《代码随想录》学习笔记,原链接:https://programmercarl.com/
链表理论基础
(1)链表的定义
链表是一种通过指针串联在一起的线性结构,每个节点由两部分组成:数据域和指针域。链表在内存中不是连续分布,而是通过指针连接各个节点。
链表包括单链表、双链表和循环链表:
- 单链表:每个节点包括一个数据域val和一个指针域next,节点的定义如下:
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val # 数据域
self.next = next # 指针域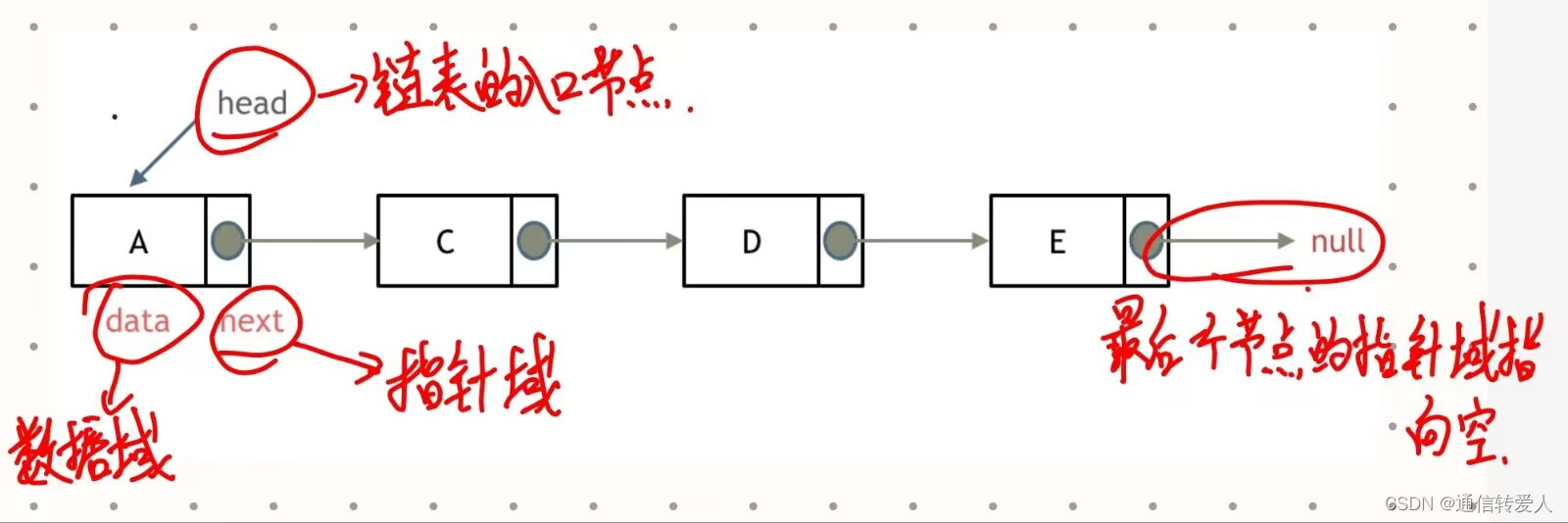
【注】由于在Python中不存在null和NULL,所以最后一个节点的指针域指向为None。
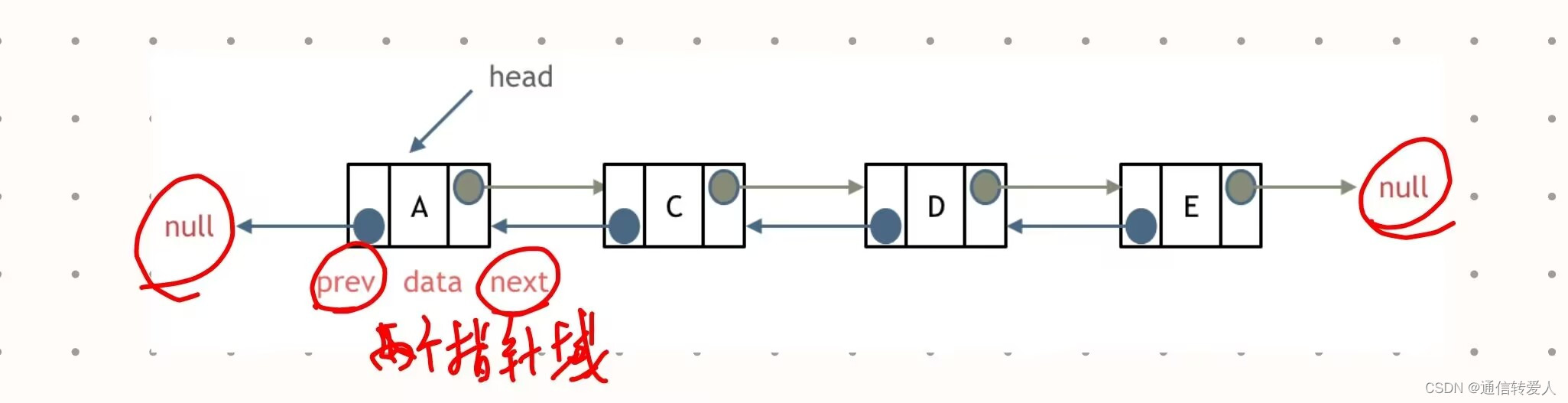
- 双链表:既可以向前,也可以向后查询,即有两个指针域。
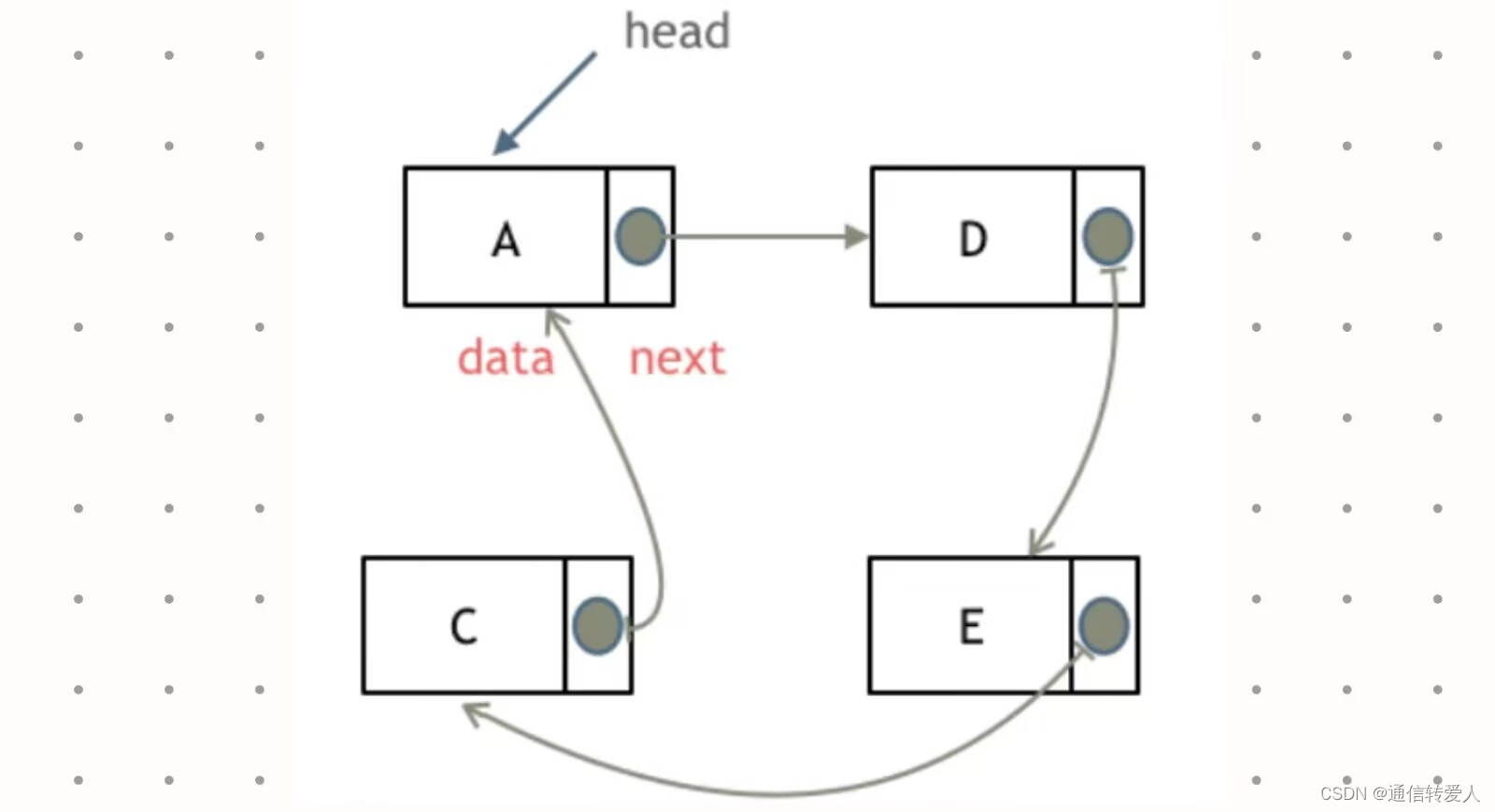
- 循环链表:首尾相连。
(2)链表的操作
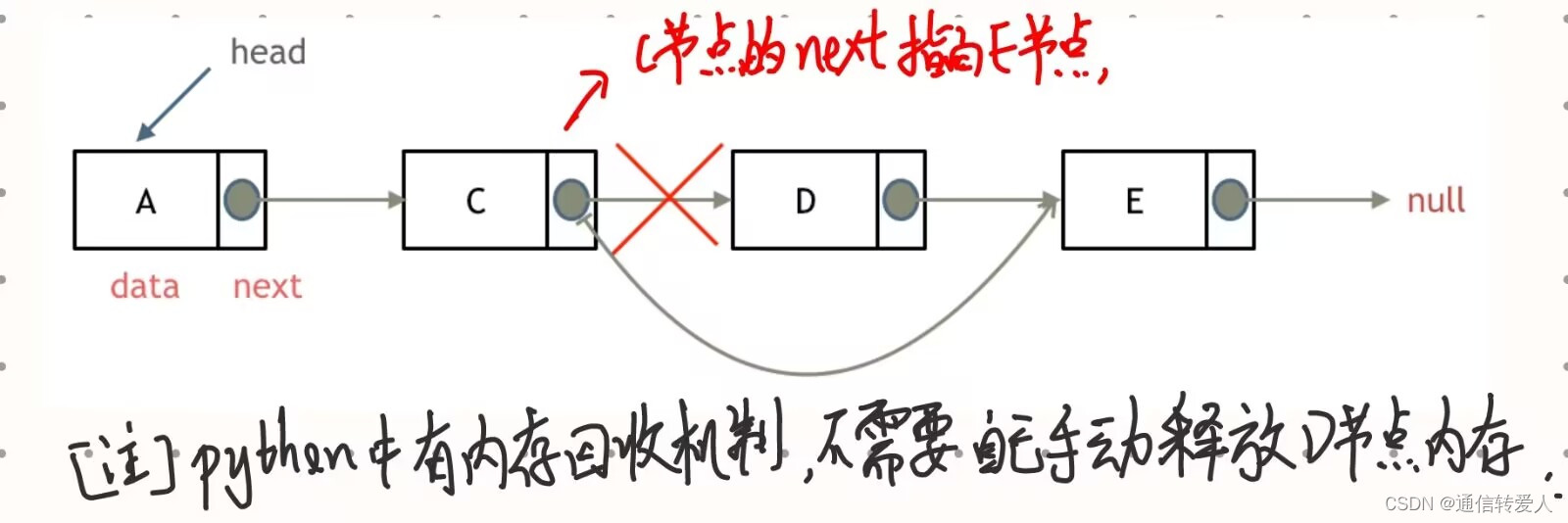
- 删除节点
- 添加节点
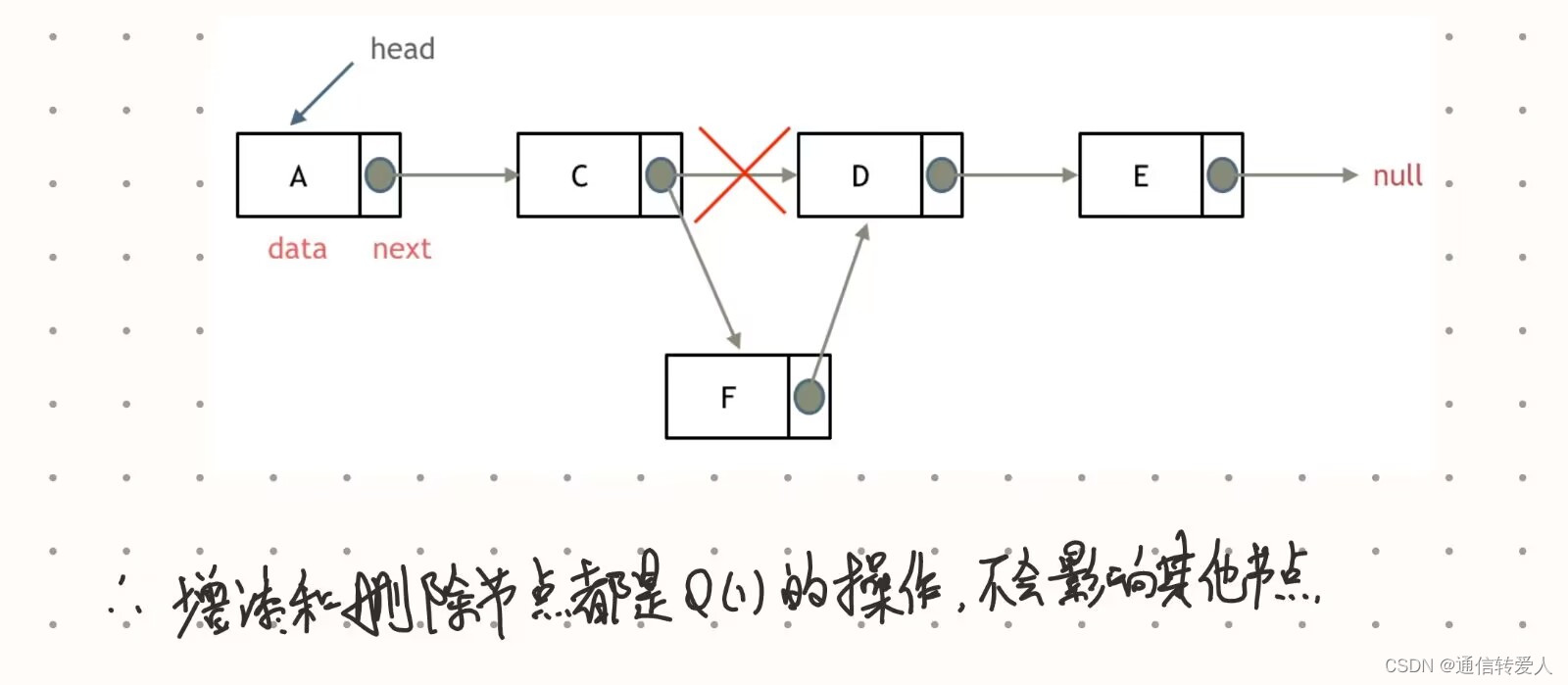
203.移除链表元素

为了保证删除head节点和删除其他节点时的操作完全相同,因此设置一个虚拟头节点。如下所示,是在这个链表中,移除元素1。

- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head: Optional[ListNode], val: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummyHead = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头结点,初始化为next = head指向第一个节点
current = dummyHead # 设定当前访问的节点current
while current.next: # 遍历整个列表,不能使用current
if current.next.val == val: # 找到要删除的节点,此时current指向该节点的前一个位置
current.next = current.next.next
else: # 这里必须使用else判断,不能直接将current后移一位
current = current.next # 访问下一个节点
return dummyHead.next # 返回删除后的列表,由于head可能已经被删除,因此不能直接返回head【注】python中使用None来表示空(空 ≠ 0个值),没有null或NULL这个关键字。
- ACM模式
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeElements(self, head, val):
dummyHead = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头结点,初始化为next = head指向第一个节点
current = dummyHead # 设定当前访问的节点current
while current.next: # 遍历整个列表,不能使用current。python中使用None来表示空(空 ≠ 0个值),没有null或NULL这个关键字
if current.next.val == val: # 找到要删除的节点,此时current指向该节点的前一个位置
current.next = current.next.next
else: # 这里必须使用else判断,不能直接将current后移一位
current = current.next # 访问下一个节点
return dummyHead.next # 返回删除后的列表,由于head可能已经被删除,因此不能直接返回head
