坏单例


面试题:
总结
死锁
public class DeadLock implements Runnable{
static Object o1 = new Object();
static Object o2 = new Object();
int flag;
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag == 1){
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("flag = "+flag);
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("拿到o2");
}
}
}
if (flag == 0){
synchronized (o2){
System.out.println("flag = "+flag);
synchronized (o1){
System.out.println("拿到o1");
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLock lock1 = new DeadLock();
DeadLock lock2 = new DeadLock();
lock1.flag = 1;
lock2.flag = 0;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(lock1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(lock2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();;
}
}
银行转账:
public class DeadLock1 implements Runnable{
static Account a = new Account(500);
static Account b = new Account(500);
int flag;
static class Account{
int balance;
public Account(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag == 1){
try {
transferMoney(a, b, 200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (flag == 0){
try {
transferMoney(b, a, 200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void transferMoney(Account from, Account to, int amount) throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (from){
// Thread.sleep(500);
synchronized (to){
if (from.balance - amount < 0){
System.out.println("余额不足");
}
from.balance -= amount;
to.balance += amount;
System.out.println("成功转账"+amount+"元");
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DeadLock1 lock1 = new DeadLock1();
DeadLock1 lock2 = new DeadLock1();
lock1.flag = 1;
lock2.flag = 0;
Thread thread1 = new Thread(lock1);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(lock2);
thread1.start();
thread2.start();;
thread1.join();
thread2.join();
System.out.println("a的"+a.balance);
System.out.println("b的"+b.balance);
}
}
定位死锁
threadMXBean
ThreadMXBean threadMXBean = ManagementFactory.getThreadMXBean();
long[] deadlockedThreads = threadMXBean.findDeadlockedThreads();
if (deadlockedThreads != null && deadlockedThreads.length > 0) {
for (int i = 0; i < deadlockedThreads.length; i++) {
ThreadInfo threadInfo = threadMXBean.getThreadInfo(deadlockedThreads[i]);
System.out.println("发现死锁" + threadInfo.getThreadName());
}
}
修复死锁


避免策略:

/**
* 描述: 转账时候遇到死锁,一旦打开注释,便会发生死锁
*/
public class TransferMoney implements Runnable {
int flag = 1;
static Account a = new Account(500);
static Account b = new Account(500);
static Object lock = new Object();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
TransferMoney r1 = new TransferMoney();
TransferMoney r2 = new TransferMoney();
r1.flag = 1;
r2.flag = 0;
Thread t1 = new Thread(r1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(r2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t1.join();
t2.join();
System.out.println("a的余额" + a.balance);
System.out.println("b的余额" + b.balance);
}
@Override
public void run() {
if (flag == 1) {
try {
transferMoney(a, b, 200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (flag == 0) {
try {
transferMoney(b, a, 200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
private void transferMoney(Account from, Account to, int amount) throws InterruptedException {
class Helper{
public void transfer(){
if (from.balance - amount < 0){
System.out.println("余额不足");
}
from.balance -= amount;
to.balance += amount;
System.out.println("成功转账"+amount+"元");
}
}
int fromHash = System.identityHashCode(from);
int toHash = System.identityHashCode(to);
if (fromHash < toHash){
synchronized (from){
synchronized (to){
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
}
else if (fromHash > toHash){
synchronized (to){
synchronized (from){
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
}else {
synchronized (lock){
synchronized (to){
synchronized (from){
new Helper().transfer();
}
}
}
}
}
static class Account {
public Account(int balance) {
this.balance = balance;
}
int balance;
}
}
哲学家问题
public class Dining {
public static class Philosopher implements Runnable{
private final Object leftChopstick;
private final Object rightChopstick;
public Philosopher(Object leftChopstick, Object rightChopstick) {
this.leftChopstick = leftChopstick;
this.rightChopstick = rightChopstick;
}
private void doActon(String acton) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+acton);
Thread.sleep((long) (Math.random()*10));
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true){
doActon("thinking ");
synchronized (leftChopstick){
doActon("拿左筷子");
synchronized (rightChopstick){
doActon("拿右筷子");
doActon("吃饭");
doActon("放下右筷子");
}
doActon("放下左筷子");
}
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Philosopher[] philosophers = new Philosopher[5];
Object[] chopsticks = new Object[philosophers.length];
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
chopsticks[i] = new Object();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Object left = chopsticks[i];
Object right = chopsticks[(i+1)%5];
philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(left, right);
new Thread(philosophers[i], "哲学家"+(i+1)).start();
}
}
}
解决:一个哲学家更换拿的顺序
if (i == philosophers.length-1)
philosophers[i] = new Philosopher(right, left);
else
检测与恢复



