参考自:RKNN3588——YOLOv8的PT模型转RKNN模型_yolov8 pt转rknn-优快云博客
【YOLOv8部署至RK3588】模型训练→转换RKNN→开发板部署_yolov8转rknn-优快云博客
一、pt转onnx
不用官方的yolov8代码,而是用瑞芯微的yolov8代码
https://github.com/airockchip/ultralytics_yolov8.git拉取到代码之后,安装依赖
cd ultralytics-main
pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
pip install -e .使用修改后的ultralytics对pt模型进行模型转换,此处的format=rknn代表支持rknn后续的转换,而不是用onnx,一定要注意!!!
yolo export model=best.pt format=rknn
报错:OnnxExporterError: Module onnx is not installed
pip install onnx==1.16.1可以解决
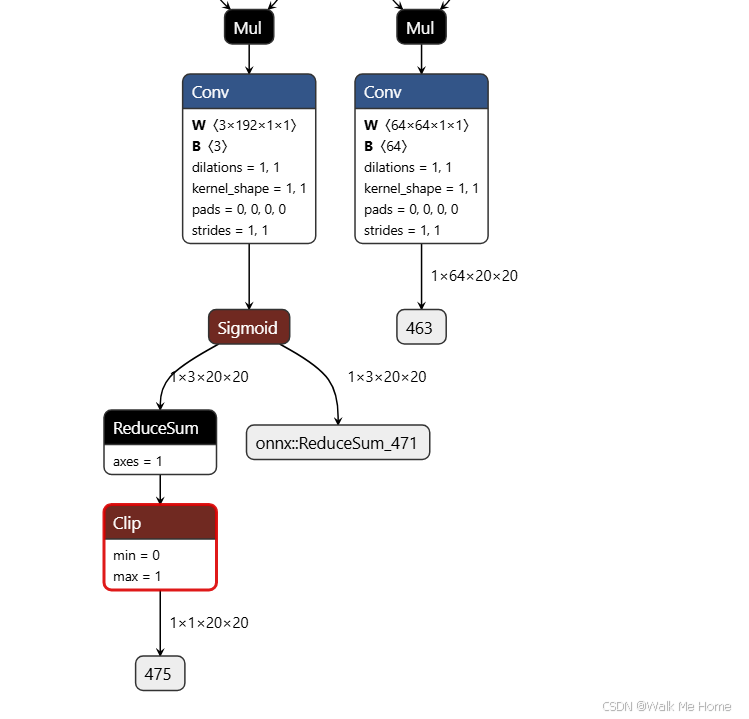
二、onnx转rknn
# 新建 Projects 文件夹
mkdir Projects && cd Projects
# 下载 RKNN-Toolkit2 仓库
git clone -b v2.3.0 https://github.com/airockchip/rknn-toolkit2.git
# 下载 RKNN Model Zoo 仓库
git clone -b v2.3.0 https://github.com/airockchip/rknn_model_zoo.git进入rknn-toolkit2-2.1.0\rknn-toolkit2-2.1.0\rknn-toolkit2\packages文件夹下
pip install -r requirements_cp38-2.1.0.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simplepip install rknn_toolkit2-2.1.0+708089d1-cp38-cp38-linux_x86_64.whl然后,我们的转rknn环境就配置完成了。
这里我也详细再说一遍转换流程:先进入rknn_model_zoo-2.1.0\examples\yolov8\python文件夹,先打开yolov8.py,进行适配参数修改:
要改class和nc数,然后下面改成rk3588

convert.py也要改,改保存路径。
修改完成后,将我们之前得到的onnx模型复制到python文件夹下:
python convert.py best.onnx rk3588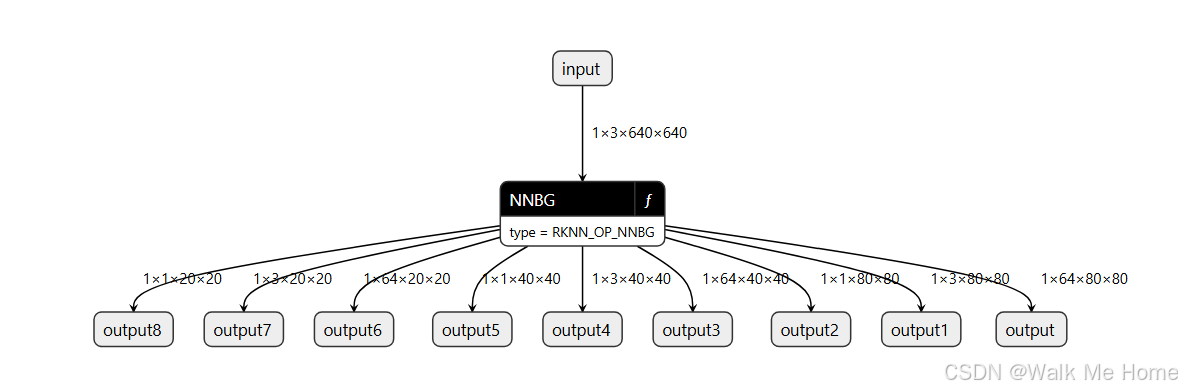
三、onnx量化
pip install onnx onnxconverter-commonimport onnx
from onnxconverter_common import float16
model = onnx.load("path/to/model.onnx")
model_fp16 = float16.convert_float_to_float16(model)
onnx.save(model_fp16,"path/to/model_fp16.onnx") 
FP16量化后不能再转rknn,会报错
四、部署到rk3588上
将modelzoo和toolkit的压缩包放到机器中
需要下载miniconda
因为我要部署的机器是arm64架构,所以使用这些命令进行下载。
mkdir -p ~/miniconda3
wget https://repo.anaconda.com/miniconda/Miniconda3-latest-Linux-aarch64.sh -O ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh
bash ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh -b -u -p ~/miniconda3
rm ~/miniconda3/miniconda.sh创建环境
conda create -n rknn python=3.9
更新环境变量
source ~/miniconda3/bin/activate激活环境
conda activate rknn安装toolkit-lite2和opencv
pip install rknn_toolkit_lite2-2.1.0-cp39-cp39-linux_aarch64.whl -i https://pypi.mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/simple/
pip install opencv-python -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
文件结构如下:dataset-1是存放的测试图片,dataset-2是保存测试结果的位置,ad.rknn是我们的rknn模型,yolov8.py是我们的测试脚本
import os
import cv2
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
import numpy as np
RKNN_MODEL = "./ad.rknn"
IMG_FOLDER = "dataset-1/images/train"
RESULT_PATH = './dataset-2'
CLASSES = ['car']