# 创建链表
def creat_list(lenth):
head = ListNode(None)
current = head
for i in range(lenth):
val = int(input(f"输入第 {i + 1} 个节点的值: "))
current.next = ListNode(val)
current = current.next
# 删除头节点
head = head.next
return head
# 输入链表长度lenth
lenth = int(input("输入链表的长度:"))
# 输入要删除的值val
val = int(input("输入要删除的值val:"))
# 移除链表元素
head = creat_list(lenth)
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeElements(head, val)
# 输出删除后的元素
result_list = []
while result:
result_list.append(result.val)
result = result.next
print(result_list)707.设计链表


- 核心代码模式
# 创建单链表
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class MyLinkedList:
# 初始化创建一个虚拟头结点
# def creat_list(lenth):
# head = ListNode(None)
# current = head
# for i in range(lenth):
# val = int(input(f"输入第 {i + 1} 个节点的值: "))
# current.next = ListNode(val)
# current = current.next
# # 删除头节点
# head = head.next
# return head
def __init__(self):
self.dummy_head = ListNode(None) # self将dummy_head和lenth变成在整个类的任意位置都可以调用的变量
self.lenth = 0
# 链表中下标为 index 的节点的值
def get(self, index: int) -> int:
if index < 0 or index >= self.lenth: # 判断要查询的节点下标,是否超出链表范围
return -1
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(0, index):
current = current.next # 找到要获取的节点的前一个节点
return current.next.val # 获取index节点的值
# 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中第一个元素之前
def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None:
new_head = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
new_head.next = self.dummy_head.next # 将新建的节点添加到列表中,注意要加self
self.dummy_head.next = new_head
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 将一个值为 val 的节点追加到链表中作为链表的最后一个元素
def addAtTail(self, val: int) -> None:
new_tail = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_tail # 将新建的节点加到最后一个节点的后面
