参考:https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/huibai1984/article/details/78012949
TensorRT有两种阶段: 第一个阶段是构建阶段,第二种阶段是执行阶段.
- 下图是构建阶段的流程图
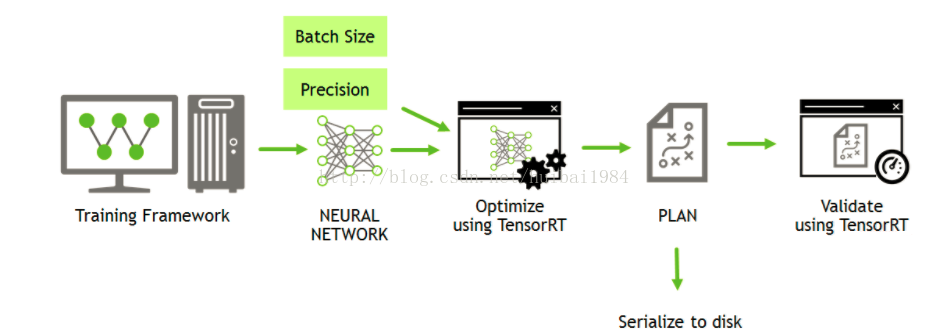
TensorRT里的sample的基本都是这个workflow. 先生成PLAN数据流,然后Validate它。
下图是execution的流程图
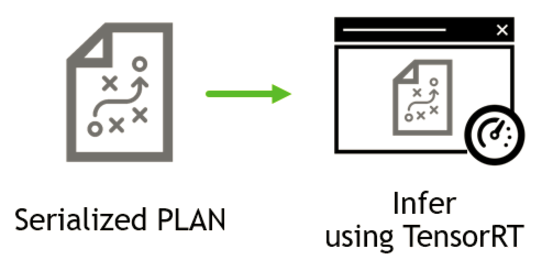
以TensorRT里的samplePlugin为例,这个PLAN文件可以在如下代码段后保存生成:
PluginFactory pluginFactory;
IHostMemory *gieModelStream{ nullptr };
caffeToGIEModel("mnist.prototxt", "mnist.caffemodel", std::vector < std::string > { OUTPUT_BLOB_NAME }, 1, &pluginFa\
ctory, gieModelStream);
pluginFactory.destroyPlugin();
这个阶段把prototxt,modelfile和plugin加载进来生成TensorRT自定定义的文件 (包含prototxt和model)。 在这段代码后,可以把gieModelStream的数据流存成PLAN文件(即 Serialize to dsik),其数据的指针为gieModelStream->data(),size是gieModelStream->size()。
- 在执行阶段,直接Serialized (load)上面生成的PLAN文件,然后执行如下code做inference。这样可以避免在每次应用启动时都执行 caffeToGIEModel() ,因为这个阶段执行时间比较长(因为不仅解析prototxt和caffemodel,还会做一些优化的工作)。
// parse the mean file and subtract it from the image
const float *meanData = reinterpret_cast<const float*>(meanBlob->getData());
float data[INPUT_H*INPUT_W];
for (int i = 0; i < INPUT_H*INPUT_W; i++)
data[i] = float(fileData[i])-meanData[i];
meanBlob->destroy();
// deserialize the engine
IRuntime* runtime = createInferRuntime(gLogger);
ICudaEngine* engine = runtime->deserializeCudaEngine(gieModelStream->data(), gieModelStream->size(), &pluginFactory)\
;
IExecutionContext *context = engine->createExecutionContext();
// run inference
float prob[OUTPUT_SIZE];
doInference(*context, data, prob, 1);
// destroy the engine
context->destroy();
engine->destroy();
runtime->destroy();
pluginFactory.destroyPlugin();





 本文介绍了TensorRT的两个主要阶段:构建阶段和执行阶段,并详细解释了如何通过样例代码生成PLAN文件,以及如何在执行阶段加载并运行该文件进行推理。
本文介绍了TensorRT的两个主要阶段:构建阶段和执行阶段,并详细解释了如何通过样例代码生成PLAN文件,以及如何在执行阶段加载并运行该文件进行推理。
















 1555
1555

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