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(len(CLASSES), 3))
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
# Compute padding
ratio = r # width, height ratios
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color) # add border
if info_need is True:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
"""Filter boxes with object threshold.
"""
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
"""Suppress non-maximal boxes.
# Returns
keep: ndarray, index of effective boxes.
"""
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
# Distribution Focal Loss (DFL)
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
# Python 忽略 score_sum 输出
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
# filter according to threshold
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# nms
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
"""
Draws bounding boxes and labels on the input image based on the detected objects.
Args:
img: The input image to draw detections on.
box: Detected bounding box.
score: Corresponding detection score.
class_id: Class ID for the detected object.
Returns:
None
"""
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
color = color_palette[class_id]
# Draw the bounding box on the image
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
# Create the label text with class name and score
label = f"{CLASSES[class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
# Calculate the dimensions of the label text
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
# Calculate the position of the label text
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
# Draw a filled rectangle as the background for the label text
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color,
cv2.FILLED)
# Draw the label text on the image
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
# Calculate scaling factors for bounding box coordinates
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor)
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor)
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
# Retrieve the color for the class ID
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
# cv2.rectangle(image, (left, top), (right, bottom), color, 2)
# cv2.putText(image, '{0} {1:.2f}'.format(CLASSES[cl], score),
# (left, top - 6),
# cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX,
# 0.6, (0, 0, 255), 2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn_lite = RKNNLite()
# 加载RKNN模型
print('--> Load RKNN model')