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中下标为 index 的节点之前。
def addAtIndex(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
if index < 0 or index > self.lenth: # 此处不能是index >= self.lenth
return
new_node = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(index):
current = current.next # 找到要index节点的前一个节点
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 如果下标有效,则删除链表中下标为 index 的节点
def deleteAtIndex(self, index: int) -> None:
if index < 0 or index >= self.lenth: # 判断要删除的节点下标,是否超出链表范围
return
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(index):
current = current.next # 找到要删除的index节点的前一个节点
current.next = current.next.next # 删除节点
self.lenth -= 1
# Your MyLinkedList object will be instantiated and called as such:
# obj = MyLinkedList()
# param_1 = obj.get(index)
# obj.addAtHead(val)
# obj.addAtTail(val)
# obj.addAtIndex(index,val)
# obj.deleteAtIndex(index)- ACM模式
# 创建单链表节点
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class MyLinkedList:
# 初始化创建一个虚拟头结点
# def creat_list(lenth):
# head = ListNode(None)
# current = head
# for i in range(lenth):
# val = int(input(f"输入第 {i + 1} 个节点的值: "))
# current.next = ListNode(val)
# current = current.next
# # 删除头节点
# head = head.next
# return head
def __init__(self):
self.dummy_head = ListNode(None) # self将dummy_head和lenth变成在整个类的任意位置都可以调用的变量
self.lenth = 0
# 链表中下标为 index 的节点的值
def get(self, index: int) -> int:
if index < 0 or index >= self.lenth: # 判断要查询的节点下标,是否超出链表范围
return -1
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(0, index):
current = current.next # 找到要获取的节点的前一个节点
return current.next.val # 获取index节点的值
# 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中第一个元素之前
def addAtHead(self, val: int) -> None:
