这种Protocol protocol = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();生成代理对象的方法在dubbo中运用的非常多。他主要运用了SPI技术。简单可以概括为(以Protocol为例):
@SPI("dubbo")
public interface Protocol {}
Protocol接口的实现类有很多: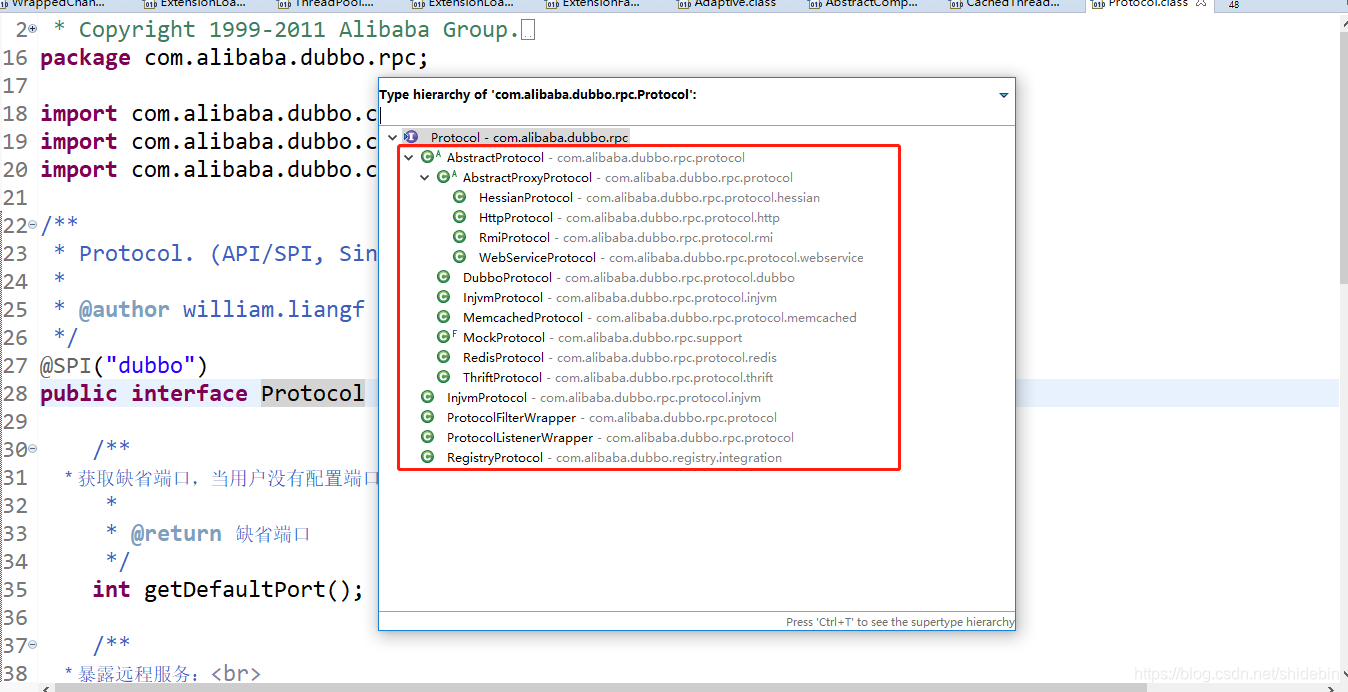
使用@SPI注解来得到默认实现,如上图Protocol的默认实现是dubbo,那么dubbo是怎么通过这个注解的值得到相应的实现的呢?