ret = rknn_lite.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
# run on RK356x/RK3588 with Debian OS, do not need specify target.
ret = rknn_lite.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 数据处理
img_list = os.listdir(IMG_FOLDER)
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img_name = img_list[i]
img_path = os.path.join(IMG_FOLDER, img_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print("{} is not found", img_name)
continue
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_src is None:
print("文件不存在\n")
# Due to rga init with (0,0,0), we using pad_color (0,0,0) instead of (114, 114, 114)
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
# img = cv2.resize(img_src, (640, 512), interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR) # direct resize
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
outputs = rknn_lite.inference([input])
boxes, classes, scores = post_process(outputs)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if boxes is not None:
draw(img_p, boxes, scores, classes)
# 保存结果
if not os.path.exists(RESULT_PATH):
os.mkdir(RESULT_PATH)
result_path = os.path.join(RESULT_PATH, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(result_path, img_p)
print('Detection result save to {}'.format(result_path))
pass
# cv2.imshow("full post process result", img_p)
rknn_lite.release()
运行yolov8.py
python yolov8.py
成功推理
五、多个rknn同时推理
由于我这个项目需要每个类别单独做一个rknn模型,所以需要加载多个rknn模型进行推理。
yolov8_multiple.py
import os
import cv2
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
import numpy as np
import time
# 定义模型路径
RKNN_MODEL_LS = "./ls.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW = "./overflow.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_AD = "./ad.rknn"
IMG_FOLDER = "dataset_ad/images/data"
RESULT_PATH = './result'
# 每个模型对应的类别
CLASSES_LS = ['ls']
CLASSES_OVERFLOW = ['overflow']
CLASSES_AD = ['ad']
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
# 为每个类别生成颜色
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(3, 3)) # 3 个类别,每个类别一个颜色
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
shape = im.shape[:2]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
ratio = r
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]
dw /= 2
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad:
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color)
if info_need:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data, class_offset=0):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# 调整类别标签,避免冲突
classes += class_offset
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
color = color_palette[class_id]
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
label = f"{['ls', 'overflow', 'ad'][class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor)
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor)
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(['ls', 'overflow', 'ad'][cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
if __name__ == '__main__':
start_time_total = time.time() # 记录总开始时间
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn_lite_ls = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_overflow = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_ad = RKNNLite()
# 加载RKNN模型
print('--> Load RKNN models')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_LS)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ls failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model overflow failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_AD)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ad failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ls failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for overflow failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ad failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 数据处理
img_list = os.listdir(IMG_FOLDER)
for i in range(len(img_list)):
img_name = img_list[i]
img_path = os.path.join(IMG_FOLDER, img_name)
if not os.path.exists(img_path):
print("{} is not found", img_name)
continue
img_src = cv2.imread(img_path)
if img_src is None:
print("文件不存在\n")
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=img_src.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
