总括
下面我将用6道例题来讲解DFS
基础方法 注意事项 常用剪枝 等等
基础为主
HUD 1010
题目
Problem Description
The doggie found a bone in an ancient maze, which fascinated him a
lot. However, when he picked it up, the maze began to shake, and the
doggie could feel the ground sinking. He realized that the bone was a
trap, and he tried desperately to get out of this maze.The maze was a rectangle with sizes N by M. There was a door in the
maze. At the beginning, the door was closed and it would open at the
T-th second for a short period of time (less than 1 second). Therefore
the doggie had to arrive at the door on exactly the T-th second. In
every second, he could move one block to one of the upper, lower, left
and right neighboring blocks. Once he entered a block, the ground of
this block would start to sink and disappear in the next second. He
could not stay at one block for more than one second, nor could he
move into a visited block. Can the poor doggie survive? Please help
him.Input
The input consists of multiple test cases. The first line of each test
case contains three integers N, M, and T (1 < N, M < 7; 0 < T < 50),
which denote the sizes of the maze and the time at which the door will
open, respectively. The next N lines give the maze layout, with each
line containing M characters. A character is one of the following:‘X’: a block of wall, which the doggie cannot enter; ‘S’: the start
point of the doggie; ‘D’: the Door; or ‘.’: an empty block.The input is terminated with three 0’s. This test case is not to be
processed.Output
For each test case, print in one line “YES” if the doggie can survive,
or “NO” otherwise.Sample Input
4 4 5 S.X. ..X. ..XD …. 3 4 5 S.X. ..X. …D 0 0 0
Sample Output
NO YES
分析
这道题和常见的DFS有两一点不同
这道题对剪枝的要求较高 常规方法基本超时
下面我们补充一种剪枝方法: 奇偶剪枝
作用:在规定某一时间到达特定位置的时候,我们可以通过奇偶性提前判断出此条路径是否可行
适用范围: 对于给定终点位置和终点时间的BFS或者DFS
使用方法 :
if (t < abs(ex - x) + abs(ey - y) || (t - (abs(ex - x) + abs(ey - y))) % 2)
return; 这里是结合本题的使用方法 简单来说就是
1.判断现在的位置和目标位置的距离是否大于等于剩余步骤
2.判断剩余步骤是否是偶数(奇偶剪枝的核心)
证明过程:
简单的说每走错(不一定是错 方向 因为墙的绕路等等)一步都需要另一步来更正 这就是2步
经过N次错误和修正之后必定为偶数
所以最终的路径长度 = 最短路径长度 + 2 * n
推广之,若 t-[abs(ex-sx)+abs(ey-sy)] 结果为非偶数(奇数),则无法在t步恰好到达;
返回,false;
上代码 + 注释分析
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
int sx, sy, ex, ey;
int n, m;
char map[10][10];
int flag, step;
int d[4][2] = { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, -1, -1, 0 };//代表可以走的4个方向
void dfs(int x, int y, int t)
{
if (flag == 1)
return;
if (t < abs(ex - x) + abs(ey - y) || (t - (abs(ex - x) + abs(ey - y))) % 2)
return;//剪枝 如果步数小于不考虑墙的最短路径
else if (t == 0) //判断退出循环的路径
{
if (x == ex&&y == ey)
{
flag = 1;
return;
}
else
return;
}
else
for (int i = 0; i<4; i++) //4个方向的移动
{
int nx = x + d[i][0], ny = y + d[i][1];
if (nx>0 && nx <= n&&ny>0 && ny <= m && (map[nx][ny] == '.' || map[nx][ny] == 'D'))
{
map[nx][ny] = 'X';
dfs(nx, ny, t - 1);
map[nx][ny] = '.';
}
}
return;
}
int main()
{
char str[10];
int t;
while (scanf_s("%d%d%d", &n, &m, &t) != EOF)
{
if (n == 0 && m == 0 && t == 0)
break;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
scanf_s("%s", str, 10);
for (int j = 1; j <= m; j++)
{
map[i][j] = str[j - 1];
if (map[i][j] == 'S') sx = i, sy = j;//标记开始和结束位置
else if (map[i][j] == 'D') ex = i, ey = j;
}
}
flag = 0;
dfs(sx, sy, t);
if (flag == 0) printf("NO\n");
else printf("YES\n");
}
return 0;
}HDU1016
题目
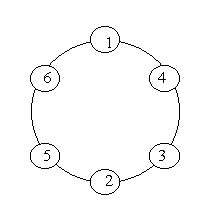
Problem Description A ring is compose of n circles as shown in
diagram. Put natural number 1, 2, …, n into each circle separately,
and the sum of numbers in two adjacent circles should be a prime.Note: the number of first circle should always be 1.
