源码下载:http://download.youkuaiyun.com/detail/redhatforyou/9870168
#1 包含的类
##1.1 data类
data类用来存储训练决策树的数据其中:
examples:表示所有的数据条目
attributes:表示数据的特征
attr_types:表示
class_index:表示
class data():
def __init__(self, classifier):
self.examples = []
self.attributes = []
self.attr_types = []
self.classifier = classifier
self.class_index = None
##1.2 treeNode类
treeNode类用来表示决策树中的节点其中不同属性表示如下所示:
is_leaf=True:默认为True用来表示是为叶子节点
classification=None:
attr_split=None:
attr_split_index=None:
self.attr_split_value = None:
self.parent = parent:
self.upper_child = None:
self.lower_child = None:
self.height = None:
class treeNode():
def __init__(self, is_leaf, classification, attr_split_index, attr_split_value, parent, upper_child, lower_child,
height):
self.is_leaf = True
self.classification = None
self.attr_split = None
self.attr_split_index = None
self.attr_split_value = None
self.parent = parent
self.upper_child = None
self.lower_child = None
self.height = None
#2 函数的具体实现
##2.1 def read_data(dataset, datafile, datatypes):函数
通过read_data()读取数据信息,读取后的数据信息存储在dataset里面。
datafile文件的格式如下所示:
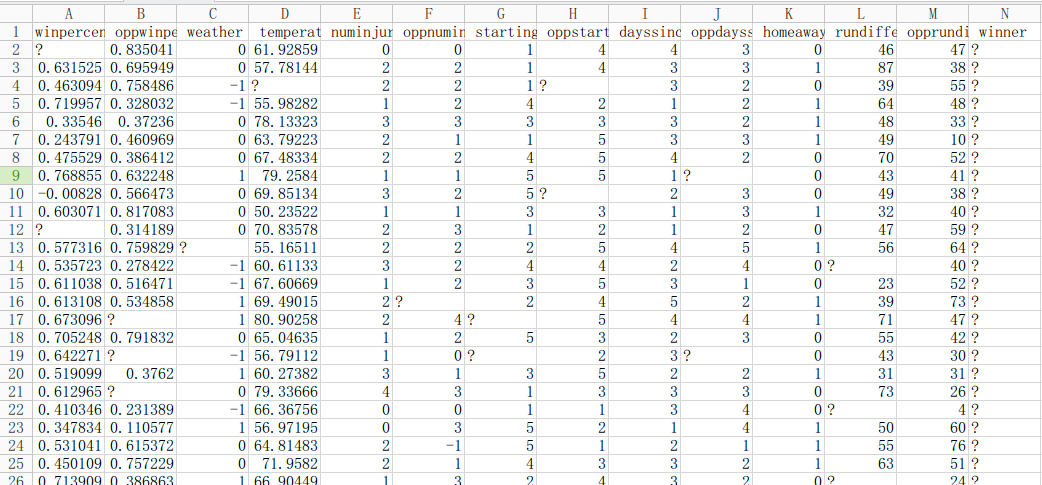
根据上述的文件格式,第一行为整个文件中各个特征的名称,接下来为所有的数据条目
def read_data(dataset, datafile, datatypes):
print "Reading data..."