new_head = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
new_head.next = self.dummy_head.next # 将新建的节点添加到列表中,注意要加self
self.dummy_head.next = new_head
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 将一个值为 val 的节点追加到链表中作为链表的最后一个元素
def addAtTail(self, val: int) -> None:
new_tail = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
while current.next:
current = current.next
current.next = new_tail # 将新建的节点加到最后一个节点的后面
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 将一个值为 val 的节点插入到链表中下标为 index 的节点之前。
def addAtIndex(self, index: int, val: int) -> None:
if index < 0 or index > self.lenth: # 此处不能是index >= self.lenth
return
new_node = ListNode(val, None) # 新建一个值为val的节点
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(index):
current = current.next # 找到要index节点的前一个节点
new_node.next = current.next
current.next = new_node
self.lenth += 1 # 链表长度+1
# 如果下标有效,则删除链表中下标为 index 的节点
def deleteAtIndex(self, index: int) -> None:
if index < 0 or index >= self.lenth: # 判断要删除的节点下标,是否超出链表范围
return
current = self.dummy_head # 初始化当前节点的位置为dummy_head,注意要加self
for i in range(index):
current = current.next # 找到要删除的index节点的前一个节点
current.next = current.next.next # 删除节点
self.lenth -= 1
# 获取要进行的操作,以及对应的输入参数列表
def param_input():
functions = []
params = []
# 输入要调用的函数列表
while True:
function_name = input("输入函数字符串(按Enter结束输入):")
if function_name == "": # 按Enter结束整个列表的输入
break
functions.append(function_name)
# 输入函数对应的输入参数
while True:
param_name = input("请输入一行元素(用逗号隔开,按Enter结束输入):")
if param_name == "":
break
param_name = [int(x) for x in param_name.split(',')]
params.append(param_name)
return functions, params
# 构建链表对象
solution = MyLinkedList()
# 获取要进行的操作列表
functions, params = param_input()
# 设计链表
for i in range(len(functions)):
if functions[i] == "get":