# 分别推理
start_time_inference = time.time() # 记录推理开始时间
outputs_ls = rknn_lite_ls.inference([input])
outputs_overflow = rknn_lite_overflow.inference([input])
outputs_ad = rknn_lite_ad.inference([input])
print(f"Inference time for image {img_name}: {end_time_inference - start_time_inference:.2f} seconds") # 输出推理时间
# 分别处理结果,并调整类别标签
boxes_ls, classes_ls, scores_ls = post_process(outputs_ls, class_offset=0) # ls 类别偏移为 0
boxes_overflow, classes_overflow, scores_overflow = post_process(outputs_overflow, class_offset=1) # overflow 类别偏移为 1
boxes_ad, classes_ad, scores_ad = post_process(outputs_ad, class_offset=2) # ad 类别偏移为 2
# 合并所有检测结果
all_boxes = []
all_scores = []
all_classes = []
if boxes_ls is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ls)
all_scores.extend(scores_ls)
all_classes.extend(classes_ls)
if boxes_overflow is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_overflow)
all_scores.extend(scores_overflow)
all_classes.extend(classes_overflow)
if boxes_ad is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ad)
all_scores.extend(scores_ad)
all_classes.extend(classes_ad)
img_p = img_src.copy()
if all_boxes:
draw(img_p, all_boxes, all_scores, all_classes)
# 保存结果
if not os.path.exists(RESULT_PATH):
os.mkdir(RESULT_PATH)
result_path = os.path.join(RESULT_PATH, img_name)
cv2.imwrite(result_path, img_p)
print('Detection result save to {}'.format(result_path))
# 释放资源
rknn_lite_ls.release()
rknn_lite_overflow.release()
rknn_lite_ad.release()
end_time_total = time.time() # 记录总结束时间
print(f"Total time: {end_time_total - start_time_total:.2f} seconds") # 输出总运行时间代码还可以输出总用时和推理一张图片的用时
3个yolov8m的rknn模型推理一张图片大概需要0.2s
推理100张图片的总用时为30.22s
如果要添加新的rknn,需要修改的地方
1. 定义新模型的路径
在代码开头部分,添加新模型的路径常量。
# 定义模型路径
RKNN_MODEL_LS = "./ls.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW = "./overflow.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_AD = "./ad.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_NEW = "./new.rknn" # 新模型的路径2. 定义新类别
在 CLASSES 列表中添加新类别的名称。
# 每个模型对应的类别
CLASSES_LS = ['ls']
CLASSES_OVERFLOW = ['overflow']
CLASSES_AD = ['ad']
CLASSES_NEW = ['new'] # 新类别3. 更新颜色调色板
如果新增了一个类别,需要为它生成一个颜色。修改 color_palette 的大小。
# 为每个类别生成颜色
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(4, 3)) # 4 个类别,每个类别一个颜色4. 创建新的 RKNN 对象
在 main 函数中,创建新模型的 RKNNLite 对象。
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn_lite_ls = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_overflow = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_ad = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_new = RKNNLite() # 新模型的 RKNN 对象5. 加载新模型
在加载模型的代码部分,添加新模型的加载逻辑。
# 加载RKNN模型
print('--> Load RKNN models')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_LS)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ls failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model overflow failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_AD)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ad failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_new.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_NEW) # 加载新模型
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model new failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')6. 初始化新模型的运行时环境
在初始化运行时环境的代码部分,添加新模型的初始化逻辑。
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ls failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for overflow failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.init_runtime()
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ad failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_new.init_runtime() # 初始化新模型的运行时环境
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for new failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')7. 推理新模型
在推理部分的代码中,添加新模型的推理逻辑。
# 分别推理
outputs_ls = rknn_lite_ls.inference([input])
outputs_overflow = rknn_lite_overflow.inference([input])
outputs_ad = rknn_lite_ad.inference([input])
outputs_new = rknn_lite_new.inference([input]) # 新模型的推理8. 处理新模型的输出
在 post_process 函数中,处理新模型的输出,并确保类别标签不冲突。
# 分别处理结果,并调整类别标签
boxes_ls, classes_ls, scores_ls = post_process(outputs_ls, class_offset=0) # ls 类别偏移为 0
boxes_overflow, classes_overflow, scores_overflow = post_process(outputs_overflow, class_offset=1) # overflow 类别偏移为 1