Input n (0 < n < 20).
Output The output format is shown as sample below. Each row represents
a series of circle numbers in the ring beginning from 1 clockwisely
and anticlockwisely. The order of numbers must satisfy the above
requirements. Print solutions in lexicographical order.You are to write a program that completes above process.
Print a blank line after each case.
Sample Input 6 8
Sample Output Case 1: 1 4 3 2 5 6 1 6 5 2 3 4
Case 2: 1 2 3 8 5 6 7 4 1 2 5 8 3 4 7 6 1 4 7 6 5 8 3 2 1 6 7 4 3 8 5
2
翻译
顺时针1 - n填圈,要求相邻两项的和是素数,其中第一项必须为1
最终按顺时针输出数字
分析
这是一个DFS全排列的改版
修改了一下判断条件 将不重复改为不重复 + 和前一项的和为奇数
另外为了省时可以将小于40的素数打表(手动输入也行)
其他的未作修改
代码 + 注释
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
int n, k;
int a[25];//纪录排好的的顺序
int b[40];//打表素数
int c[25];//用来标记已经使用过的量
void DFS(int n,int cur);
int main(void)
{
for (int i = 1; i < 40; i++)//打表素数
{
b[i] = 1;
for (int j = 2; j < i; j++)
if (i % j == 0)
b[i] = 0;
}
k = 0;
while (scanf_s("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
k++;
printf("Case %d:\n", k);
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
memset(c, 0, sizeof(c));
a[1] = 1;
DFS(n, 2);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
void DFS(int n, int cur)
{
if (cur - 1 == n && b[a[cur - 1] + a[1]] == 1)//当a数组填满的时候 输出全部数组
{
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
printf("%d ", a[i]);
printf("%d\n", a[n]);
}
else
{
int i;
for (i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
if (c[i] == 0 && b[a[cur - 1] + i] == 1)
{
c[i] = 1;//标记数组
a[cur] = i;
DFS(n, cur + 1);//递归调用
c[i] = 0;//因为是 一定要改回来
}
}
}
}HDU 1072
题目
Problem Description Ignatius had a nightmare last night. He found
himself in a labyrinth with a time bomb on him. The labyrinth has an
exit, Ignatius should get out of the labyrinth before the bomb
explodes. The initial exploding time of the bomb is set to 6 minutes.
To prevent the bomb from exploding by shake, Ignatius had to move
slowly, that is to move from one area to the nearest area(that is, if
Ignatius stands on (x,y) now, he could only on (x+1,y), (x-1,y),
(x,y+1), or (x,y-1) in the next minute) takes him 1 minute. Some area
in the labyrinth contains a Bomb-Reset-Equipment. They could reset the
exploding time to 6 minutes.Given the layout of the labyrinth and Ignatius’ start position, please
tell Ignatius whether he could get out of the labyrinth, if he could,
output the minimum time that he has to use to find the exit of the
labyrinth, else output -1.Here are some rules:
1. We can assume the labyrinth is a 2 array.
2. Each minute, Ignatius could only get to one of the nearest area, and he should not walk out of the border, of course he could not walk
on a wall, too.
3. If Ignatius get to the exit when the exploding time turns to 0, he can’t get out of the labyrinth.
4. If Ignatius get to the area which contains Bomb-Rest-Equipment when the exploding time turns to 0, he can’t use the equipment to reset the
bomb.
5. A Bomb-Reset-Equipment can be used as many times as you wish, if it is needed, Ignatius can get to any areas in the labyrinth as many
times as you wish.