result = solution.get(params[i][0])
print(result)
elif functions[i] == "addAtHead":
result = solution.addAtHead(params[i][0])
print(result)
elif functions[i] == "addAtTail":
result = solution.addAtTail(params[i][0])
print(result)
elif functions[i] == "addAtIndex":
result = solution.addAtIndex(params[i][0], params[i][1])
print(result)
else:
result = solution.deleteAtIndex(params[i][0])
print(result)
206.反转链表

- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
# 双指针法
# class Solution:
# def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# pre, cur = None, head # 初始化当前节点和前一个节点
# while cur: # 这里不能写cur.next != None,否则会在cur访问到最后一个节点时,直接跳出循环。
# temp = cur.next # 暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点
# cur.next = pre
# # 更新指针指向的节点
# pre = cur
# cur = temp
# return pre
# 递归法
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
return self.reverse_node(None, head) # 调用类内函数要使用self,初始化pre和cur的参数
def reverse_node(self, pre: ListNode, cur: ListNode) -> Optional[ListNode]:
# 递归结束条件
if cur is None:
return pre # 返回反转后的链表
temp = cur.next
# 翻转两个节点的指向
cur.next = pre
# 递归调用
return self.reverse_node(cur, temp)- ACM模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
# 双指针法
# class Solution:
# def reverseList(self, head):
# pre, cur = None, head # 初始化当前节点和前一个节点
# while cur: # 这里不能写cur.next != None,否则会在cur访问到最后一个节点时,直接跳出循环。
# temp = cur.next # 暂时保存当前节点的下一个节点
# cur.next = pre
# # 更新指针指向的节点
# pre = cur
# cur = temp
# return pre
# 递归法
class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head):
return self.reverse_node(None, head) # 调用类内函数要使用self,初始化pre和cur的参数
def reverse_node(self, pre, cur):
# 递归结束条件
if cur is None:
return pre # 返回反转后的链表
temp = cur.next
# 翻转两个节点的指向
cur.next = pre
# 递归调用
return self.reverse_node(cur, temp)
