Given a binary tree, find the lowest common ancestor (LCA) of two given nodes in the tree.
According to the definition of LCA on Wikipedia: “The lowest common ancestor is defined between two nodes p and q as the lowest node in T that has both p and q as descendants (where we allow a node to be a descendant of itself).”
Given the following binary tree: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4]
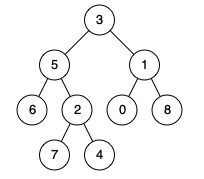
Example 1:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 1
Output: 3
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 1 is 3.
Example 2:
Input: root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], p = 5, q = 4
Output: 5
Explanation: The LCA of nodes 5 and 4 is 5, since a node can be a descendant of itself according to the LCA definition.
c++: 递归
以根节点为起点,往左右分支上寻找,如果找到了 p 或 q 节点,则返回该节点。否则,继续向叶子节点寻找,假想一下,如果一直递归到 null 还是找不到该节点,那么说明这个分支上不存在该节点。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
//如果找到 p 或者 q 那么就没有必要接着递归,因为共同祖先只可能是该节点或该节点祖先
//如果 root 为空了,说明这条路径上不可能有 p 或 q 节点,返回空
if (!root || p == root || q == root) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);//往左分支上寻找
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p , q);//往右分支上寻找
if (left && right) return root; //说明 p 和 q 是分布在 root 两侧,返回即可
return left ? left : right;//说明在 left 分支上找到 p 或 q 节点,返回即可
}
};
python:
class Solution(object):
def lowestCommonAncestor(self, root, p, q):
"""
:type root: TreeNode
:type p: TreeNode
:type q: TreeNode
:rtype: TreeNode
"""
if root == None or root == p or root == q:
return root
left = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.left,p,q)
right = self.lowestCommonAncestor(root.right,p,q)
if left==None:
return right
elif right ==None:
return left
else:
return root





 本文介绍了一种在二叉树中查找两个指定节点的最低公共祖先(LCA)的算法,提供了C++和Python的实现代码。LCA定义为树中同时拥有p和q作为后代的最深节点,允许节点作为自己的后代。通过递归搜索左右子树来找到p和q,如果它们分别位于根节点的两侧,则根节点即为LCA。
本文介绍了一种在二叉树中查找两个指定节点的最低公共祖先(LCA)的算法,提供了C++和Python的实现代码。LCA定义为树中同时拥有p和q作为后代的最深节点,允许节点作为自己的后代。通过递归搜索左右子树来找到p和q,如果它们分别位于根节点的两侧,则根节点即为LCA。
















 417
417

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