实际开发避免死锁




lock:
public class tryLock implements Runnable {
int flag;
static Lock lock1 = new ReentrantLock();
static Lock lock2 = new ReentrantLock();
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
if (flag == 1){
try {
if (lock1.tryLock(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)){
System.out.println("线程1获取1");
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
if (lock2.tryLock(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)){
System.out.println("线程1获取2");
System.out.println("线程1获取两把");
lock2.unlock();
lock1.unlock();
break;
}else {
System.out.println("线程1获取2失败");
lock1.unlock();
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
}
}else {
System.out.println("线程1获取1失败");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (flag == 0){
try {
if (lock2.tryLock(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)){
System.out.println("线程2获取2");
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
if (lock1.tryLock(800, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)){
System.out.println("线程2获取1");
System.out.println("线程2获取两把");
lock2.unlock();
lock1.unlock();
break;
}else {
System.out.println("线程2获取1失败");
lock2.unlock();
Thread.sleep(new Random().nextInt(1000));
}
}else {
System.out.println("线程2获取2失败");
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
tryLock r1 = new tryLock();
tryLock r2 = new tryLock();
r1.flag = 1;
r2.flag = 0;
new Thread(r1).start();
new Thread(r2).start();
}
}


活锁


/**
* 描述: 演示活锁问题
*/
public class LiveLock {
static class Spoon {
private Diner owner;
public Spoon(Diner owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
public Diner getOwner() {
return owner;
}
public void setOwner(Diner owner) {
this.owner = owner;
}
public synchronized void use() {
System.out.printf("%s吃完了!", owner.name);
}
}
static class Diner {
private String name;
private boolean isHungry;
public Diner(String name) {
this.name = name;
isHungry = true;
}
public void eatWith(Spoon spoon, Diner spouse) {
while (isHungry) {
if (spoon.owner != this) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
continue;
}
Random random = new Random();
if (spouse.isHungry && random.nextInt(10) < 9) {
System.out.println(name + ": 亲爱的" + spouse.name + "你先吃吧");
spoon.setOwner(spouse);
continue;
}
spoon.use();
isHungry = false;
System.out.println(name + ": 我吃完了");
spoon.setOwner(spouse);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Diner husband = new Diner("牛郎");
Diner wife = new Diner("织女");
Spoon spoon = new Spoon(husband);
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
husband.eatWith(spoon, wife);
}
}, "牛郎").start();
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
wife.eatWith(spoon, husband);
}
}, "织女").start();
}
}