# 创建链表
def creat_list(lenth):
dummy_head = ListNode(None, None)
current = dummy_head
for i in range(lenth):
val = int(input("输入链表第{}个节点的值:".format(i + 1))) # 获取第i个节点值
current.next = ListNode(val, None) # 创建第i个节点,并将其接入链表
current = current.next
head = dummy_head.next
return head
# 输出链表
def output_list(head):
result = []
temp = head
while temp:
result.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return result
# 创建链表
lenth = int(input("输入要创建的链表长度lenth:"))
head = creat_list(lenth)
# 反转链表
solution = Solution()
result = solution.reverseList(head)
# 输出反转后的结果
result = output_list(result)
print(result)
24.两两交换链表中的节点

- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头节点
cur = dummy_head # 将cur初始为指向虚拟头节点
while cur.next != None and cur.next.next != None: # 判断cur之后是否还剩余2个及以上节点
temp = cur.next # 构建一个临时指针
cur.next = cur.next.next # 0 指向 2
temp.next = cur.next.next # 1 指向 3
cur.next.next = temp # 2 指向 1
cur = cur.next.next # cur向后移动两位
return dummy_head.next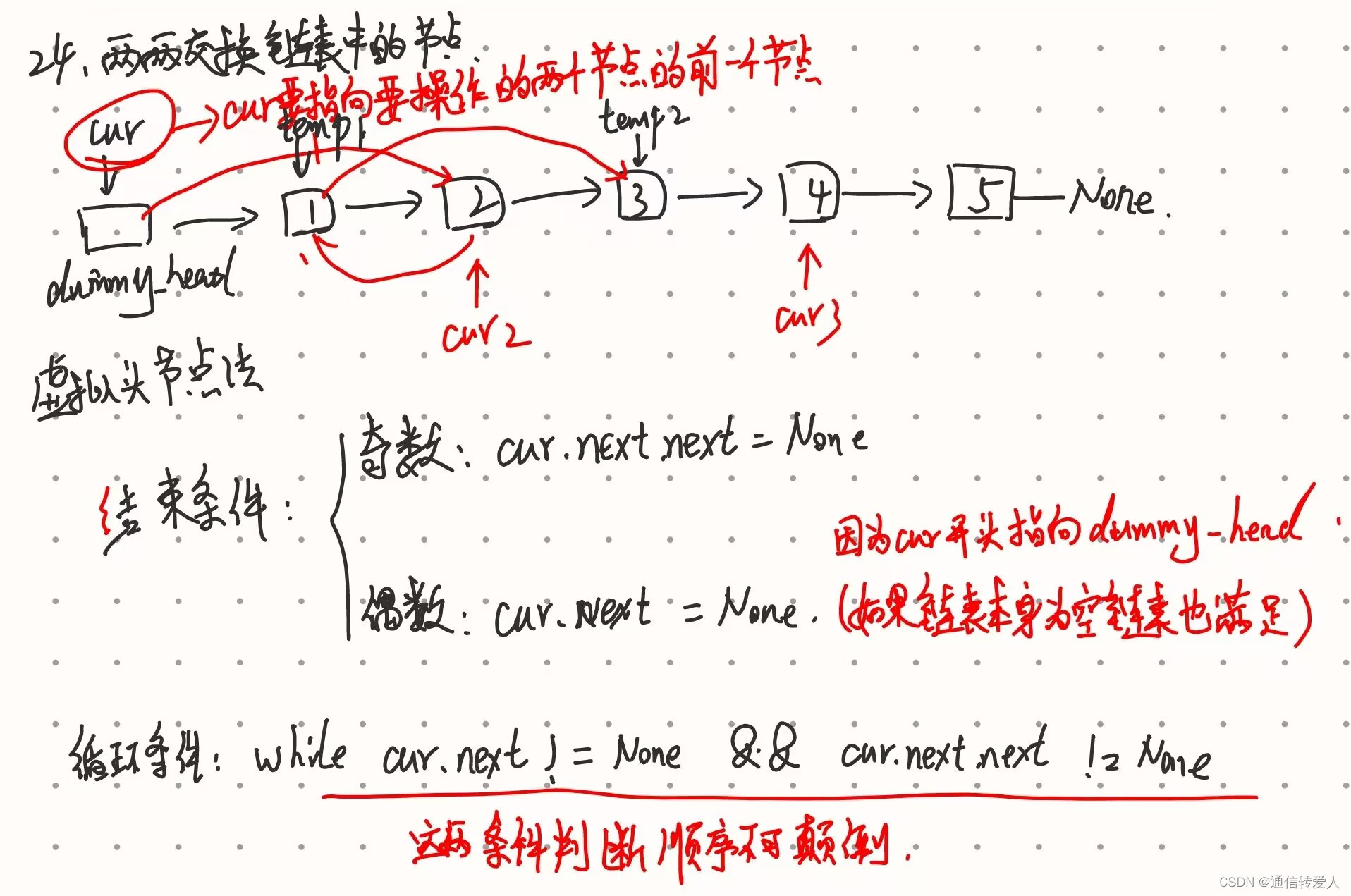
- ACM模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def swapPairs(self, head):
dummy_head = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头节点
cur = dummy_head # 将cur初始为指向虚拟头节点
while cur.next != None and cur.next.next != None: # 判断cur之后是否还剩余2个及以上节点
temp = cur.next # 构建一个临时指针
cur.next = cur.next.next # 0 指向 2
temp.next = cur.next.next # 1 指向 3
cur.next.next = temp # 2 指向 1
cur = cur.next.next # cur向后移动两位
return dummy_head.next
# 创建链表
def creat_list(lenth):
dummy_head = ListNode(None, None)
current = dummy_head
for i in range(lenth):
val = int(input("输入链表第{}个节点的值:".format(i + 1))) # 获取第i个节点值
current.next = ListNode(val, None) # 创建第i个节点,并将其接入链表
current = current.next
head = dummy_head.next
return head
# 输出链表
def output_list(head):