f = open(datafile)
original_file = f.read()
#split the data by lines
rowsplit_data = original_file.splitlines()
# split the data by ','
dataset.examples = [rows.split(',') for rows in rowsplit_data]
# list attributes
dataset.attributes = dataset.examples.pop(0)
# create array that indicates whether each attribute is a numerical value or not
attr_type = open(datatypes)
orig_file = attr_type.read()
dataset.attr_types = orig_file.split(',')
根据上述的图示和代码可知,在该函数中一共包含三个部分的功能:
(1)读取datafile信息并获取example
读取文件,每个数据项目以逗号隔开,通过逗号隔开的数据信息存储在example里面
f = open(datafile)
original_file = f.read()
#split the data by lines
rowsplit_data = original_file.splitlines()
# split the data by ','
dataset.examples = [rows.split(',') for rows in rowsplit_data]
(2)读取datafile信息并获取attributes信息
获取标签特征的信息,获取首行标签特征的信息。
# list attributes
dataset.attributes = dataset.examples.pop(0)
(3)读取datatypes文件
读取datatypes文件中的数据信息,其中datatypes文件的格式如下所示:

# create array that indicates whether each attribute is a numerical value or not
attr_type = open(datatypes)
orig_file = attr_type.read()
dataset.attr_types = orig_file.split(',')
##2.2 def preprocess2(dataset):函数
(1)获取class的标签的值并计算标签树木的大小
根据下述的代码,在dataset中用class_index存储标签的所存在的列的下标。通过class_mode来存储标签中出现最多的数据项个数。
#get the class value in the example
class_values = [example[dataset.class_index] for example in dataset.examples]
class_mode = Counter(class_values)
#find the most common one in the calss mode
class_mode = class_mode.most_common(1)[0][0]
(2)通过filter获取每一个attr_index的数据信息,并根据对应的数据信息找到对应的标签的值。
ex_0class = filter(lambda x: x[dataset.class_index] == '0', dataset.examples)
values_0class = [example[attr_index] for example in ex_0class]
#get the example data of 1 of attributes at the index of attr_index
ex_1class = filter(lambda x: x[dataset.class_index] == '1', dataset.examples)
values_1class = [example[attr_index] for example in ex_1class]
##2.3 def compute_tree(dataset, parent_node, classifier):函数
(1)构建一棵决策树的节点,并进行初始化设置
判断该节点是否具有父亲节点,如果没有父亲节点则其高度设置为0,否则在其父亲节点的高度上加1。
判断该节点中数据树木的大小,如果在该节点中没有数据项或者数据项目都属于一个类,则返回该节点为一个叶子节点。
node = treeNode(True, None, None, None, parent_node, None, None, 0)
#compute the node height
if (parent_node == None):
node.height = 0
else:
node.height = node.parent.height + 1
ones = one_count(dataset.examples, dataset.attributes, classifier)
if (len(dataset.examples) == ones):
node.classification = 1
node.is_leaf = True
return node
elif (ones == 0):
node.classification = 0
node.is_leaf = True
return node
else:
node.is_leaf = False
(2)初始化决策树的参数,并计算数据集的信息熵
attr_to_split:用来存储分裂的下标。
max_gain:用来存储最佳分裂的标签。
split_val:用来存储进行分裂的值。
min_gain:停止分裂的阈值。
attr_to_split = None # The index of the attribute we will split on
max_gain = 0 # The gain given by the best attribute
split_val = None
min_gain = 0.01
dataset_entropy = calc_dataset_entropy(dataset, classifier)
(3)获取对每一个标签标签的每一个可能分裂值进行分类判断并得到最佳的结果。
if (dataset.attributes[attr_index] != classifier):
local_max_gain = 0
local_split_val = None
attr_value_list = [example[attr_index] for example in
dataset.examples] # these are the values we can split on, now we must find the best one
attr_value_list = list(set(attr_value_list)) # remove duplicates from list of all attribute values
(4)在分裂值的数目大于100的情况下,将10个数据划分成一组得到新的分类值序列。
if (len(attr_value_list) > 100):
attr_value_list = sorted(attr_value_list)
total = len(attr_value_list)
ten_percentile = int(total / 10)
new_list = []
for x in range(1, 10):
new_list.append(attr_value_list[x * ten_percentile])
attr_value_list = new_list
(5)计算信息增益并将信息增益和这组标签中所有的分类值的信息增益结果想比较,如果具有较好的效果则替代,并记录分裂标签和分裂值。
for val in attr_value_list:
# calculate the gain if we split on this value
# if gain is greater than local_max_gain, save this gain and this value
local_gain = calc_gain(dataset, dataset_entropy, val,
attr_index) # calculate the gain if we split on this value
if (local_gain > local_max_gain):
local_max_gain = local_gain
local_split_val = val
(6)将最大的信息增益结果与全局的信息增益结果比较,如果有较好的分裂结果则替代,并记录分裂标签和分裂值。
if (local_max_gain > max_gain):
max_gain = local_max_gain
split_val = local_split_val
attr_to_split = attr_index
(7)对获得的信息增益进行判断,判断是否符合叶子节点的条件,如果符合则停止分裂返回一个叶子节点,并记录叶子该叶子节点属于哪种类型。
# attr_to_split is now the best attribute according to our gain metric
if (split_val is None or attr_to_split is None):
print "Something went wrong. Couldn't find an attribute to split on or a split value."
