1.1二阶构造函数
1.1.1 问题提出
- 如何判断构造函数的执行结果?
- 如果在构造中遇到
return会怎样? - 构造函数执行结束是否意味着对象构造成功?
1.1.2 示例程序
#include <stdio.h>
class Test
{
int mi;
int mj;
bool mStatus;
public:
Test(int i, int j) : mStatus(false) //初始化为false
{
mi = i;
return; //遇到return 直接返回,导致初始化的状态有问题,但是不影响对象的创建
mj = j;
mStatus = true;
}
int getI()
{
return mi;
}
int getJ()
{
return mj;
}
int status()
{
return mStatus;
}
};
int main()
{
Test t1(1, 2);
if( t1.status() )
{
printf("t1.mi = %d\n", t1.getI());
printf("t1.mj = %d\n", t1.getJ());
}
return 0;
}
1.1.3 结论
- 构造函数只提供自动初始化成员变量的机会
- 不能保证初始化逻辑一定成功
- 执行return 语句后构造函数立即结束
- 注意:构造函数只是决定对象的初始化状态,不能决定对象的诞生
1.1.4 半成品对象的概念
初始化操作不能按照预期完成而得到的对象半成品对象是合法的C++对象,也是Bug 的重要来源。
1.2
1.2.1 工程中的二阶构造
工程开发中的构造过程可分为:
- 资源无关的初始化操作
- 不可能出现异常情况的操作
- 需要使用系统资源的操作
- 可能出现异常情况,如内存申请,访问文件。

1.2.2 二阶构造示例伪代码
- 二阶构造示例1:
class TwoPhaseCons{
private:
TwoPhaseCons(){ //第一阶段构造函数 ,适用于不可能出现异常情况的操作
}
bool construct() // 第二阶段构造函数
{
return true;
}
public:
static TwoPhaseCons * NewInstance(); // 对象创建函数
};
- 二阶构造示例2
TwoPhaseCons* TwoPhaseCons::NewInstance(){
TwoPhaseCons * ret = new TwoPhaseCons();
//若第二季度构造失败,返回NULL
if(!(ret &&ret->construct()))
{
delete ret ;
ret = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
1.2.3实例代码
class Test
{
private:
int age;
char * name;
//first phase
Test(int age)
{
this->age= age;
}
bool construct(const char * name)
{
bool ret = true;
int len = strlen(name);
this->name = new char[len+1];
if(this->name)
{
strcpy(this->name ,name);
}
else{
ret = false;
}
return ret;
}
public:
static Test* newInstance(int age, const char * name)
{
Test *ret = new Test(age);
if(!(ret && ret->construct(name)))
{
delete ret;
ret = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
void print()
{
printf("age = %d\n",this->age);
printf("name = %s\n",this->name);
}
~Test()
{
delete [] name;
}
};
int main()
{
int age =20;
char * name = "zhhsansndsfa";
Test * test = Test::newInstance(age, name);
test->print();
delete test;
return 0;
}
1.2.4 继承中的二阶构造
下面是继承中的二阶构造,下面我在程序中将自己编写遇到的问题进行标注
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
class Test
{
protected:
char * name;
int age;
Test(int age)
{
this->age =age;
}
bool twoConstructor(const char* name)
{
bool ret = true;
this->name = new char[strlen(name)+1];
if(this->name != NULL)
{
strcpy(this->name,name);
}
else
{
ret =false;
}
return ret;
}
public:
static Test* newInstance(int age,const char*name)
{
Test * ret = new Test(age);
if(!(ret && ret->twoConstructor(name)))
{
delete ret;
ret =NULL;
}
return ret;
}
void print()
{
printf("age = %d\n",age);
printf("name = %s\n",name);
}
~Test()
{
delete name;
printf("~Test()\n");
}
};
class Child: public Test
{
protected:
int age2;
char * name2;
Child(int age1,int age2):Test(age1)
{
this->age2 =age2;
}
bool twoConstructor2(const char * name1,const char* name2)
{
bool ret = true;
ret = Test::twoConstructor(name1);
if(ret)
{
this->name2 = new char[strlen(name2)+1] ; //这里我编程的时候写成了
// name2 = new char[strlen(name2)+1] 导致程序出错。
if(name2 != NULL)
{
strcpy(this->name2,name2);
}
else
{
ret = false;
}
}
return ret;
}
public:
static Child * newInstance(const char* name1,const char*name2,int age1,int age2)
{
Child * ret = new Child(age1,age2);
if(!(ret&&ret->twoConstructor2(name1,name2))) // 这里我写成了
//!(ret) && ret->twoConstructor2(name1,name2),然后找到了错误
{
delete ret;
ret = NULL;
}
return ret;
}
void print()
{
printf("age1 = %d\n",age);
printf("age2 = %d\n",age2);
printf("name = %s\n",name);
printf("name2 = %s\n",name2);
}
~Child()
{
delete name2;
printf("~Child() delete name2\n");
}
};
int main()
{
Child * c1 =Child::newInstance("zhangsan","lisi",10,20);
c1->print();
delete c1;
return 0;
}
运行结果:
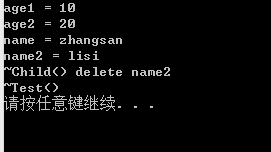
1.2.3
1.3实例
1.3.1
1.3.2
1.3.3
参考一 :狄泰软件学院C++进阶剖析








 博客围绕C++二阶构造函数展开,先提出构造函数执行结果判断等问题,指出构造函数仅提供初始化机会,不能保证初始化成功,引出半成品对象概念。接着介绍工程中的二阶构造,包括资源无关和需使用系统资源的操作,还给出示例伪代码、实例代码及继承中的二阶构造情况。
博客围绕C++二阶构造函数展开,先提出构造函数执行结果判断等问题,指出构造函数仅提供初始化机会,不能保证初始化成功,引出半成品对象概念。接着介绍工程中的二阶构造,包括资源无关和需使用系统资源的操作,还给出示例伪代码、实例代码及继承中的二阶构造情况。
















 4707
4707

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