result = []
temp = head
while temp:
result.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return result
# 创建链表
lenth = int(input("输入要创建的链表长度lenth:"))
head = creat_list(lenth)
# 两两交换链表中的节点
solution = Solution()
result = solution.swapPairs(head)
# 输出结果
result = output_list(result)
print(result)19.删除链表的倒数第N个节点

- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
# self.val = val
# self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head: Optional[ListNode], n: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
dummy_head = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头节点,其next值在构建时直接初始化
slow = fast = dummy_head # 创建快、慢指针
for i in range(n + 1): # 删除倒数第n个节点,让fast先移动n + 1个位置
fast = fast.next
# 找到倒数第n个节点的前一个节点
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next # 删除倒数第n个节点
return dummy_head.next # 由于链表第一个节点可能被删除,因此返回的是dummy_head.next而不是head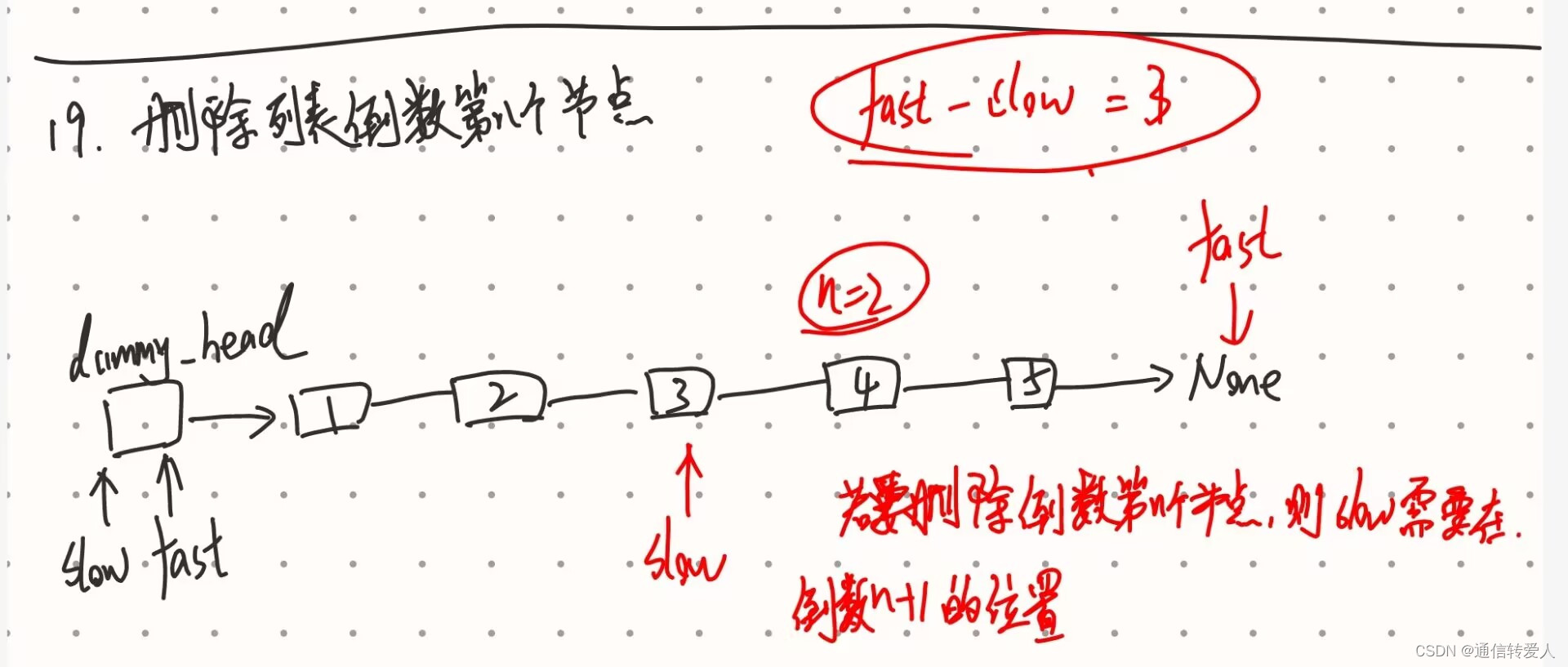
- ACM模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
class ListNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
class Solution:
def removeNthFromEnd(self, head, n):
dummy_head = ListNode(None, head) # 构建虚拟头节点,其next值在构建时直接初始化
slow = fast = dummy_head # 创建快、慢指针
for i in range(n + 1): # 删除倒数第n个节点,让fast先移动n + 1个位置
fast = fast.next
# 找到倒数第n个节点的前一个节点
while fast:
slow = slow.next
fast = fast.next
slow.next = slow.next.next # 删除倒数第n个节点
return dummy_head.next # 由于链表第一个节点可能被删除,因此返回的是dummy_head.next而不是head
# 创建链表
def creat_list(lenth):
dummy_head = ListNode(None, None)
current = dummy_head
for i in range(lenth):
val = int(input("输入链表第{}个节点的值:".format(i + 1))) # 获取第i个节点值
current.next = ListNode(val, None) # 创建第i个节点,并将其接入链表
current = current.next
head = dummy_head.next
return head
# 输出链表
def output_list(head):
result = []