boxes_ad, classes_ad, scores_ad = post_process(outputs_ad, class_offset=2) # ad 类别偏移为 2
boxes_new, classes_new, scores_new = post_process(outputs_new, class_offset=3) # 新模型类别偏移为 39. 合并新模型的检测结果
在合并检测结果的代码部分,添加新模型的检测结果。
# 合并所有检测结果
all_boxes = []
all_scores = []
all_classes = []
if boxes_ls is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ls)
all_scores.extend(scores_ls)
all_classes.extend(classes_ls)
if boxes_overflow is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_overflow)
all_scores.extend(scores_overflow)
all_classes.extend(classes_overflow)
if boxes_ad is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ad)
all_scores.extend(scores_ad)
all_classes.extend(classes_ad)
if boxes_new is not None: # 合并新模型的检测结果
all_boxes.extend(boxes_new)
all_scores.extend(scores_new)
all_classes.extend(classes_new)10. 更新绘制逻辑
在 draw_detections 和 draw 函数中,确保新类别的标签和颜色正确映射。
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
color = color_palette[class_id]
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
label = f"{['ls', 'overflow', 'ad', 'new'][class_id]}: {score:.2f}" # 添加新类别
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)11. 释放新模型的资源
在释放资源的代码部分,添加新模型的释放逻辑。
# 释放资源
rknn_lite_ls.release()
rknn_lite_overflow.release()
rknn_lite_ad.release()
rknn_lite_new.release() # 释放新模型的资源sudo cat /sys/kernel/debug/rknpu/load查看负载

能看每个盒的负载情况
六、引入多线程
由于设备有三个核,因此引入多线程来加快推理。并且将rknn调用设为全局变量,这样在推理的时候就不用重新加载模型。
import os
import cv2
import time
import threading
from rknnlite.api import RKNNLite
import numpy as np
# 定义模型路径
RKNN_MODEL_LS = "./ls.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW = "./overflow.rknn"
RKNN_MODEL_AD = "./ad.rknn"
# 每个模型对应的类别
CLASSES_LS = ['ls']
CLASSES_OVERFLOW = ['overflow']
CLASSES_AD = ['ad']
OBJ_THRESH = 0.45
NMS_THRESH = 0.45
MODEL_SIZE = (640, 640)
# 为每个类别生成颜色
color_palette = np.random.uniform(0, 255, size=(3, 3)) # 3 个类别,每个类别一个颜色
# 全局变量,用于保存加载的模型
rknn_lite_ls = None
rknn_lite_overflow = None
rknn_lite_ad = None
# 全局变量,用于保存推理结果
outputs_ls = None
outputs_overflow = None
outputs_ad = None
# 线程锁,用于保护共享资源
lock = threading.Lock()
def sigmoid(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def letter_box(im, new_shape, pad_color=(0, 0, 0), info_need=False):
shape = im.shape[:2]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
ratio = r
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r))
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1]
dw /= 2
dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad:
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1))
im = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=pad_color)
if info_need:
return im, ratio, (dw, dh)
else:
return im
def filter_boxes(boxes, box_confidences, box_class_probs):
box_confidences = box_confidences.reshape(-1)
candidate, class_num = box_class_probs.shape
class_max_score = np.max(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
classes = np.argmax(box_class_probs, axis=-1)
_class_pos = np.where(class_max_score * box_confidences >= OBJ_THRESH)
scores = (class_max_score * box_confidences)[_class_pos]
boxes = boxes[_class_pos]
classes = classes[_class_pos]
return boxes, classes, scores
def nms_boxes(boxes, scores):
x = boxes[:, 0]
y = boxes[:, 1]
w = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0]
h = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1]
areas = w * h
order = scores.argsort()[::-1]
keep = []
while order.size > 0:
i = order[0]
keep.append(i)
xx1 = np.maximum(x[i], x[order[1:]])
yy1 = np.maximum(y[i], y[order[1:]])
xx2 = np.minimum(x[i] + w[i], x[order[1:]] + w[order[1:]])
yy2 = np.minimum(y[i] + h[i], y[order[1:]] + h[order[1:]])
w1 = np.maximum(0.0, xx2 - xx1 + 0.00001)
h1 = np.maximum(0.0, yy2 - yy1 + 0.00001)
inter = w1 * h1
ovr = inter / (areas[i] + areas[order[1:]] - inter)
inds = np.where(ovr <= NMS_THRESH)[0]
order = order[inds + 1]
keep = np.array(keep)
return keep
def softmax(x, axis=None):
x = x - x.max(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
y = np.exp(x)
return y / y.sum(axis=axis, keepdims=True)
def dfl(position):
n, c, h, w = position.shape
p_num = 4
mc = c // p_num
y = position.reshape(n, p_num, mc, h, w)
y = softmax(y, 2)
acc_metrix = np.array(range(mc), dtype=float).reshape(1, 1, mc, 1, 1)
