文章目录
1. Context继承关系
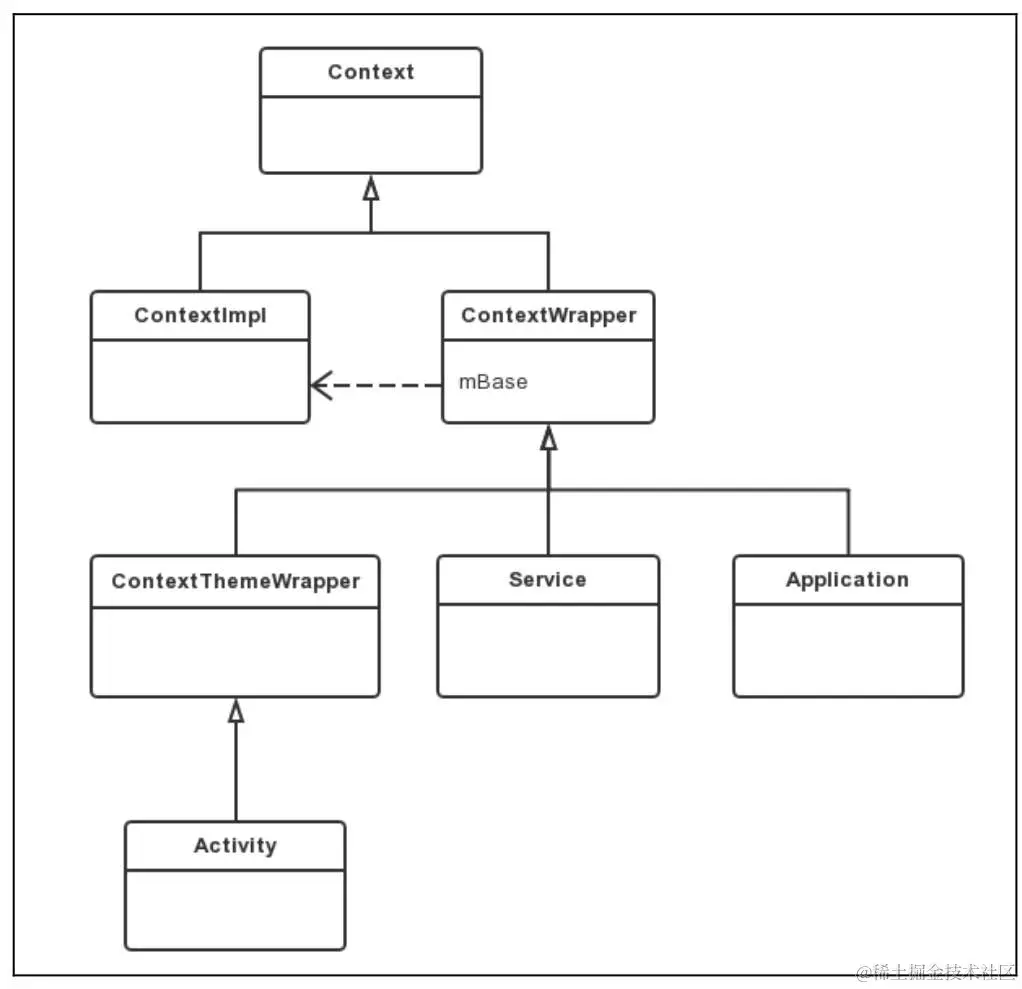
- Activity 、 Service 和 Application 都间接地继承自 Context
- ContextImpl 和 ContextWrapper 继承自 Context ,ContextWrapper 内部包含 Context类型的 mBase 对象,mBase 具体指向 ContextImpl (装饰模式)
- ContextThemeWrapper类,如其名所言,其内部包含了与主题(Theme)相关的接口,这里所说的主题就是指在AndroidManifest.xml中通过android:theme为Application元素或者Activity元素指定的主题
2. Context的作用
Context的中文翻译为:语境; 上下文; 背景; 环境,在开发中我们经常说称之为“上下文”,那么这个“上下文”到底是指什么意思呢?在语文中,我们可以理解为语境,在程序中,我们可以理解为当前对象在程序中所处的一个环境,一个与系统交互的过程。比如微信聊天,此时的“环境”是指聊天的界面以及相关的数据请求与传输,Context在加载资源、启动Activity、获取系统服务、创建View等操作都要参与。
/**
* Interface to global information about an application environment. This is
* an abstract class whose implementation is provided by
* the Android system. It
* allows access to application-specific resources and classes, as well as
* up-calls for application-level operations such as launching activities,
* broadcasting and receiving intents, etc.
*/
public abstract class Context {
/**
* File creation mode: the default mode, where the created file can only
* be accessed by the calling application (or all applications sharing the
* same user ID).
* @see #MODE_WORLD_READABLE
* @see #MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE
*/
public static final int MODE_PRIVATE = 0x0000;
public static final int MODE_WORLD_WRITEABLE = 0x0002;
public static final int MODE_APPEND = 0x8000;
public static final int MODE_MULTI_PROCESS = 0x0004;
.