elif (max_gain <= min_gain or node.height > 20):
node.is_leaf = True
node.classification = classify_leaf(dataset, classifier)
return node
(8)如果不是叶子节点则对节点的基本信息和子节点的信息进行记录,并分类该节点递归地调用分裂函数。
node.attr_split_index = attr_to_split
node.attr_split = dataset.attributes[attr_to_split]
node.attr_split_value = split_val
# currently doing one split per node so only two datasets are created
upper_dataset = data(classifier)
lower_dataset = data(classifier)
upper_dataset.attributes = dataset.attributes
lower_dataset.attributes = dataset.attributes
upper_dataset.attr_types = dataset.attr_types
lower_dataset.attr_types = dataset.attr_types
for example in dataset.examples:
if (attr_to_split is not None and example[attr_to_split] >= split_val):
upper_dataset.examples.append(example)
elif (attr_to_split is not None):
lower_dataset.examples.append(example)
node.upper_child = compute_tree(upper_dataset, node, classifier)
node.lower_child = compute_tree(lower_dataset, node, classifier)
return node
##2.4 def classify_leaf(dataset, classifier):函数
判断一个叶子节点属于哪种类型
def classify_leaf(dataset, classifier):
ones = one_count(dataset.examples, dataset.attributes, classifier)
total = len(dataset.examples)
zeroes = total - ones
if (ones >= zeroes):
return 1
else:
return 0
##2.5 def calc_dataset_entropy(dataset, classifier):函数
在这里通过calc_dataset_entropy计算数据集合的信息熵。通过one_count计算节点中的数据项数。
在这里默认地对结果的处理中只有两种类型的数据结果。通过公式:
H(x)=E(I(x))=∑i=1np(xi)I(xi)=−∑i=1np(xi)logbp(xi)H(x)=E(I(x))=\sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_i)I(x_i)=-\sum_{i=1}^{n}p(x_i)log_bp(x_i)H(x)=E(I(x))=i=1∑np(xi)I(xi)=−i=1∑np(xi)logbp(xi)
计算信息熵的值。
def calc_dataset_entropy(dataset, classifier):
ones = one_count(dataset.examples, dataset.attributes, classifier)
total_examples = len(dataset.examples);
entropy = 0
p = ones / total_examples
if (p != 0):
entropy += p * math.log(p, 2)
p = (total_examples - ones) / total_examples
if (p != 0):
entropy += p * math.log(p, 2)
entropy = -entropy
return entropy
##2.6 def calc_gain(dataset, entropy, val, attr_index):函数
通过该函数计算信息增益,信息增益的计算方式如下:
g(D,A)=H(D)−H(D∣A)g(D,A)=H(D)-H(D|A)g(D,A)=H(D)−H(D∣A)
上述不同的参数分别表示的含义如下:
(1)dataset:用来存储列表中所有的数据项目。
(2)entropy:用来传递分裂前的信息熵。
(3)val:用来传递分裂的值。
(4)attr_index:用来存储分裂标签的索引
def calc_gain(dataset, entropy, val, attr_index):
classifier = dataset.attributes[attr_index]
attr_entropy = 0
total_examples = len(dataset.examples);
gain_upper_dataset = data(classifier)
gain_lower_dataset = data(classifier)
gain_upper_dataset.attributes = dataset.attributes
gain_lower_dataset.attributes = dataset.attributes
gain_upper_dataset.attr_types = dataset.attr_types
gain_lower_dataset.attr_types = dataset.attr_types
for example in dataset.examples:
if (example[attr_index] >= val):
gain_upper_dataset.examples.append(example)
elif (example[attr_index] < val):
gain_lower_dataset.examples.append(example)
if (len(gain_upper_dataset.examples) == 0 or len(
gain_lower_dataset.examples) == 0): # Splitting didn't actually split (we tried to split on the max or min of the attribute's range)
return -1
attr_entropy += calc_dataset_entropy(gain_upper_dataset, classifier) * len(
gain_upper_dataset.examples) / total_examples
attr_entropy += calc_dataset_entropy(gain_lower_dataset, classifier) * len(
gain_lower_dataset.examples) / total_examples
return entropy - attr_entropy
##2.7 def one_count(instances, attributes, classifier):函数
计算instances中属于类1数据项的个数并返回,其中attributes表示特征,classifier表示标签所在的列。
def one_count(instances, attributes, classifier):
count = 0
class_index = None
# find index of classifier
for a in range(len(attributes)):
if attributes[a] == classifier:
class_index = a
else:
class_index = len(attributes) - 1
for i in instances:
if i[class_index] == "1":
count += 1
return count
##2.8 def prune_tree(root, node, dataset, best_score):函数
传入的参数为:
(1)root:训练后的决策树根节点
(2)node:一个节点
(3)dataset:验证集
(4)best_score:验证集的验证结果。
在prune_tree中实现对生成的决策树的剪枝操作,在剪枝操作中,对每一个叶子节点进行剪枝并通过验证集去判断新生成的决策树在验证集上的正确率,如果大于原来的正确率则进行剪枝得到新的决策树,否则使用原有的决策树。