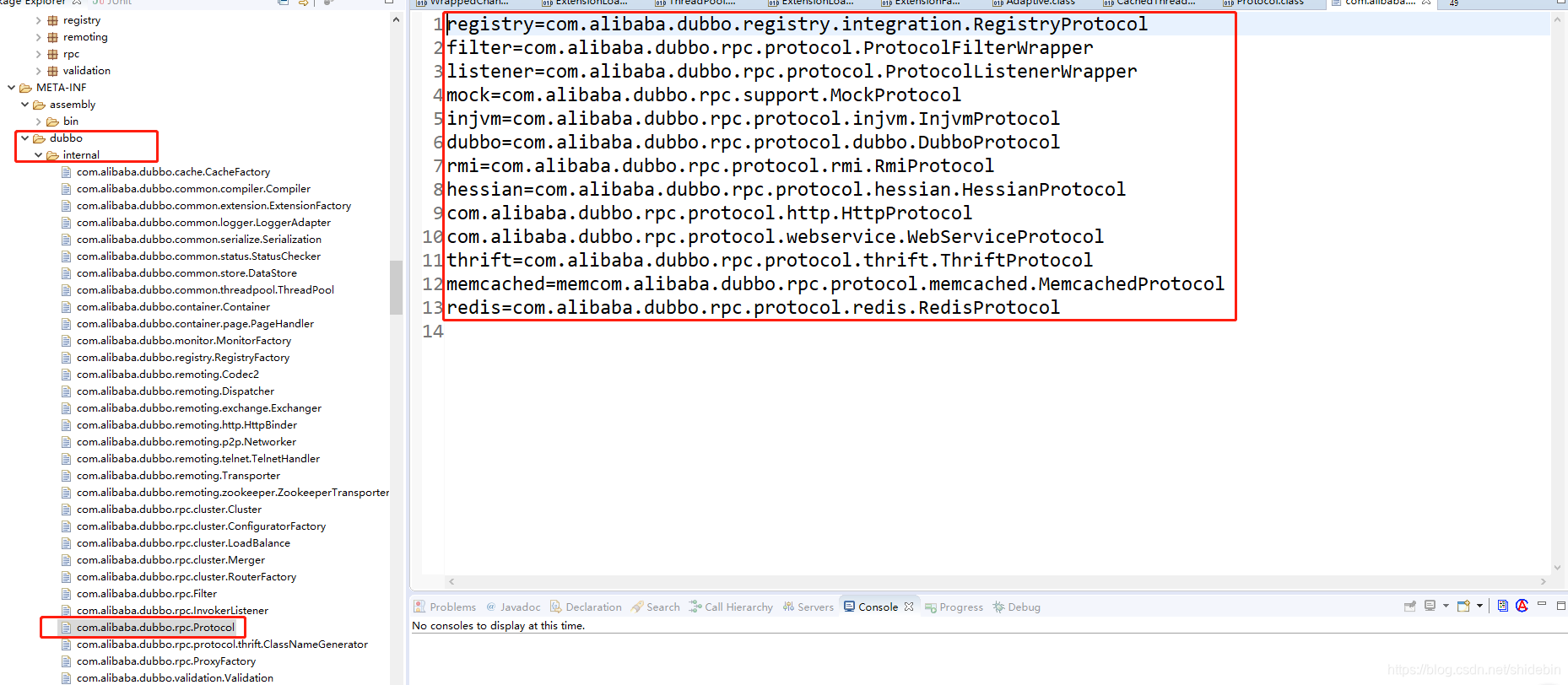
答案在这里,dubbo通过解析这个配置文件来得到对应的实现类。
当然,ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension()这段代码的实现很复杂。接下来慢慢解析一下(只粘出了部分源码):
1.首先是getExtensionLoader方法:
ExtensionLoader<T> loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
if (loader == null) {
EXTENSION_LOADERS.putIfAbsent(type, new ExtensionLoader<T>(type));
loader = (ExtensionLoader<T>) EXTENSION_LOADERS.get(type);
}
EXTENSION_LOADERS是一个缓存的map,key为class,value为ExtensionLoader,意思是先从缓存中取ExtensionLoader,没有就执行new ExtensionLoader(type)。
2.getAdaptiveExtension()方法:
public T getAdaptiveExtension() {
Object instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
if (createAdaptiveInstanceError == null) {
synchronized (cachedAdaptiveInstance) {
instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();
if (instance == null) {
try {
instance = createAdaptiveExtension();
cachedAdaptiveInstance.set(instance);
} catch (Throwable t) {
createAdaptiveInstanceError = t;
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + t.toString(), t);
}
}
}
} else {
throw new IllegalStateException("fail to create adaptive instance: " + createAdaptiveInstanceError.toString(), createAdaptiveInstanceError);
}
}
return (T) instance;
}
此方法主要功能是获得代理对象,cachedAdaptiveInstance是一个对象容器,先从容器里面拿,如果没有说明是首次生成代理对象,然后通过同步锁进行创建,如果此时有多个线程同时进来,只能由一个线程进行创建,待其创建完通过instance = cachedAdaptiveInstance.get();来取。
3.接下来是createAdaptiveExtension方法,此方法简单就不说了。
4.getAdaptiveExtensionClass方法:此方法简单就不说了。
5.getExtensionClasses方法,实现并发的思想跟上面差不多,此方法简单就不说了。
6.loadExtensionClasses方法:
private Map<String, Class<?>> loadExtensionClasses() {
final SPI defaultAnnotation = type.getAnnotation(SPI.class);
if (defaultAnnotation != null) {
String value = defaultAnnotation.value();
if (value != null && (value = value.trim()).length() > 0) {
String[] names = NAME_SEPARATOR.split(value);
if (names.length > 1) {
throw new IllegalStateException("more than 1 default extension name on extension " + type.getName()
+ ": " + Arrays.toString(names));
}
if (names.length == 1) cachedDefaultName = names[0];
}
}