y = (y * acc_metrix).sum(2)
return y
def box_process(position):
grid_h, grid_w = position.shape[2:4]
col, row = np.meshgrid(np.arange(0, grid_w), np.arange(0, grid_h))
col = col.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
row = row.reshape(1, 1, grid_h, grid_w)
grid = np.concatenate((col, row), axis=1)
stride = np.array([MODEL_SIZE[1] // grid_h, MODEL_SIZE[0] // grid_w]).reshape(1, 2, 1, 1)
position = dfl(position)
box_xy = grid + 0.5 - position[:, 0:2, :, :]
box_xy2 = grid + 0.5 + position[:, 2:4, :, :]
xyxy = np.concatenate((box_xy * stride, box_xy2 * stride), axis=1)
return xyxy
def post_process(input_data, class_offset=0):
boxes, scores, classes_conf = [], [], []
defualt_branch = 3
pair_per_branch = len(input_data) // defualt_branch
for i in range(defualt_branch):
boxes.append(box_process(input_data[pair_per_branch * i]))
classes_conf.append(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1])
scores.append(np.ones_like(input_data[pair_per_branch * i + 1][:, :1, :, :], dtype=np.float32))
def sp_flatten(_in):
ch = _in.shape[1]
_in = _in.transpose(0, 2, 3, 1)
return _in.reshape(-1, ch)
boxes = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in boxes]
classes_conf = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in classes_conf]
scores = [sp_flatten(_v) for _v in scores]
boxes = np.concatenate(boxes)
classes_conf = np.concatenate(classes_conf)
scores = np.concatenate(scores)
boxes, classes, scores = filter_boxes(boxes, scores, classes_conf)
# 调整类别标签,避免冲突
classes += class_offset
nboxes, nclasses, nscores = [], [], []
for c in set(classes):
inds = np.where(classes == c)
b = boxes[inds]
c = classes[inds]
s = scores[inds]
keep = nms_boxes(b, s)
if len(keep) != 0:
nboxes.append(b[keep])
nclasses.append(c[keep])
nscores.append(s[keep])
if not nclasses and not nscores:
return None, None, None
boxes = np.concatenate(nboxes)
classes = np.concatenate(nclasses)
scores = np.concatenate(nscores)
return boxes, classes, scores
def draw_detections(img, left, top, right, bottom, score, class_id):
color = color_palette[class_id]
cv2.rectangle(img, (int(left), int(top)), (int(right), int(bottom)), color, 2)
label = f"{['ls', 'overflow', 'ad'][class_id]}: {score:.2f}"
(label_width, label_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
label_x = left
label_y = top - 10 if top - 10 > label_height else top + 10
cv2.rectangle(img, (label_x, label_y - label_height), (label_x + label_width, label_y + label_height), color, cv2.FILLED)
cv2.putText(img, label, (label_x, label_y), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (0, 0, 0), 1, cv2.LINE_AA)
def draw(image, boxes, scores, classes):
img_h, img_w = image.shape[:2]
x_factor = img_w / MODEL_SIZE[0]
y_factor = img_h / MODEL_SIZE[1]
for box, score, cl in zip(boxes, scores, classes):
x1, y1, x2, y2 = [int(_b) for _b in box]
left = int(x1 * x_factor)
top = int(y1 * y_factor)
right = int(x2 * x_factor)
bottom = int(y2 * y_factor)
print('class: {}, score: {}'.format(['ls', 'overflow', 'ad'][cl], score))
print('box coordinate left,top,right,down: [{}, {}, {}, {}]'.format(left, top, right, bottom))
draw_detections(image, left, top, right, bottom, score, cl)
def load_models():
global rknn_lite_ls, rknn_lite_overflow, rknn_lite_ad
# 创建RKNN对象
rknn_lite_ls = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_overflow = RKNNLite()
rknn_lite_ad = RKNNLite()
# 加载RKNN模型
print('--> Load RKNN models')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_LS)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ls failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_OVERFLOW)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model overflow failed')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.load_rknn(RKNN_MODEL_AD)
if ret != 0:
print('Load RKNN model ad failed')
exit(ret)
print('done')
# 初始化 runtime 环境
print('--> Init runtime environment')
ret = rknn_lite_ls.init_runtime(core_mask=RKNNLite.NPU_CORE_0)
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ls failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_overflow.init_runtime(core_mask=RKNNLite.NPU_CORE_1)
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for overflow failed!')