def prune_tree(root, node, dataset, best_score):
# if node is a leaf
if (node.is_leaf == True):
# get its classification
classification = node.classification
# run validate_tree on a tree with the nodes parent as a leaf with its classification
node.parent.is_leaf = True
node.parent.classification = node.classification
if (node.height < 20):
new_score = validate_tree(root, dataset)
else:
new_score = 0
# if its better, change it
if (new_score >= best_score):
return new_score
else:
node.parent.is_leaf = False
node.parent.classification = None
return best_score
# if its not a leaf
else:
# prune tree(node.upper_child)
new_score = prune_tree(root, node.upper_child, dataset, best_score)
# if its now a leaf, return
if (node.is_leaf == True):
return new_score
# prune tree(node.lower_child)
new_score = prune_tree(root, node.lower_child, dataset, new_score)
# if its now a leaf, return
if (node.is_leaf == True):
return new_score
return new_score
##2.9 def validate_tree(node, dataset):函数
对数据集中的每一个examples进行验证,并根据返回的结果计数,最后计算分类的准确率。
def validate_tree(node, dataset):
total = len(dataset.examples)
correct = 0
for example in dataset.examples:
# validate example
correct += validate_example(node, example)
return correct / total
##2.10 def validate_example(node, example):函数
对每一个example节点的数据通过决策树进行判断其所属的类,并判断划分结果是否正确,如果正确则返回1否则返回0
def validate_example(node, example):
if (node.is_leaf == True):
projected = node.classification
actual = int(example[-1])
if (projected == actual):
return 1
else:
return 0
value = example[node.attr_split_index]
if (value >= node.attr_split_value):
return validate_example(node.upper_child, example)
else:
return validate_example(node.lower_child, example)
##2.11 def test_example(example, node, class_index):函数
功能:判断每一项数据的属于哪一个类。
传入的参数:
example:表示每一条数据项目。
node:表示该数据沿着决策树分裂路径所到的节点
class_index:表示分类标签的索引。
def test_example(example, node, class_index):
if (node.is_leaf == True):
return node.classification
else:
if (example[node.attr_split_index] >= node.attr_split_value):
return test_example(example, node.upper_child, class_index)
else:
return test_example(example, node.lower_child, class_index)
##2.12 def print_tree(node):函数
输出决策树的结构
def print_tree(node):
if (node.is_leaf == True):
for x in range(node.height):
print "\t",
print "Classification: " + str(node.classification)
return
for x in range(node.height):
print "\t",
print "Split index: " + str(node.attr_split)
for x in range(node.height):
print "\t",
print "Split value: " + str(node.attr_split_value)
print_tree(node.upper_child)
print_tree(node.lower_child)
##2.13 def print_disjunctive(node, dataset, dnf_string):函数
通过disjunctive normal form格式输出决策树。
def print_disjunctive(node, dataset, dnf_string):
if (node.parent == None):
dnf_string = "( "
if (node.is_leaf == True):
if (node.classification == 1):
dnf_string = dnf_string[:-3]
dnf_string += ") ^ "
print dnf_string,
else:
return
else:
upper = dnf_string + str(dataset.attributes[node.attr_split_index]) + " >= " + str(
node.attr_split_value) + " V "
print_disjunctive(node.upper_child, dataset, upper)
lower = dnf_string + str(dataset.attributes[node.attr_split_index]) + " < " + str(node.attr_split_value) + " V "
print_disjunctive(node.lower_child, dataset, lower)
return
#3 运行一个决策树的实例
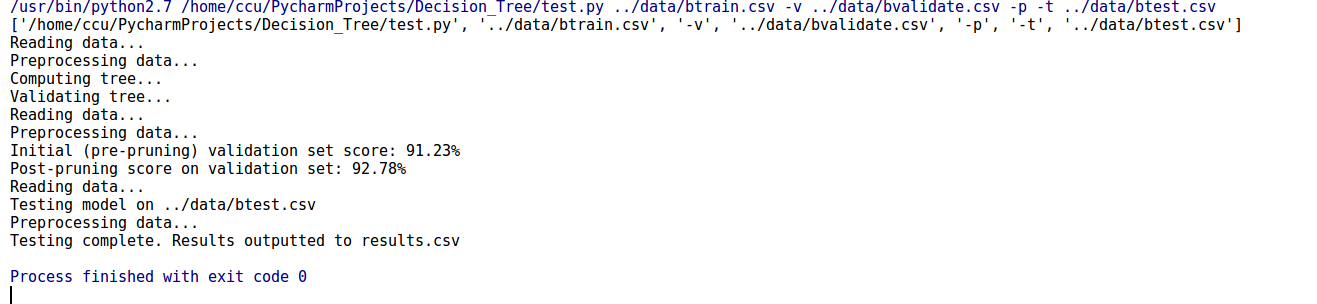
如上图为运行结果:运行代码如下所示,设置的运行参数为:…/data/btrain.csv -v …/data/bvalidate.csv -p -t …/data/btest.csv
import sys
import ast
import csv
from com.DecisionTree.DecisionTree import *
##################################################
# main function, organize data and execute functions based on input
# need to account for missing data
##################################################
def main():
#get the parameter of the args
args = str(sys.argv)
args = ast.literal_eval(args)
print args
# get the length of the parameter
if (len(args) < 2):
print "You have input less than the minimum number of arguments. Go back and read README.txt and do it right next time!"