Map<String, Class<?>> extensionClasses = new HashMap<String, Class<?>>();
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_INTERNAL_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, DUBBO_DIRECTORY);
loadFile(extensionClasses, SERVICES_DIRECTORY);
return extensionClasses;
}
此方法主要实现如下功能;
1.获得Protocol上的spi注解并得到value赋值给cachedDefaultName变量。
2.执行loadFile方法
7.loadFile方法:代码太长分析一部分
ClassLoader classLoader = findClassLoader();
if (classLoader != null) {
urls = classLoader.getResources(fileName);
} else {
urls = ClassLoader.getSystemResources(fileName);
}
通过文件名字读取配置文件。
String name = null;
int i = line.indexOf('=');
if (i > 0) {
name = line.substring(0, i).trim();
line = line.substring(i + 1).trim();
}
if (line.length() > 0) {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(line, true, classLoader);
如dubbo=com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol那么name=dubbo,line =com.alibaba.dubbo.rpc.protocol.dubbo.DubboProtocol,然后通过类全名得到class
for (String n : names) {
if (!cachedNames.containsKey(clazz)) {
cachedNames.put(clazz, n);
}
Class<?> c = extensionClasses.get(n);
if (c == null) {
extensionClasses.put(n, clazz);
} else if (c != clazz) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Duplicate extension " + type.getName() + " name " + n + " on " + c.getName() + " and " + clazz.getName());
}
}
cachedNames是一个map,key为上面生成的class,value为name,extensionClasses也是一个map,key为上面生成的name,value为class.
8.createAdaptiveExtensionClass方法:主要生成各种代理信息。
在spring中如果有一个接口有多个实现类时,可以这样做:
@Resource 默认是按照 byName 的方式注入的, 如果通过 byName 的方式匹配不到,再按 byType 的方式去匹配。所以上面的引用可以替换为:
@Qualifier 注解也是 byName的方式,但是与@Resource 有区别,@Qualifier 使用的是 类名。





 本文深入解析了Dubbo中SPI(Service Provider Interface)机制的工作原理,包括如何通过SPI注解获取默认实现,以及ExtensionLoader如何生成代理对象。文章详细介绍了getExtensionLoader、getAdaptiveExtension等方法的实现过程,展示了Dubbo如何利用SPI技术实现接口的动态扩展。
本文深入解析了Dubbo中SPI(Service Provider Interface)机制的工作原理,包括如何通过SPI注解获取默认实现,以及ExtensionLoader如何生成代理对象。文章详细介绍了getExtensionLoader、getAdaptiveExtension等方法的实现过程,展示了Dubbo如何利用SPI技术实现接口的动态扩展。

















 2828
2828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