.
.
}
- 弹出Toast
- 启动Activity
- 启动Service
- 发送广播
- 操作数据库
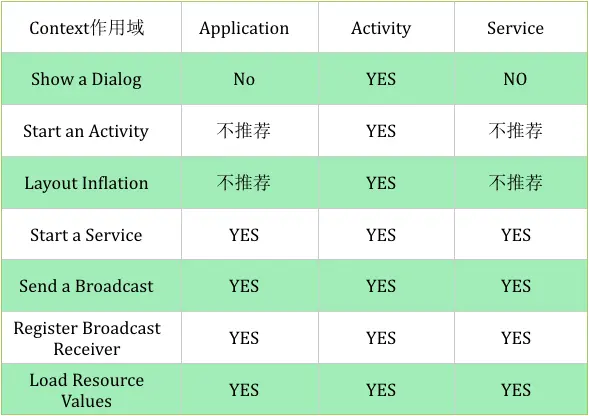
3. Context的作用域
4. 获取Context
- View.getContext,返回当前View对象的Context对象,通常是当前正在展示的Activity对象。
- Activity.getApplicationContext,获取当前Activity所在的(应用)进程的Context对象,通常我们使用Context对象时,要优先考虑这个全局的进程Context。
- ContextWrapper.getBaseContext():用来获取一个ContextWrapper进行装饰之前的Context,可以使用这个方法,这个方法在实际开发中使用并不多,也不建议使用。
- Activity.this 返回当前的Activity实例,如果是UI控件
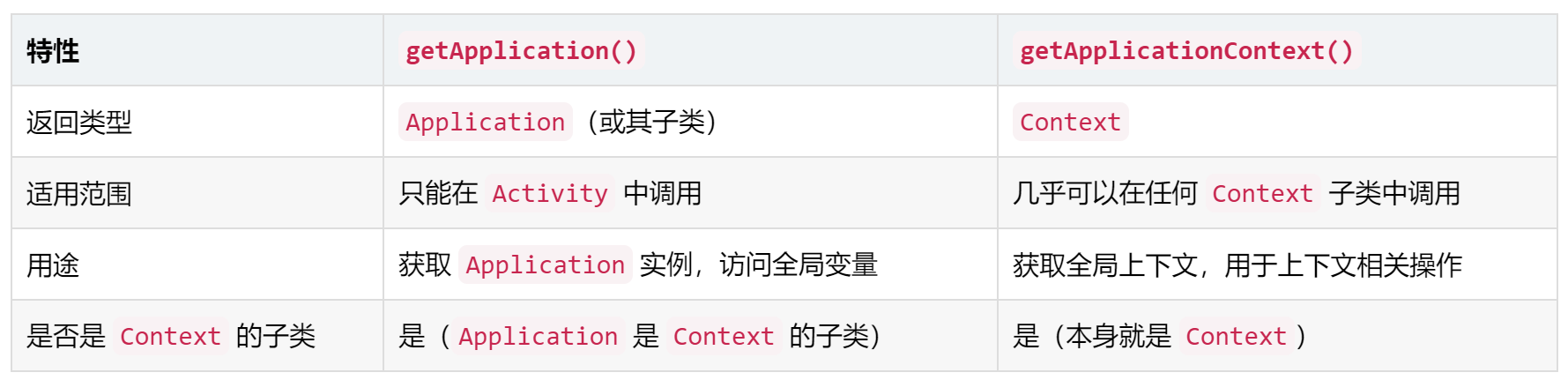
- getApplication()和getApplicationContext()区别
5. Context内存泄漏问题
- 单例中持有 Activity 的 Context
public class MySingleton {
private static MySingleton instance;
private Context context;
private MySingleton(Context context) {
this.context = context; // 持有 Activity 的引用
}
public static MySingleton getInstance(Context context) {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new MySingleton(context);
}
return instance;
}
}
- 非静态内部类持有外部类 Context
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
private Object backgroundTask;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
// 启动一个后台任务(非静态内部类)
backgroundTask = new BackgroundTask();
}
private class BackgroundTask {
void doWork() {
new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper()).postDelayed(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
// 做一些耗时操作
Log.d("BackgroundTask", "工作完成");
}
}, 60000); // 延迟1分钟执行
}
}
}
// BackgroundTask 是 MainActivity 的非静态内部类。
// 非静态内部类会隐式持有外部类的引用(即 MainActivity.this)。
- 正确使用Context
1:当Application的Context能搞定的情况下,并且生命周期长的对象,优先使用Application的Context。
2:不要让生命周期长于Activity的对象持有到Activity的引用。
3:尽量不要在Activity中使用非静态内部类,因为非静态内部类会隐式持有外部类实例的引用,如果使用静态内部类,将外部实例引用作为弱引用持有。
6. 为什么Diaglog不能用Apllication的Context
参考资料
报错点:WindowManagerService中的addWindow方法























 1245
1245

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