6. The time to reset the exploding time can be ignore, in other words, if Ignatius get to an area which contain Bomb-Rest-Equipment, and the
exploding time is larger than 0, the exploding time would be reset to
6.Input The input contains several test cases. The first line of the
input is a single integer T which is the number of test cases. T test
cases follow. Each test case starts with two integers N and
M(1<=N,Mm=8) which indicate the size of the labyrinth. Then N lines
follow, each line contains M integers. The array indicates the layout
of the labyrinth. There are five integers which indicate the different
type of area in the labyrinth: 0: The area is a wall, Ignatius should
not walk on it. 1: The area contains nothing, Ignatius can walk on it.
2: Ignatius’ start position, Ignatius starts his escape from this
position. 3: The exit of the labyrinth, Ignatius’ target position. 4:
The area contains a Bomb-Reset-Equipment, Ignatius can delay the
exploding time by walking to these areas.Output For each test case, if Ignatius can get out of the labyrinth,
you should output the minimum time he needs, else you should just
output -1.Sample Input 3 3 3 2 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 3 4 8 2 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 0 4 1 1 0 4
1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 3 5 8 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 4 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
1 4 1 0 1 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 0 3 0 1 1 1 4 1 1 1 1 1
Sample Output
4
-1
13
分析
因为在这里有定时器的时间问题所以剪枝的难度很大
比如我们同一个位置经历过两遍 但是在这两遍中定时器的时间不同
值就是两种不同的情况 不能轻易排除
当然经过分析我们可以知道
如果经过同一点有更优的计数器时间(计数器的示数更大) 那么这就是当前的更优解
所以我们在开地图数组的同时开 时间 和 步数 数组
分别用来记录走到当前位置的时间和步数最优解
只有当当前步骤的(计数器示数小于已知最优) && (步数大于已知最优)的时候才能直接剪枝
上代码 + 注释分析
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
int dir[4][2] = { { 1, 0 }, { 0, 1 }, { -1, 0 }, { 0, -1 } };
int map[10][10], time[10][10], step[10][10];
int n, m, sx, sy, dx, dy, minx;
void dfs(int x, int y, int len, int cnt)
{
if (x < 0 || x >= n || y < 0 || y >= m)
return;
if (len <= 0 || cnt >= minx)
return;
if (map[x][y] == 0)
return;
if (map[x][y] == 3)
{
if (cnt < minx)
minx = cnt;
return;
}
if (map[x][y] == 4)
len = 6;
if (cnt >= step[x][y] && time[x][y] >= len)//如果时间和步数都没有亮点 就飞了它
return;
step[x][y] = cnt;//计入当前值
time[x][y] = len;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
int tx = x + dir[i][0];
int ty = y + dir[i][1];
dfs(tx, ty, len - 1, cnt + 1);
}
}
int main(void)
{
int i, j, l, len, cnt, t;
while (scanf_s("%d", &t) != EOF)
{
for (l = 1; l <= t; l++)
{
scanf_s("%d %d", &n, &m);
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
for (j = 0; j < m; j++)
{
scanf_s("%d", &map[i][j]);
time[i][j] = 0;
step[i][j] = INT_MAX - 1;
if (map[i][j] == 2)
{
sx = i;
sy = j;
}
if (map[i][j] == 3)
{
dx = i;
dy = j;
}
}
}
len = 6;
cnt = 0;
minx = INT_MAX;
dfs(sx, sy, len, cnt);
if (minx == INT_MAX)
printf("-1\n");
else
printf("%d\n", minx);
}
}
return 0;
}



 本文通过三个实例详细解析深度优先搜索(DFS)算法的基础应用及高级技巧,包括剪枝方法、奇偶剪枝等,帮助读者深入理解DFS算法并掌握其在解决实际问题中的运用。
本文通过三个实例详细解析深度优先搜索(DFS)算法的基础应用及高级技巧,包括剪枝方法、奇偶剪枝等,帮助读者深入理解DFS算法并掌握其在解决实际问题中的运用。
















 361
361

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