#judge the type of the file
elif (args[1][-4:] != ".csv"):
print "Your training file (second argument) must be a .csv!"
else:
datafile = args[1]
#instantiation a dataset class number
dataset = data("")
#judge the data type of the types
if ("-d" in args):
datatypes = args[args.index("-d") + 1]
else:
datatypes = '../data/datatypes.csv'
#read data from datafile
read_data(dataset, datafile, datatypes)
arg3 = args[2]
#choose the attributes as classifier
if (arg3 in dataset.attributes):
classifier = arg3
else:
classifier = dataset.attributes[-1]
#dataset.classifier = 'Winner'
dataset.classifier = classifier
# find index of classifier default the index is the end of the attribustes
for a in range(len(dataset.attributes)):
if dataset.attributes[a] == dataset.classifier:
dataset.class_index = a
else:
dataset.class_index = range(len(dataset.attributes))[-1]
unprocessed = copy.deepcopy(dataset)
#preprocess the data
preprocess2(dataset)
print "Computing tree..."
root = compute_tree(dataset, None, classifier)
if ("-s" in args):
print_disjunctive(root, dataset, "")
print "\n"
if ("-v" in args):
datavalidate = args[args.index("-v") + 1]
print "Validating tree..."
validateset = data(classifier)
read_data(validateset, datavalidate, datatypes)
for a in range(len(dataset.attributes)):
if validateset.attributes[a] == validateset.classifier:
validateset.class_index = a
else:
validateset.class_index = range(len(validateset.attributes))[-1]
preprocess2(validateset)
best_score = validate_tree(root, validateset)
all_ex_score = copy.deepcopy(best_score)
print "Initial (pre-pruning) validation set score: " + str(100 * best_score) + "%"
if ("-p" in args):
if ("-v" not in args):
print "Error: You must validate if you want to prune"
else:
post_prune_accuracy = 100 * prune_tree(root, root, validateset, best_score)
print "Post-pruning score on validation set: " + str(post_prune_accuracy) + "%"
if ("-t" in args):
datatest = args[args.index("-t") + 1]
testset = data(classifier)
read_data(testset, datatest, datatypes)
for a in range(len(dataset.attributes)):
if testset.attributes[a] == testset.classifier:
testset.class_index = a
else:
testset.class_index = range(len(testset.attributes))[-1]
print "Testing model on " + str(datatest)
for example in testset.examples:
example[testset.class_index] = '0'
testset.examples[0][testset.class_index] = '1'
testset.examples[1][testset.class_index] = '1'
testset.examples[2][testset.class_index] = '?'
preprocess2(testset)
b = open('results.csv', 'w')
a = csv.writer(b)
for example in testset.examples:
example[testset.class_index] = test_example(example, root, testset.class_index)
saveset = testset
saveset.examples = [saveset.attributes] + saveset.examples
a.writerows(saveset.examples)
b.close()
print "Testing complete. Results outputted to results.csv"
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()





 本文深入解析决策树算法的实现细节,包括数据预处理、决策树构建、剪枝优化及分类预测过程。通过具体实例,展示如何利用决策树解决分类问题。
本文深入解析决策树算法的实现细节,包括数据预处理、决策树构建、剪枝优化及分类预测过程。通过具体实例,展示如何利用决策树解决分类问题。
















 1137
1137

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