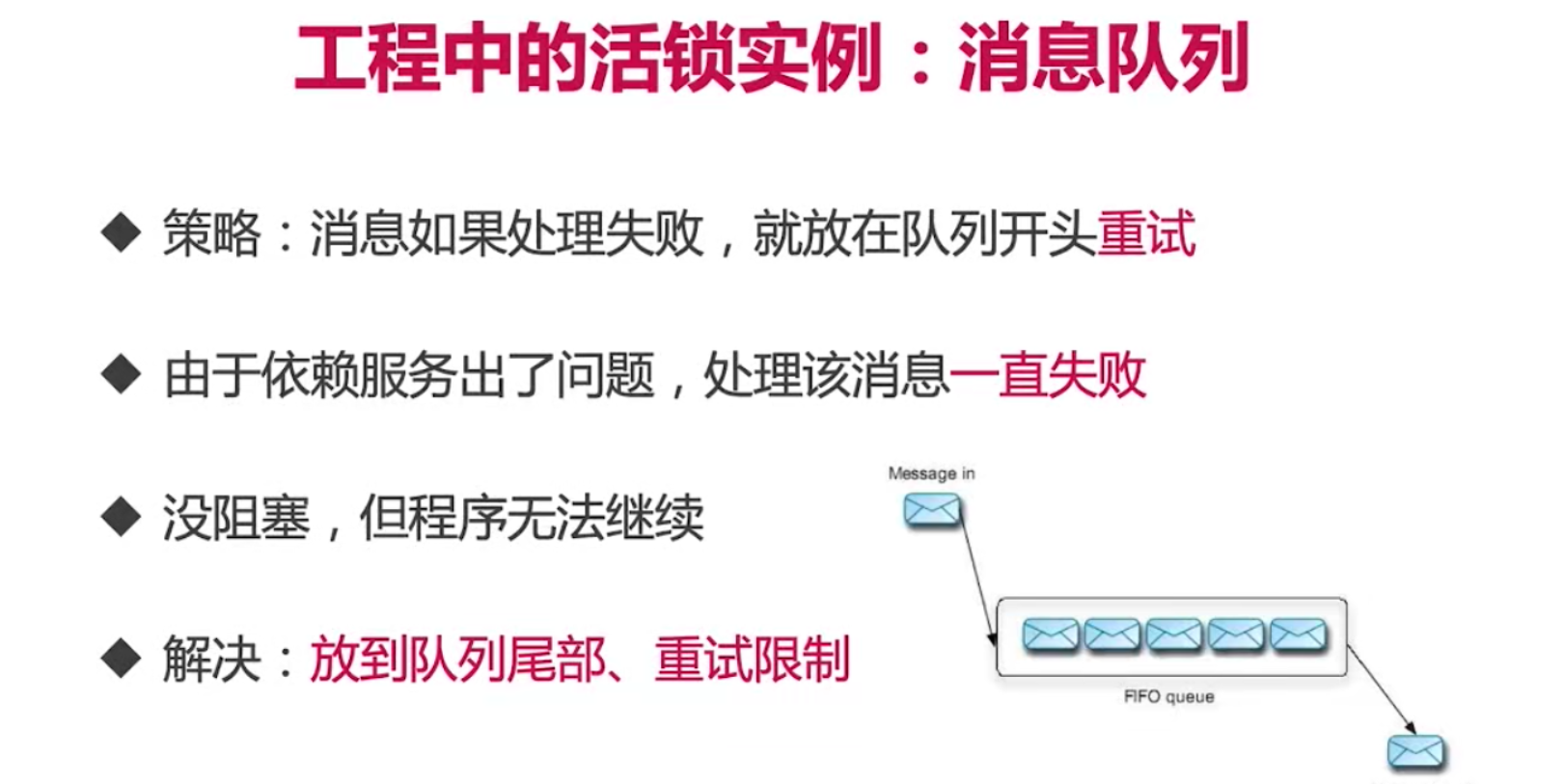
饥饿

面试
syn关键字:
用法:对象锁和类锁
对象锁包括方法锁和同步代码块锁:
同步代码块:this和自己建对象,手动指定锁的对象
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest instance = new ThreadTest();
Object lock1 = new Object();
Object lock2 = new Object();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (lock1){
System.out.println("lock1 "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock1 end");
}
synchronized (lock1){
System.out.println("lock2"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock2 end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
方法锁:修饰普通方法,锁对象默认为this
类锁:是Class对象的锁,只能在同一时刻被一个对象拥有
加在static方法上:
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest2 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest2 instance1 = new ThreadTest2();
static ThreadTest2 instance2 = new ThreadTest2();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static synchronized void method() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("方法"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
.class代码块:
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest3 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest3 instance1 = new ThreadTest3();
static ThreadTest3 instance2 = new ThreadTest3();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public void method() throws InterruptedException {
synchronized (ThreadTest3.class){
System.out.println("方法"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
面试常考:
1.两个线程同时访问一个对象的同步方法:非并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest4 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest4 instance = new ThreadTest4();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
System.out.println("this"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
2.两个线程同时访问2个对象的同步方法:非并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest4 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest4 instance1 = new ThreadTest4();
static ThreadTest4 instance2 = new ThreadTest4();
@Override
public void run() {
synchronized (this){
System.out.println("this"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"lock1 end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
3.两个线程同时访问syn静态方法:非并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest2 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest2 instance1 = new ThreadTest2();
static ThreadTest2 instance2 = new ThreadTest2();
@Override
public void run() {
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static synchronized void method() throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("方法"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance2);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
4.同时访问同步与非同步方法:并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest5 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest5 instance = new ThreadTest5();
@Override
public void run() {
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-0")){
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
try {
method1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void method() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("方法"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public void method1() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("无锁方法"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
5.访问同一个对象的不同的普通同步方法:非并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest6 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest6 instance = new ThreadTest6();
@Override
public void run() {
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-0")){
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
try {
method1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void method() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("方法1"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public synchronized void method1() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("方法2"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
6.同时访问静态syn方法和非静态syn方法:并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest7 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest7 instance = new ThreadTest7();
@Override
public void run() {
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-0")){
try {
method();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
try {
method1();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static synchronized void method() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("静态方法1"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public synchronized void method1() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("方法2"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
7.方法抛出异常,释放锁:并行
package syn;
/**
* @param:
* @return:
* @time: 2021/7/26
*/
public class ThreadTest8 implements Runnable{
static ThreadTest8 instance = new ThreadTest8();
@Override
public void run() {
if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("Thread-0")){
try {
method1();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}else {
try {
method2();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public synchronized void method1() {
{
System.out.println("异常方法1"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
throw new RuntimeException();
}
}
public synchronized void method2() throws InterruptedException {
{
System.out.println("方法2"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
Thread.sleep(3000);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" end");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(instance);
Thread t2 = new Thread(instance);
t1.start();
t2.start();
while (t1.isAlive() || t2.isAlive()){
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
总结:
1.一把锁只能被一个线程获取,没有拿到锁的必等待,对应1和5
2.每个实例都对应自己的一把锁,不同实例之间不影响,锁对象是.class和static时候,所有对象共同同一把类锁,对应2,3,4,6.
3.抛出异常会释放锁。
被syn的方法里调用没有被syn的方法,不是线程安全的。
syn的性质:
可重入性,不可中断
原理:加锁和释放锁的原理:内置锁
等价:
public synchronized void method(){
System.out.println("syn");
}
void method2(){
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println("lock");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
可重入原理:加锁次数计数器
jvm跟踪对象被加锁的次数,相同的线程在此对象上再次获得锁时候,锁会减少,到0了释放
可见性原理:java内存模型
缺陷:
效率低:锁的释放情况少,试图获得锁时不能设定超时,不能中断一个正在试图获得锁的线程。
不灵活:加锁和释放的时机单一,每个锁仅有单一的条件,可能是不够的。
无法知道是否成功得到锁
面试题:注意点:锁对象不能为空,作用域不宜过大,避免死锁
Lock和syn选择:线程工具、syn
多线程访问同步方法的各种情况
总结:jvm自动通过monitor加锁解锁,保证同时只有一个线程可以执行指定代码,从而保证了线程安全,同时具有可重入和不可中断





















 10万+
10万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