exit(ret)
ret = rknn_lite_ad.init_runtime(core_mask=RKNNLite.NPU_CORE_2)
if ret != 0:
print('Init runtime environment for ad failed!')
exit(ret)
print('done')
def inference_ls(input):
global outputs_ls
outputs_ls = rknn_lite_ls.inference([input])
def inference_overflow(input):
global outputs_overflow
outputs_overflow = rknn_lite_overflow.inference([input])
def inference_ad(input):
global outputs_ad
outputs_ad = rknn_lite_ad.inference([input])
def check(frame):
global outputs_ls, outputs_overflow, outputs_ad
# 数据处理
pad_color = (0, 0, 0)
img = letter_box(im=frame.copy(), new_shape=(MODEL_SIZE[1], MODEL_SIZE[0]), pad_color=(0, 0, 0))
input = np.expand_dims(img, axis=0)
# 创建线程
thread_ls = threading.Thread(target=inference_ls, args=(input,))
thread_overflow = threading.Thread(target=inference_overflow, args=(input,))
thread_ad = threading.Thread(target=inference_ad, args=(input,))
# 启动线程
thread_ls.start()
thread_overflow.start()
thread_ad.start()
# 等待线程完成
thread_ls.join()
thread_overflow.join()
thread_ad.join()
# 分别处理结果,并调整类别标签
boxes_ls, classes_ls, scores_ls = post_process(outputs_ls, class_offset=0) # ls 类别偏移为 0
boxes_overflow, classes_overflow, scores_overflow = post_process(outputs_overflow, class_offset=1) # overflow 类别偏移为 1
boxes_ad, classes_ad, scores_ad = post_process(outputs_ad, class_offset=2) # ad 类别偏移为 2
# 合并所有检测结果
all_boxes = []
all_scores = []
all_classes = []
if boxes_ls is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ls)
all_scores.extend(scores_ls)
all_classes.extend(classes_ls)
if boxes_overflow is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_overflow)
all_scores.extend(scores_overflow)
all_classes.extend(classes_overflow)
if boxes_ad is not None:
all_boxes.extend(boxes_ad)
all_scores.extend(scores_ad)
all_classes.extend(classes_ad)
img_p = frame.copy()
if all_boxes:
draw(img_p, all_boxes, all_scores, all_classes)
# 显示结果
cv2.imshow('Detection Result', img_p)
cv2.waitKey(1)
# 打开摄像头
cap = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
if not cap.isOpened():
print("无法打开摄像头")
exit()
# 加载模型(只加载一次)
load_models()
frame_count = 0 # 用于保存帧的计数器
while True:
# 读取一帧图像
ret, frame = cap.read()
if not ret:
print("无法读取图像")
break
# 显示原始图像
cv2.imshow('Camera View', frame)
# 每隔一定帧数抽帧并调用 check 方法
if frame_count % 30 == 0: # 例如每30帧抽一帧
check(frame) # 调用 check 方法进行识别
frame_count += 1 # 帧计数器增加
# 按下 'q' 键退出
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# 释放摄像头并关闭所有窗口
cap.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 释放模型资源
if rknn_lite_ls is not None:
rknn_lite_ls.release()
if rknn_lite_overflow is not None:
rknn_lite_overflow.release()
if rknn_lite_ad is not None:
rknn_lite_ad.release()-
新增模型路径和类别:
-
增加了
RKNN_MODEL_NEW和CLASSES_NEW。
-
-
新增模型对象和推理结果:
-
增加了
rknn_lite_new和outputs_new。
-
-
修改
load_models函数:-
加载并初始化新增模型,复用
core0。
-
-
新增推理函数:
-
增加了
inference_new函数用于新增模型的推理。
-
-
修改
check函数:-
增加对新模型推理结果的处理。
-
-
调整核心分配:
-
新增模型复用
core0,其他模型保持不变。
-





















 5748
5748

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








