链表分割:
链接: link.
编写代码,以给定值x为基准将链表分割成两部分,所有小于x的结点排在大于或等于x的结点之前
给定一个链表的头指针 ListNode* pHead,请返回重新排列后的链表的头指针。注意:分割以后保持原来的数据顺序不变。
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x) {
// write code here
if(!pHead)
{
return pHead;
}
ListNode* p = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* q = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode* ph = p;
ListNode* qh= q;
while(pHead)
{
if(pHead->val < x)
{
p->next = pHead;
p = p->next;
}
else
{
q->next = pHead;
q = q->next;
}
pHead = pHead->next;
}
q->next = nullptr;
qh = qh->next;
p->next = qh;
return ph->next;
}
};
删除链表中的重复结点
链接: link.
在一个排序的链表中,存在重复的结点,请删除该链表中重复的结点,重复的结点不保留,返回链表头指针。 例如,链表1->2->3->3->4->4->5 处理后为 1->2->5
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) :
val(x), next(NULL) {
}
};
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* deleteDuplication(ListNode* pHead)
{
ListNode* newhead = new ListNode(-1);
newhead->next = pHead;
ListNode* prev = newhead;
ListNode* cur = pHead;
ListNode* next;
while(cur&&cur->next)
{
next = cur->next;
if(cur->val == next->val)
{
while(next!=NULL && cur->val == next->val)
{
next = next->next;
}
prev->next = next;
cur= next;
}
else
{
prev = cur;
cur = cur->next;
}
}
return newhead->next;
}
};
链表的回文结构
链接: link.
对于一个链表,请设计一个时间复杂度为O(n),额外空间复杂度为O(1)的算法,判断其是否为回文结构。
给定一个链表的头指针A,请返回一个bool值,代表其是否为回文结构。保证链表长度小于等于900。
测试样例:
1->2->2->1
返回:true
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* A) {
// write code here
ListNode* fast = A;
ListNode* slow = A;
while(fast != NULL && fast->next !=NULL)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
ListNode* mid = slow;
ListNode* midnext = slow->next;
slow->next = NULL;
ListNode* prev = NULL;
ListNode* next = NULL;
while(midnext)
{
next = midnext->next;
midnext->next = prev;
prev = midnext;
midnext = next;
}
while(A!=NULL && prev != NULL)
{
if(A->val != prev->val)
{
return false;
}
A = A->next;
prev = prev->next;
}
return true;
}
相交链表
链接: link.
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
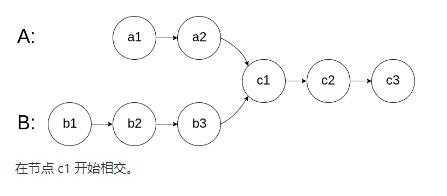
示例 1:
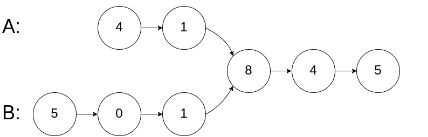
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Reference of the node with value = 8
输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
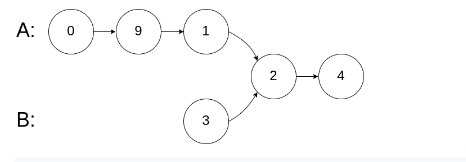
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Reference of the node with value = 2
输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个列表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
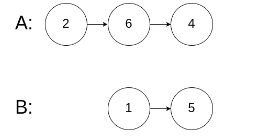
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null.
在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。
可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。
程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB) {
struct ListNode* fast = headA;
struct ListNode* slow = headB;
struct ListNode* tmp = NULL;
if(headA == NULL&& headB == NULL)
return NULL;
int count1 = 0;
int count2 = 0;
while(fast)
{
fast = fast->next;
count1++;
}
while(slow)
{
slow = slow->next;
count2++;
}
int step = abs(count1-count2);
if(count1-count2>0)
{
fast = headA;
slow = headB;
}
else
{
fast = headB;
slow = headA;
}
while(step--)
{
fast = fast->next;
}
while(fast && slow)
{
if(fast == slow)
{
tmp = fast;
break;
}
fast = fast->next;
slow = slow->next;
}
return tmp;
}
环形链表
链接: link.
给定一个链表,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
示例 1:
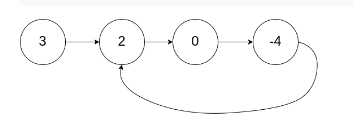
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
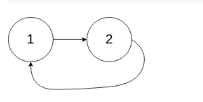
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:
输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。

/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head) {
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while(fast && fast->next && slow)
{
fast = fast->next->next;
slow = slow->next;
if(fast == slow)
return true;
}
return false;
}








 这篇博客介绍了四种链表操作:以指定值x分割链表,删除排序链表中的重复结点,判断链表是否为回文结构,以及找出两个链表的相交节点。提供了相关链接并讨论了时间复杂度和空间复杂度的优化。
这篇博客介绍了四种链表操作:以指定值x分割链表,删除排序链表中的重复结点,判断链表是否为回文结构,以及找出两个链表的相交节点。提供了相关链接并讨论了时间复杂度和空间复杂度的优化。
















 1189
1189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