temp = head
while temp:
result.append(temp.val)
temp = temp.next
return result
# 创建链表
lenth = int(input("输入要创建的链表长度lenth:"))
head = creat_list(lenth)
n = int(input("输入要删除的倒数第n个节点:"))
# 删除链表的倒数第N个节点
solution = Solution()
result = solution.removeNthFromEnd(head, n)
# 输出结果
result = output_list(result)
print(result)面试题 02.07.链表相交

- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def getIntersectionNode(self, headA: ListNode, headB: ListNode) -> ListNode:
curA, curB = headA, headB # 构建两个指针,分别用于访问两个链表
lenthA, lenthB = 0, 0 # 记录两个链表的长度
# 统计链表A的长度
while curA:
curA = curA.next
lenthA += 1
# 统计链表B的长度
while curB:
curB = curB.next
lenthB += 1
# 重新初始化两个指针
curA, curB = headA, headB
# 让curB指向较长的那个链表
if lenthA > lenthB:
# 交换curA和curB指向的链表
curA, curB = curB, curA
lenthA, lenthB = lenthB, lenthA
# 让curB和curA的位置相对于链尾对齐
for _ in range(lenthB - lenthA):
curB = curB.next
# 找到两个链表的相交位置
while curA:
if curA == curB:
return curA
curA = curA.next
curB = curB.next
# 未找到链表相交的位置
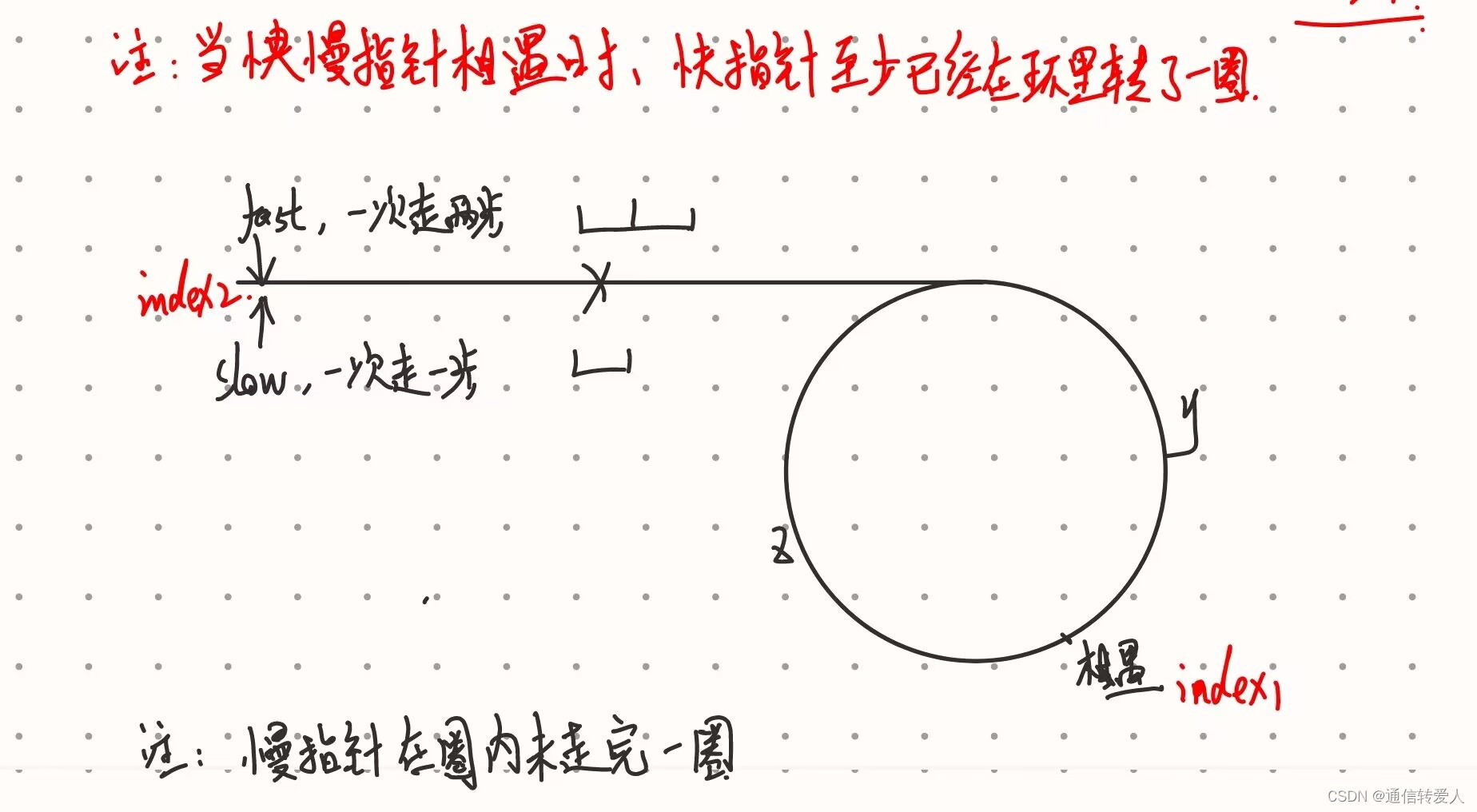
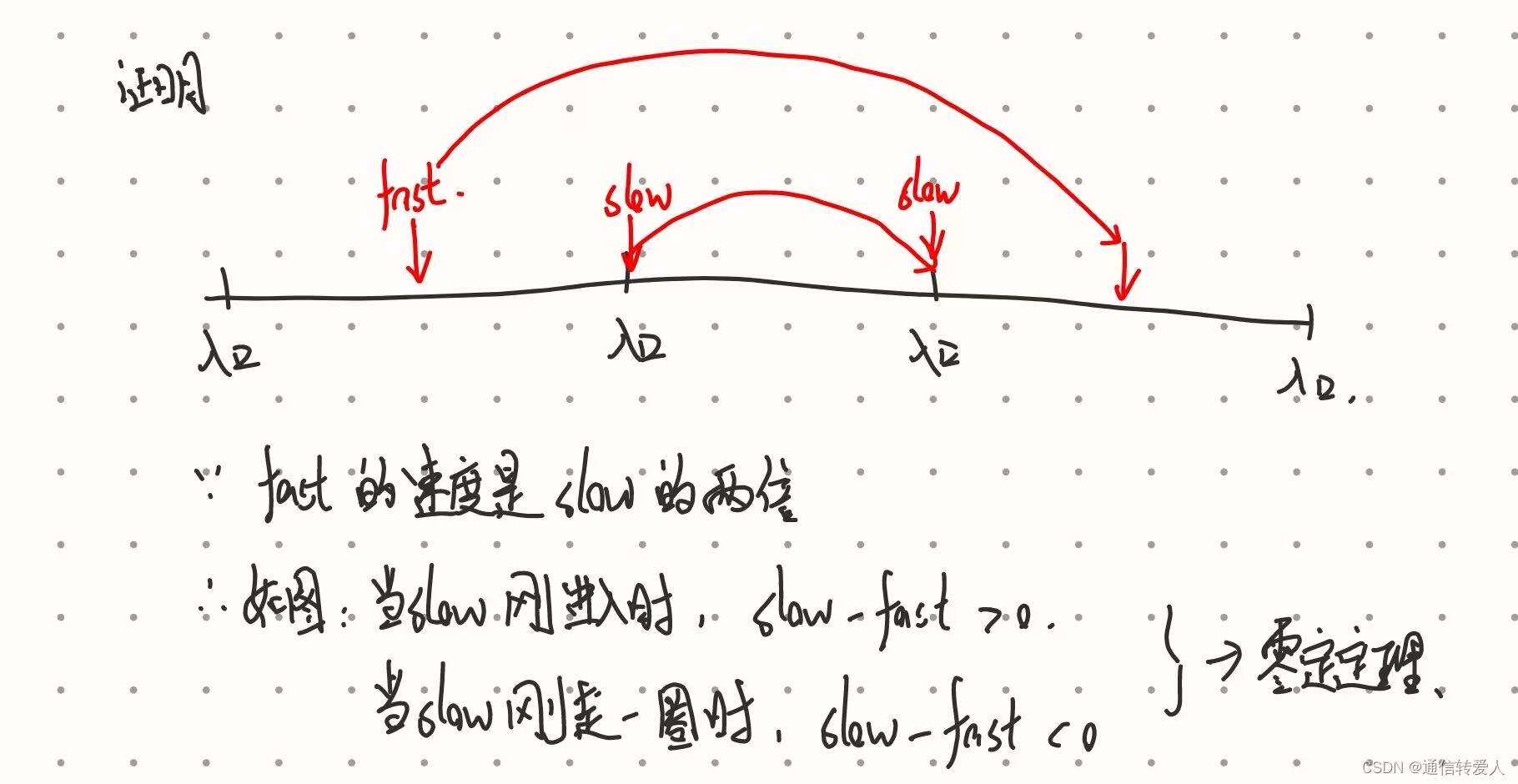
return None142.环形链表II


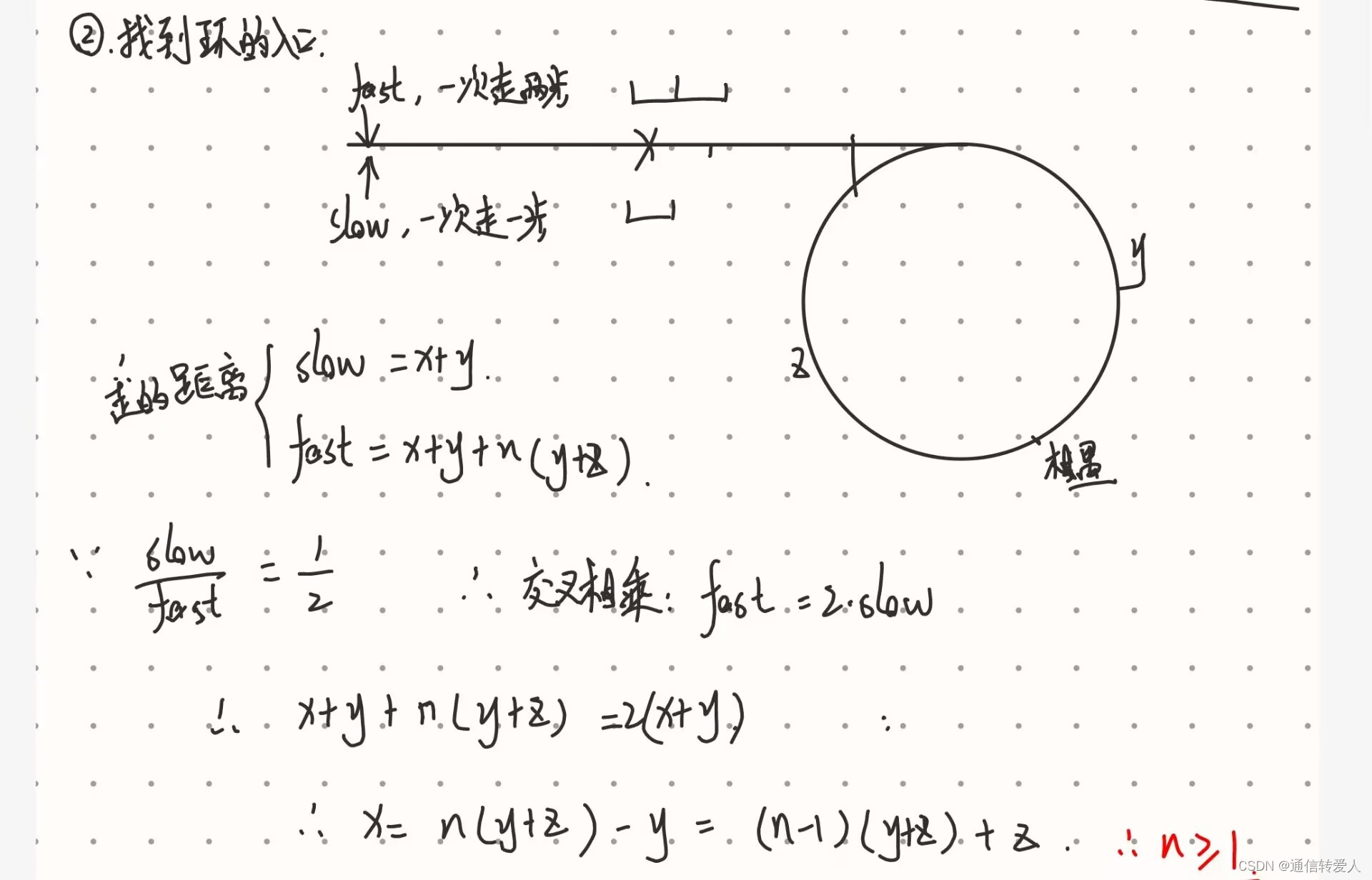
- 核心代码模式
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None
class Solution:
def detectCycle(self, head: Optional[ListNode]) -> Optional[ListNode]:
fast = slow = head # 双指针法,构建快慢指针,fast每次移动两个节点,slow每次移动一个节点
# 判断链表是否本身为空链表
if fast is None:
return None
# fast每次走两步,slow每次走一步,两者速度差为1
while fast.next and fast.next.next:
fast = fast.next.next
slow = slow.next
# 找到slow和fast之间的相遇点
if slow == fast:
index1 = fast
index2 = head
# 找到链表的入环第一个节点
while index1 != index2:
index1 = index1.next
index2 = index2.next
# 返回入环点的序号
return index1
# 链表无环
return None






















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








